- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Technology
- By Omega Team

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has progressed from rule-based systems to deep learning, but the next frontier is Agentic AI—intelligent systems that exhibit autonomy, adaptability, and goal-oriented behavior. Unlike traditional AI, which passively processes inputs, agentic AI can make decisions, interact with environments, and dynamically execute tasks, unlocking immense potential across industries such as business automation, scientific discovery, personalized healthcare, and autonomous systems. By integrating reasoning, planning, and self-improvement, these AI agents can operate with minimal human intervention, making them highly efficient. However, their deployment also raises critical challenges, including ethical concerns, safety, and control, which must be carefully addressed. This article explores Agentic AI solutions, their components, benefits, real-world applications, challenges, and the future of autonomous AI agents.
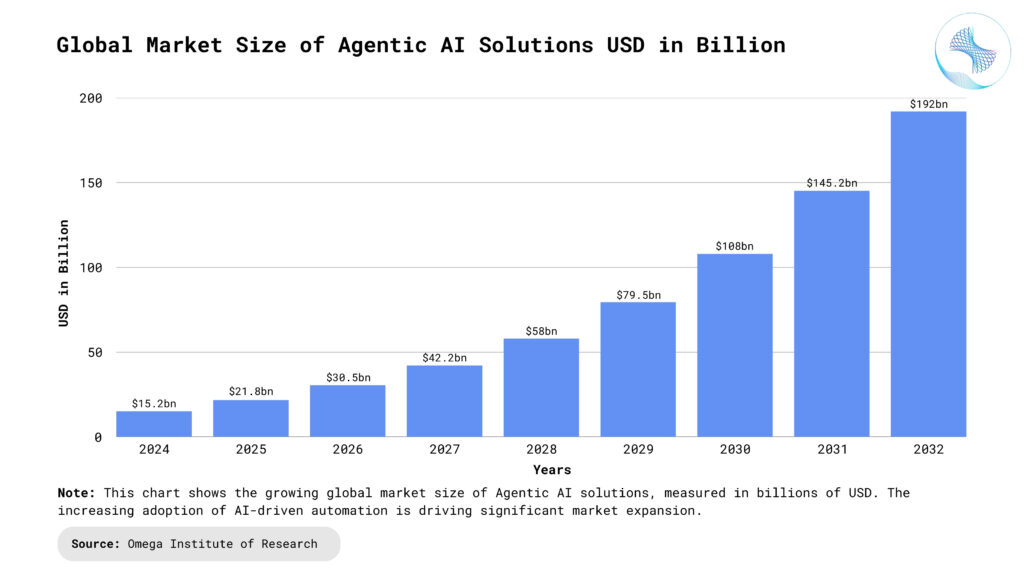
What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to AI models that can autonomously perform tasks, set goals, and make decisions in an ever-changing environment. Unlike traditional AI, which relies on predefined rules or passive input processing, agentic AI actively engages with its surroundings, adapting to new conditions and making independent choices. These AI agents can analyze complex situations, formulate strategies, and iteratively refine their actions to achieve long-term objectives, making them highly valuable in automation, problem-solving, and autonomous decision-making.
Characteristics of Agentic AI
Autonomy: Operates with minimal human intervention, making independent decisions based on real-time data and predefined objectives. This allows it to function in dynamic environments without waiting for human input. Autonomous AI is crucial for applications like self-driving cars, automated trading systems, and industrial robotics.
Adaptability: Learns from new experiences, adjusting strategies dynamically to optimize performance in evolving scenarios. Unlike static rule-based systems, it continuously refines its models based on feedback and changing conditions. This makes it effective in handling novel problems, such as fraud detection or personalized customer service.
Goal-Oriented Behavior: Takes deliberate actions that align with a broader mission, prioritizing efficiency and effectiveness in execution. It can weigh multiple factors to make strategic choices that align with long-term success. This characteristic is essential in AI-driven decision-making, such as business process optimization and medical diagnosis.
Multi-Step Reasoning: Breaks down complex tasks into smaller steps, continuously assessing and refining processes to enhance outcomes. It can plan, execute, and adjust its approach dynamically rather than following a rigid sequence. This capability is vital for AI in research, logistics, and software development, where iterative problem-solving is required.
Interactivity: Engages with users, external systems, and other AI tools in real-time, facilitating collaboration and seamless integration. It can process natural language, respond to user queries, and interact with digital or physical environments. This is particularly beneficial for AI-powered assistants, customer support bots, and intelligent automation platforms.
Memory & Learning: Retains past experiences, using them to improve future decisions, recognize patterns, and anticipate challenges more effectively. Instead of starting from scratch with each task, it builds on prior knowledge to enhance efficiency. This is critical in recommendation systems, cybersecurity threat detection, and predictive maintenance.
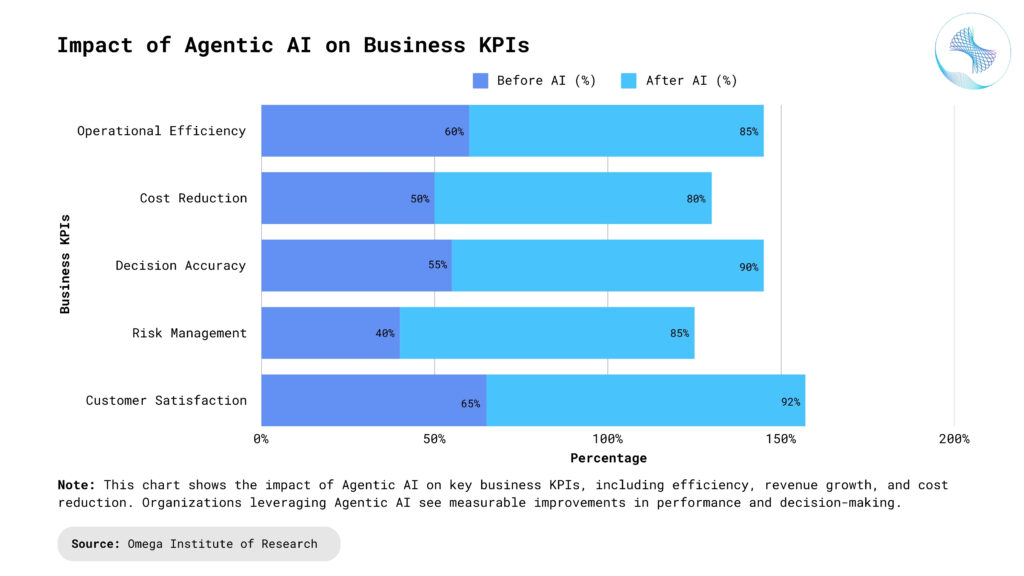
Key Components of Agentic AI Solutions
Cognitive Architectures: Agentic AI leverages cognitive architectures that mimic human intelligence, enabling advanced reasoning, decision-making, and learning capabilities. These architectures provide the structural foundation for AI agents to process information, store knowledge, and adapt based on experience. They integrate perception, memory, and action execution, allowing AI to function more like a human mind. By incorporating these architectures, AI can better understand, predict, and respond to complex scenarios in real time. Examples include:
- SOAR (State, Operator, and Result): A framework designed for problem-solving and learning, commonly used in AI research and intelligent systems. It helps AI break down problems into manageable steps and continuously improve its performance.
- ACT-R (Adaptive Control of Thought-Rational): Simulates human cognitive functions by modeling how the brain processes information, making it useful in psychology and AI. This approach allows AI to develop human-like reasoning for complex decision-making.
- LIDA (Learning Intelligent Distribution Agent): Inspired by human consciousness, it focuses on perception, memory, and decision-making for autonomous AI agents. LIDA enables AI to process sensory inputs, recall relevant information, and take appropriate actions dynamically.
Reinforcement Learning & Self-Optimization: Many agentic AI models use Reinforcement Learning (RL), where AI interacts with an environment, receives rewards or penalties, and optimizes its actions accordingly. RL enables AI to improve decision-making over time through trial and error, making it well-suited for real-world applications requiring adaptability. Advanced variations like Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) combine neural networks with RL to handle complex tasks, such as robotics control and game AI. Self-optimization mechanisms ensure the AI refines its strategies dynamically, improving efficiency and accuracy with continued learning.
Multi-Agent Systems (MAS): Agentic AI often operates in multi-agent systems (MAS), where multiple intelligent agents collaborate, compete, or coordinate to achieve complex goals. These systems allow AI agents to share knowledge, negotiate solutions, and distribute workloads, enhancing efficiency and problem-solving. Swarm Intelligence, inspired by biological systems like ant colonies, enables decentralized coordination among AI agents. Distributed AI leverages MAS principles to solve large-scale challenges, such as optimizing supply chains, managing smart grids, and automating financial markets through collective intelligence.
Memory & Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Unlike traditional AI models that process each task in isolation, Agentic AI retains memory, allowing it to recall past interactions and improve future responses. This persistent memory enhances long-term learning and personalization in AI applications. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) further strengthens AI’s capabilities by integrating large language models (LLMs) with external knowledge bases. RAG enables AI to dynamically retrieve and incorporate relevant data, improving accuracy and contextual awareness in tasks such as customer service, research, and complex decision-making.
Planning & Execution Frameworks: Agentic AI solutions rely on planning and execution frameworks to break down high-level objectives into actionable steps. These frameworks enable AI to analyze different strategies, predict outcomes, and execute tasks efficiently. By utilizing these methods, AI can optimize task completion, reduce errors, and improve overall performance in complex environments. Some key planning methodologies include:
- Hierarchical Task Networks (HTN): Decomposes complex goals into smaller subtasks, allowing AI to manage large-scale projects systematically. This approach ensures that AI can address challenges in a structured manner, preventing overwhelm and increasing task efficiency.
- Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS): Simulates multiple action sequences and evaluates their outcomes to determine the best course of action, widely used in game AI and strategic decision-making. MCTS enables AI to explore a wide range of possibilities, providing more informed and optimized decisions in uncertain environments.
- Goal-Oriented Action Planning (GOAP): Common in game AI and robotics, enabling AI agents to make dynamic decisions that align with their overarching goals while adapting to changing environments. GOAP empowers AI to adjust its plan based on real-time data, ensuring actions are always aligned with long-term objectives.
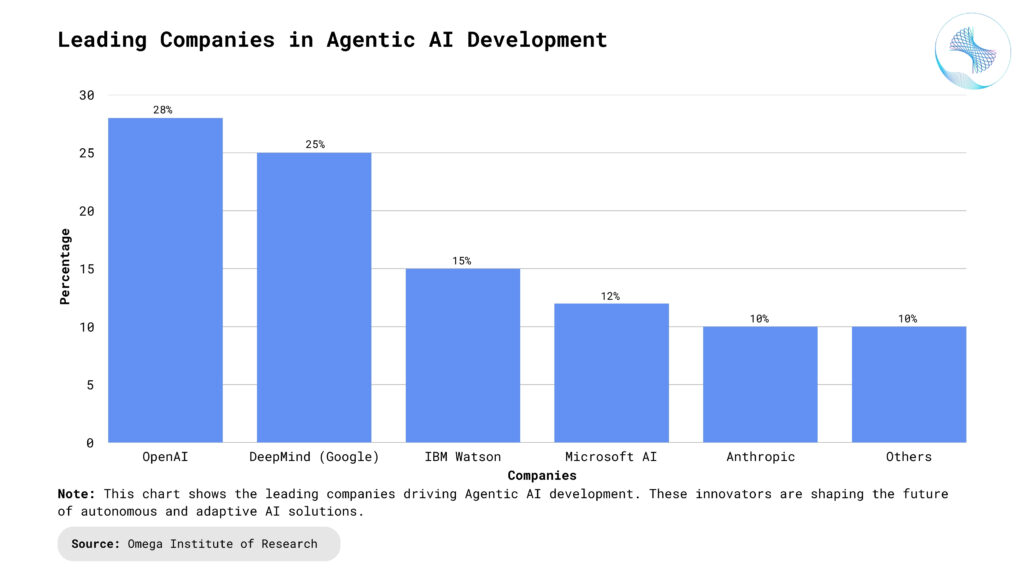
Benefits of Agentic AI Solutions
Increased Autonomy & Productivity: Agentic AI reduces human oversight by automating complex tasks, leading to higher efficiency and faster decision-making. It operates independently, executing repetitive and time-consuming tasks, which allows human workers to focus on more strategic and creative activities. This autonomy significantly reduces human error and speeds up workflows, making organizations more agile and competitive. As AI agents evolve, their ability to handle more nuanced and complex operations further enhances overall productivity, enabling businesses to stay ahead in rapidly changing environments.
Improved Decision-Making: By continuously learning from real-time data and past experiences, agentic AI refines decision-making processes for better accuracy. It can process large amounts of data at speeds far beyond human capabilities, identifying patterns and trends that might be missed otherwise. This ability allows AI to recommend or implement decisions based on the most relevant and up-to-date information. Over time, agentic AI’s learning algorithms improve its decision-making, leading to more effective strategies, improved outcomes, and reduced risks in areas like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing.
Adaptive & Resilient Systems: Unlike static models, agentic AI adapts to dynamic environments, making it ideal for business automation, security, and logistics. It can identify changes in its environment and adjust its behavior accordingly, ensuring it remains effective even as conditions evolve. This adaptability makes agentic AI highly resilient to disruptions and capable of managing uncertainty and complexity in real-time. Whether it’s responding to market shifts, detecting emerging security threats, or optimizing supply chains, agentic AI’s ability to adjust ensures continuous performance under changing conditions.
Seamless Human-AI Collaboration: With interactive capabilities, agentic AI acts as a digital assistant, working alongside humans to enhance workflows. It can handle routine tasks like data processing, scheduling, or customer inquiries, freeing up human workers to focus on more impactful, value-added activities. This collaboration fosters a more efficient, productive work environment by streamlining operations and augmenting human capabilities with AI’s speed and precision. Furthermore, agentic AI’s ability to communicate and learn from human feedback enhances its performance over time, leading to increasingly effective partnerships between humans and machines.
Scalability Across Industries: From healthcare to finance, agentic AI solutions scale effortlessly, optimizing operations with minimal resource investment. Its ability to handle increasing workloads and adapt to different sectors makes it a versatile tool for businesses looking to expand or improve existing processes. Whether automating customer service, enhancing supply chain management, or assisting in clinical diagnostics, agentic AI provides organizations with the tools they need to grow and scale without significant additional costs. As it learns and improves, its capabilities can be expanded across multiple departments, regions, or even industries, providing a significant competitive advantage.
Real-World Applications of Agentic AI
Autonomous Agents in Business Automation: AI-driven executive assistants automate email responses, schedule meetings, and generate reports, reducing the time spent on routine administrative tasks. These intelligent systems can manage calendars, prioritize emails, and even draft responses to common inquiries, streamlining workflows for executives and teams. By handling these repetitive tasks, AI frees up human employees to focus on strategic decision-making and higher-value activities. Additionally, AI-powered customer support agents handle queries, reducing human workload and providing 24/7 assistance to customers, improving satisfaction and efficiency. Procurement bots analyze supply chains, predict demand, and optimize vendor selection, ensuring cost-effective and efficient procurement processes.
Healthcare: AI-Driven Diagnostics & Treatment Plans: Agentic AI monitors patient health, analyzing real-time data from wearables or medical devices, and recommends personalized treatments tailored to the individual’s condition. This dynamic approach allows for proactive care, where AI can alert healthcare providers to potential issues before they become critical. AI-powered robotic surgery adapts to real-time changes in the body, adjusting its movements based on the patient’s anatomy, ensuring precision and minimizing human error. Additionally, AI agents assist in drug discovery, optimizing molecular simulations and predicting the effectiveness of new drugs, dramatically reducing the time and costs associated with research and development.
Finance & Trading: AI-Driven Investment Strategies: AI autonomously manages portfolios, using historical data and predictive algorithms to forecast market trends and make investment decisions. These systems can react to market shifts in real time, adjusting portfolios to mitigate risk and maximize returns. Fraud detection agents monitor transactions for suspicious activity, identifying unusual patterns and stopping fraudulent actions before they cause significant damage. In trading, AI-powered algorithms are capable of high-frequency trading, executing thousands of trades in seconds, ensuring optimal entry and exit points based on market data, and offering a competitive advantage in fast-moving financial markets.
Autonomous Vehicles & Robotics: Self-driving cars use agentic AI to navigate unpredictable roads, adjusting to traffic patterns, road conditions, and other dynamic factors in real time. These vehicles communicate with other cars, infrastructure, and their environment to make decisions that ensure safety and efficiency. AI-powered drones execute military reconnaissance and disaster relief missions, adapting to unpredictable environments by adjusting flight paths, detecting hazards, and gathering critical data for first responders. These autonomous drones can cover large areas quickly and perform tasks like delivering supplies, surveying damage, or locating survivors in disaster zones.
Cybersecurity & Threat Detection: AI-driven security agents identify and neutralize cyber threats before they escalate by continuously monitoring networks, detecting anomalies, and responding to potential breaches in real time. These agents can automatically deploy countermeasures, patch vulnerabilities, and isolate infected systems without requiring human intervention, improving organizational security. Autonomous penetration testing bots simulate cyberattacks on systems, identifying weaknesses and improving defenses before real attackers can exploit them. These bots can test multiple systems simultaneously and execute sophisticated testing scenarios, ensuring that security measures are robust and up-to-date.
Scientific Research & Space Exploration: NASA’s Perseverance rover uses AI agents to autonomously explore Mars, navigate the planet’s surface, and gather data on its geology and atmosphere. These AI systems can adapt to the terrain and make decisions based on environmental factors, significantly reducing the need for real-time human control. In scientific research, AI-driven molecular modeling accelerates drug development by simulating chemical interactions and predicting molecular behavior, cutting down the time required to discover effective drugs. Additionally, AI assists in predicting experimental outcomes, optimizing research methodologies, and even suggesting new hypotheses based on vast datasets, enhancing the pace and scope of scientific discovery.
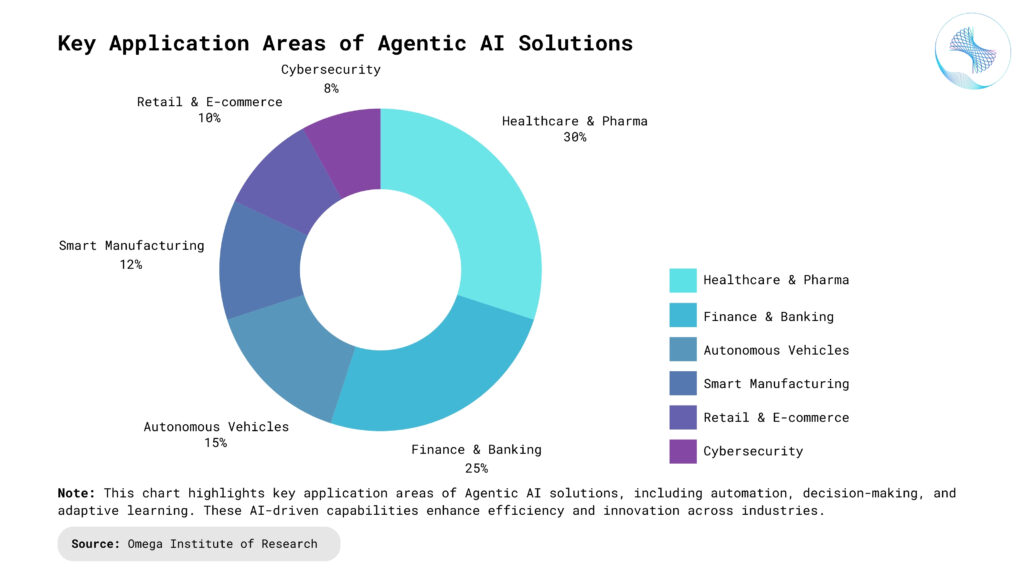
Challenges of Agentic AI
Ethical & Safety Concerns: Autonomous AI decisions must be transparent and explainable to avoid bias, ensuring that their actions can be understood and scrutinized by humans. This transparency is essential in fostering trust and accountability in AI systems, particularly in critical sectors like healthcare, finance, and law enforcement. AI agents must align with ethical AI principles to prevent unintended consequences, such as discriminatory practices or harmful behaviors. Additionally, ensuring that AI decisions are consistent with societal values, respect privacy, and promote fairness will be a key challenge as these systems become more autonomous and widespread.
Computational Complexity & Cost: Agentic AI demands high processing power, requiring cloud computing and advanced hardware to handle the vast amounts of data and complex calculations needed for real-time decision-making. The computational resources needed for running these systems can lead to significant infrastructure costs, especially for industries adopting AI at scale. Moreover, the continuous need for updates, optimization, and real-time analysis can strain existing systems and require ongoing investments in technology. Overcoming these challenges will be crucial for making agentic AI solutions affordable and accessible across various industries.
Regulatory & Compliance Barriers: Governments must establish AI governance frameworks to regulate AI autonomy and ensure that its use aligns with societal values and legal standards. These frameworks need to balance innovation with safety, ensuring that AI systems are held accountable for their actions. Regulatory bodies will also need to keep pace with the rapid advancements in AI technology, developing new rules to govern areas like data privacy, liability, and the ethical use of AI. Without proper regulation, there is a risk of misuse or harmful outcomes that could affect individuals and organizations.
Human-AI Alignment Issues: Ensuring AI agents remain aligned with human values and objectives is crucial as these systems become more autonomous. Misalignments could lead to unintended outcomes, where the actions taken by the AI do not match human intentions or ethical standards. Continuous monitoring, refinement, and input from diverse human stakeholders will be necessary to maintain alignment. Developing methods for AI to understand human values, such as through reinforcement learning or ethical programming, is essential to avoid negative consequences and ensure that AI systems work in harmony with human interests.
The Future of Agentic AI
Hybrid Human-AI Decision-Making: AI agents will assist rather than replace human decision-makers, providing valuable insights, predictions, and recommendations to inform better decision-making. By leveraging AI’s data processing power and predictive capabilities, human decision-makers can act more strategically and make well-informed choices faster. These hybrid models will help bridge the gap between human intuition and data-driven analysis, ensuring that AI complements human judgment without replacing it. In sectors like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing, this collaboration will enhance productivity and drive innovation.
General-Purpose AI Agents: Future models of agentic AI will handle a wide range of tasks, moving closer to Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), where an AI system can perform any cognitive task that a human can. This evolution will enable AI to transfer knowledge across different domains and adapt to a broad spectrum of activities, from managing a business’s operations to conducting scientific research. As these general-purpose AI agents emerge, they will be able to autonomously learn new skills and improve their performance, leading to more versatile, intelligent, and capable systems.
Interoperability Across Systems: AI agents will seamlessly integrate with various platforms, improving workflows and ensuring that information can flow freely between different systems. This interoperability will allow AI to enhance the efficiency and productivity of organizations by automating cross-platform processes, from supply chain management to customer service. AI’s ability to work across different systems and environments will lead to greater flexibility, enabling companies to innovate without being constrained by technological silos. The development of standard protocols and open-source frameworks will be essential for achieving this level of integration.
Self-Evolving AI Agents: AI systems will autonomously upgrade and refine their own models for enhanced performance, reducing the need for manual intervention and continuously improving their capabilities. These self-evolving agents will adapt to new data, environments, and tasks without requiring frequent human input, making them more efficient and scalable. The ability to self-optimize could significantly reduce operational costs and accelerate progress across industries. However, ensuring that these systems evolve in a controlled and safe manner will be critical to preventing unforeseen consequences.
Conclusion
Agentic AI solutions represent a paradigm shift in artificial intelligence, enabling autonomous decision-making, adaptability, and goal-driven behavior, which is poised to revolutionize sectors such as business automation, healthcare, finance, cybersecurity, and space exploration. While these technologies promise substantial advancements, ethical considerations, regulatory oversight, and AI alignment are essential to ensure the responsible deployment of autonomous AI systems. As agentic AI continues to evolve, it will play a defining role in shaping the future of intelligent automation and decision-making, driving innovation while maintaining accountability and safety. To stay ahead of the curve and explore how agentic AI can transform your industry, contact Omega today to learn how we can help integrate these groundbreaking technologies into your business strategy.
- https://www.uipath.com/ai/agentic-ai
- https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/agentic-ai-vs-generative-ai
- https://www.digitalocean.com/resources/articles/agentic-ai
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.00289
- https://www.ssonetwork.com/intelligent-automation/articles/what-is-agentic-ai
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions