- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Information Technology
- By Omega Team

6G is the sixth generation of wireless technology. A 6G network follows up on 4G and 5G, using higher frequency bands and agile, cloud-based networking technology to deliver record-breaking speeds and microsecond latency. As experts imagine it, 6G isn’t just going to support mobile phones. 6G makes it possible to move in a cyber-physical continuum, between the connected physical world of senses, conduct, and guests and its programmable digital representation.
The network provides intelligence, measureless connectivity, and full synchronization of the physical and digital worlds. Vast quantities of detectors bedded in the physical world shoot data to modernize the digital representation in real time. Selectors in the real world carry out commands from intelligent agents in the digital world. It becomes possible to trace back and dissect events, observe, and act in real-time, as well as to pretend, prognosticate, and program unborn conduct. To meet the unborn challenges, 6G needs to continue to push beyond the specialized limits of 5G, moving toward critical services, immersive communication, and universal IoT.
Unborn networks will be an element for the functioning of nearly all corridors of life, society, and diligence, fulfilling the communication requirements of humans as well as intelligent machines. To take the stylish out of this situation, both the assiduity and exploration community should work together toward a common vision.
Four main motorists with corresponding challenges are:
- Arising for the 6G period responsibility of the systems at the heart of society
- Sustainability through the effectiveness of mobile technology
- Accelerated automatization and digitalization to simplify and ameliorate people’s lives
- Measureless connectivity meeting the demands for enhancing communication anywhere, anytime, and for anything.
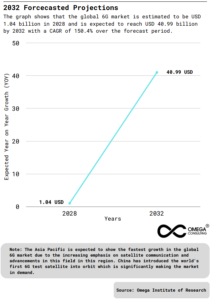
Exhibit 1: 2032 Forecasted Projections
How to Understand the Differences Between 5G and 6G
The Science Behind Spectrum Usage
5G and 6G use wireless and advanced range for data transmission briskly than 2G, 3G, and 4G networks. Still, when comparing 5G vs 6G, the former bone is allocated for low band and high band frequency–sub-6 GHz (Gigahertz) and above 24.25 GHz independently. The ultimate bone will be operative at the frequency range 95 GHz to 3 THz (Terahertz). Since different diapasons are used, 5G vs. 6G technology can have multiple use cases for a variety of artificial sectors to enhance their effectiveness. 6G wireless accelerates IoT after 5G-Internet of Things (IoT) is perpetuating a moment with the perpetration of 5G grounded results following expansive 5G network testing which wasn’t possible with former networks like 4G LTE due to poor planning of frequency. This is where 5G fills in the gap and moving ahead with 6G we anticipate to connect ten times further bias per forecourt kilometer with an increase in the number of connected biases in the forthcoming times.
Mastering Low Latency in Gaming and Streaming
The time taken by a packet of information transmitted over a frequency is known as latency. 4G networks had a latency of about 50 milliseconds whereas 5G networks had ten times lower latency than 4G i.e., 5ms. With 6G internet, latency will slip down to range 1 millisecond to 1 microsecond, lowering latency to five times than that of fifth-generation network making massive data transmissions possible.
The Future of Connectivity: 6G Development Trends to Watch
- In January of 2022, the Samsung Electronics collaborated with Korea University to establish a department dedicated to the research and development of 6G.
- In July of 2021, the University of Texas at Austin launched a 6G research center with the support of major wireless industry players, including AT&T, Samsung and Qualcomm.
- In December of 2021, LG Electronics announced the results of its R&D efforts towards 6G communications at Korea Science & Technology Fair 2021, which is held at KINTEX in Goyang, Gyeonggi Province.
Exhibit 2: 6G Market Analysis

Technology Elements of 6G
- Better End to End Connectivity: Network capabilities need to be available end-to-end and match the elaboration of operations and internet technology. This will affect, for case, operation–network collaboration, adaptability mechanisms, the elaboration of the end-to-end transport protocols, and ways to deal with quiescence. Operations that demand adaptability, both for their connectivity and their end-to-end communication, need to be supported. Also, the necessary internet structure needs to be available, flexible, and resistant to marketable surveillance. At the same time, it’s anticipated that unborn dispatches will employ further multi-access technology and operations to come with indeed stricter conditions.
- Environment of Embedded Systems: Unborn services will bear connectivity far and wide and in everything. 6G networks can support trillions of embeddable bias and give secure connections that are available all the time.
Benefits
Every single enhancement in network connectivity that 5G will bring to the end-user will get further perfected with 6G. Whether it’s smart metropolises, granges or manufactories, and robotics, 6G will take it to the coming position. Looking at the history, it’s clear that each generation optimizes the use cases of the prior generation and introduces new ones. This will continue to be the case.
6G will also promote sustainability in a variety of ways. By enabling faster and lower cost per bit connectivity, it would be suitable to support data collection and unrestricted- circle control of multitudinous appliances. The data can be anatomized using sophisticated tools to ameliorate energy effectiveness in diligence. The advanced multi-sensory telepresence that’s created with veritably high data rates will reduce the need for trip through the preface of multi-modal mixed reality telepresence and remote collaboration.
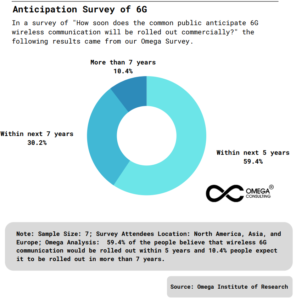
Exhibit 3: Anticipation Survey of 6G
The Omega Conclusion: Unraveling its Significance
Geographically, North America is expected to account for the largest share of 34.8% in the global 6G market owed to the huge presence of key players, government initiatives, and many more factors in this region. The Asia Pacific is expected to show the fastest growth in the global 6G market due to the increasing emphasis on satellite communication and advancements in this field in this region. China has introduced the world’s first 6G test satellite into orbit which is significantly increasing demand. Global 6G Market is estimated to reach USD 1.04 Billion in 2028 and is expected to reach USD 40.99 Billion by 2032 with a CAGR of 150.4% over the forecast period.
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions