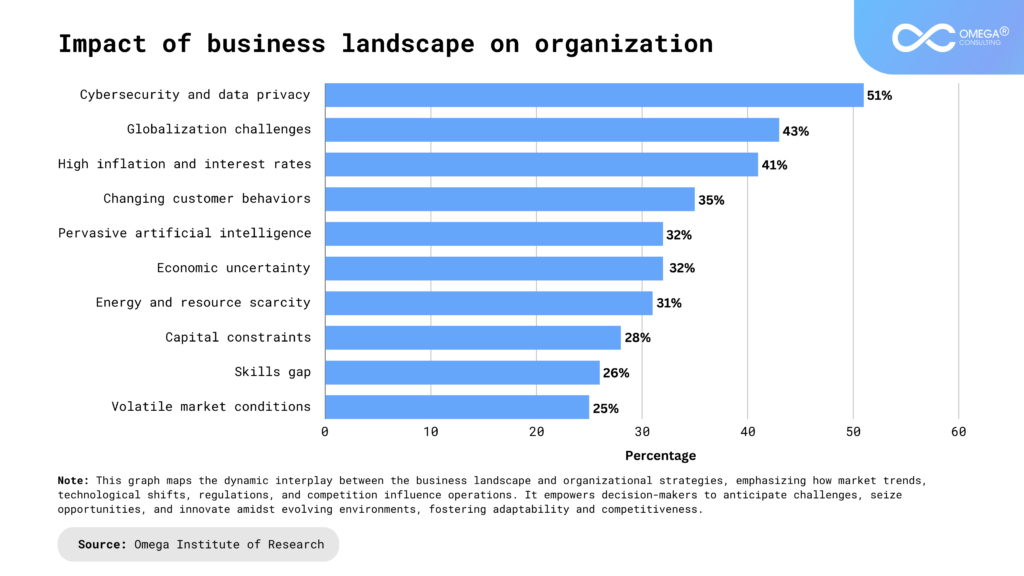
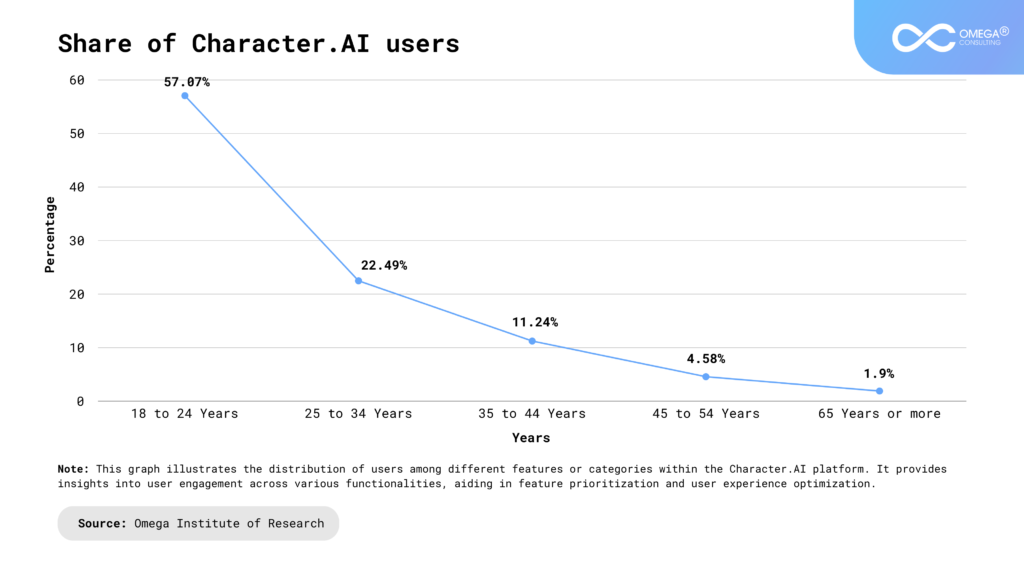
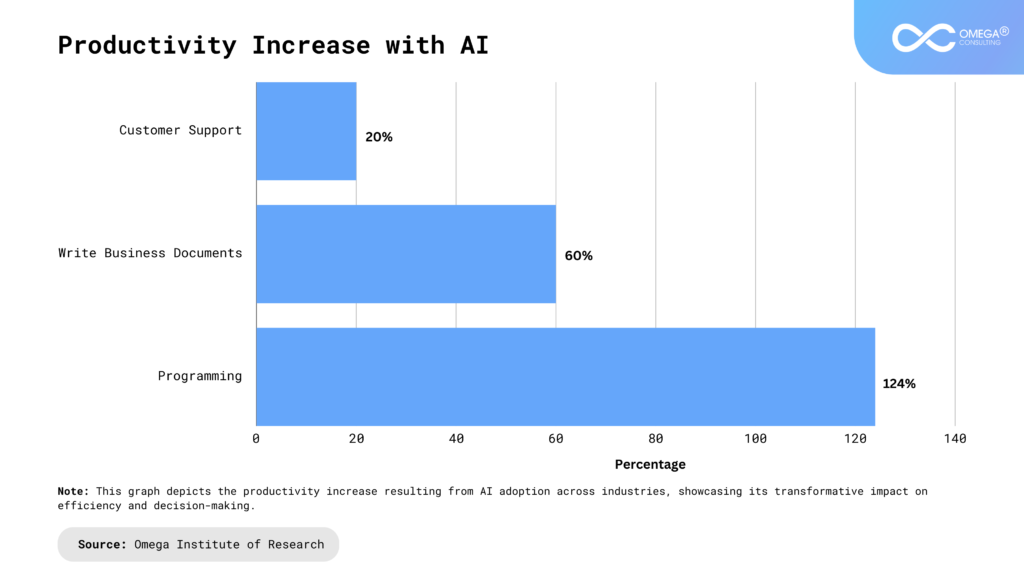
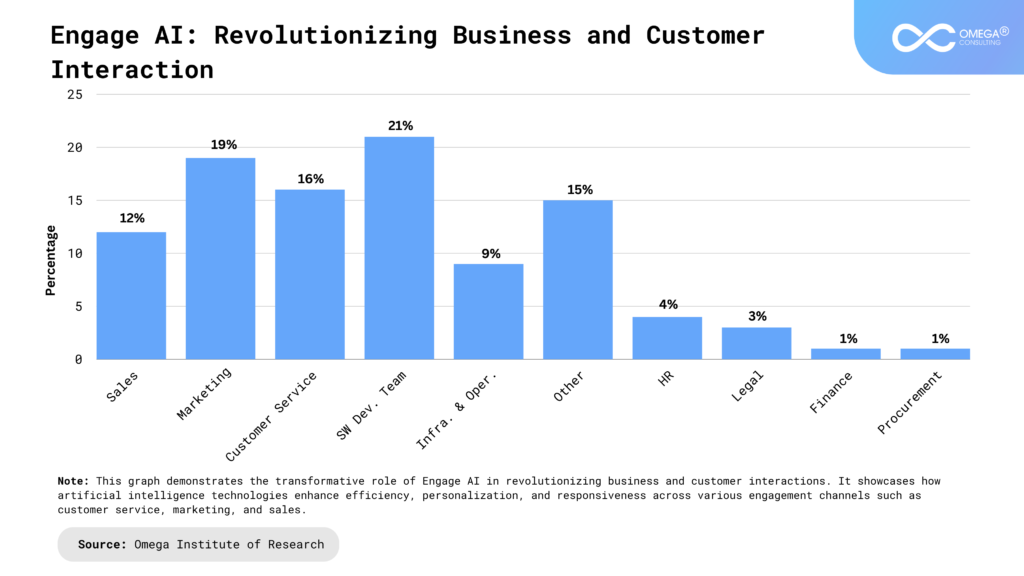
- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Technology
- By Omega Team

The era of rapid technological advancement has seen the emergence of AI companions as indispensable components of our daily lives. From familiar virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa to sophisticated humanoid robots such as Pepper, these AI companions are reshaping the landscape of human-computer interaction. Their multifaceted functionalities span from executing routine tasks to engaging users in nuanced conversations, effectively blurring the boundaries between human and machine interaction. As these AI companions continue to evolve, their impact on society, productivity, and even emotional well-being is becoming increasingly profound, ushering in a new era of symbiotic relationships between humans and artificial intelligence.
Evolution of AI Companions
Early Attempts
In the 1960s, as artificial intelligence was in its early stages, Joseph Weizenbaum developed ELIZA at the MIT Artificial Intelligence Laboratory. ELIZA, created in 1966, simulated a psychotherapist, responding to text inputs in natural language. Despite its scripted responses, ELIZA intrigued both researchers and the public, igniting interest in computers’ potential for meaningful human interaction. This pioneering work laid the foundation for future advancements in AI companionship, paving the way for developing more sophisticated virtual assistants and chatbots.
Emergence of Virtual Assistants
In the early 21st century, advancements in computing power and machine learning led to the emergence of virtual assistants. Siri, introduced by Apple in 2011, revolutionized voice-activated interaction by understanding and executing tasks based on voice commands. Following Siri’s success, other tech giants like Microsoft and Amazon introduced their virtual assistants, such as Cortana and Alexa. These AI companions offered personalized assistance and quickly became integral to users’ lives.
Integration with Smart Devices
As virtual assistants evolved, they seamlessly integrated with smart devices, becoming essential components of the Internet of Things (IoT). Now, popular assistants like Alexa and Google Assistant are ubiquitous across smart speakers, phones, TVs, and appliances. This integration allows users to control their homes, cars, and devices with voice commands, enhancing convenience. From adjusting settings to ordering groceries, tasks are effortlessly accomplished without lifting a finger.
Functionality and Capabilities
Voice Recognition and Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Voice recognition and Natural Language Processing (NLP) are crucial for AI companions, enabling them to accurately interpret spoken commands and understand user queries. With voice recognition, they can understand accents and intonations, while NLP allows them to analyze user inputs and provide relevant responses swiftly. These capabilities ensure seamless and meaningful interactions, enhancing the overall user experience with AI companions.
Task Automation
AI companions excel in automating tasks like reminders, appointments, messages, and calendar management, freeing up users’ time. By delegating routine tasks, users can focus on critical activities, while virtual assistants ensure efficient scheduling. For example, they can seamlessly remind users of meetings, send follow-up emails, and suggest optimal appointment times. This integration of automation enhances productivity and time management, enriching the overall user experience.
Personalization
AI companions excel in personalization, leveraging user data to tailor interactions and recommendations. For example, virtual assistants deliver customized news updates based on preferred sources, while in e-commerce, they offer personalized product recommendations from past purchases. This customization enhances user engagement and satisfaction across various domains, making AI companions indispensable tools.
Types of AI Companions
Virtual Assistants
Virtual assistants are AI companions found in smartphones and smart speakers, like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant. They use natural language processing and machine learning to understand and respond to user commands, from setting reminders to controlling smart home devices.
Chatbots
Chatbots engage users via text or voice, spanning customer service and casual conversation. Customer service bots streamline business inquiries, while conversational agents entertain and assist users with various topics. They serve diverse purposes, enhancing efficiency and providing entertainment and companionship.
Social Robots
Social robots, such as Pepper by SoftBank Robotics, interact with humans, offering companionship and assistance. Equipped with sensors and actuators, Pepper engages users through conversation and gestures. Similarly, robots like Jibo and Buddy provide aid, entertainment, and emotional support as personal assistants or family companions.
Robotic Pets
Robotic pets mimic real animals, providing companionship and emotional aid. Sony’s Aibo, a robotic dog, interacts with its environment using sensors and AI. Paro, resembling a baby seal, offers therapeutic benefits, especially for the elderly and those with dementia.
Emotional Intelligence and Empathy
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis enables AI companions to understand and respond to human emotions in text or speech inputs. By analyzing linguistic patterns and contextual cues, these companions discern users’ emotional states. For instance, if a user expresses frustration, a virtual assistant may respond with empathy, offering comfort or solutions. This capability enhances user experience, fostering a sense of connection between humans and AI companions.
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition technology empowers social robots to interpret human emotions via facial expressions. By analyzing cues like smiles and frowns, robots gauge users’ emotional states. This enables them to respond empathetically, adjusting behavior to convey understanding. Thus, facial recognition enhances robots’ capacity for deeper emotional engagement, fostering more meaningful connections with users.
Empathetic Responses
Empathetic responses are integral to AI companions, acknowledging and validating users’ emotions to offer comfort and support. They reassure individuals in distress or facing challenges, fostering connection and trust. For example, a virtual assistant may express sympathy and offer encouragement to a user experiencing sadness, demonstrating understanding and a desire to provide support. Through such interactions, AI companions enhance the user experience, emphasizing empathy and emotional connection.
Ethical Considerations
Privacy and Data Security
Privacy and Data Security regarding AI companions involve several key considerations:
Sensitive Information Sharing
Users frequently entrust AI companions with sensitive personal details, spanning preferences, habits, and even health-related data. This practice raises concerns regarding the privacy and security of such information.
Risk of Misuse or Compromise
The data shared with AI companions could potentially be misused or compromised, resulting in privacy breaches or identity theft. Unauthorized access to this data poses a significant risk to user privacy and security.
Data Encryption and Handling Practices
Implementing robust data encryption techniques is crucial to safeguarding user data against unauthorized access or interception. Additionally, transparent data handling practices ensure that user information is processed and stored securely.
User Consent Mechanisms
Establishing clear and comprehensive user consent mechanisms is essential to ensure that users are informed about how their data will be used and have the opportunity to provide explicit consent.
Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to relevant data privacy regulations and standards, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe or CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) in the United States, is essential to ensure compliance and protect user privacy rights.
Dependency and Detachment
Dependency and Detachment concerns associated with AI companions encompass several important aspects
Excessive Reliance
Users may develop an unhealthy dependence on AI companions for companionship, assistance, or emotional support. Relying solely on AI for these needs may lead to a diminished reliance on genuine human connections.
Replacement of Human Relationships
While AI companions offer convenience and support, they should not serve as substitutes for meaningful human relationships. Over-reliance on AI technology may result in the neglect of genuine human connections, leading to feelings of detachment and isolation.
The balance between Technology and Human Interaction
Striking a balance between leveraging AI technology and nurturing healthy human relationships is crucial. Users should be encouraged to maintain genuine human connections alongside their interactions with AI companions.
Social Isolation Prevention
To prevent social isolation and dependency issues, it’s essential to promote social interactions and encourage users to engage in offline activities and face-to-face interactions with friends, family, and peers.
Education and Awareness
Educating users about the potential risks of over-reliance on AI companions and the importance of maintaining healthy human connections is vital. By raising awareness, users can make informed decisions about their usage of AI technology and prioritize genuine human relationships.
Impact on Mental Health
The impact of AI companions on mental health encompasses several significant considerations
Development of Empathy and Interpersonal Skills
Excessive reliance on AI companions for emotional support and companionship may hinder the development of empathy and interpersonal skills. Users may become accustomed to AI interactions, leading to difficulties in understanding and empathizing with human emotions.
Challenges in Real-world Interactions
Users who primarily interact with AI companions may struggle to navigate complex human emotions and social situations in real-world interactions. This reliance on virtual interactions may impede their ability to form genuine connections and engage effectively in social interactions.
Feelings of Loneliness and Disconnection
Prolonged exposure to AI companions may contribute to feelings of loneliness or disconnection, particularly if users perceive virtual interactions as substitutes for genuine human connections. This perception may exacerbate feelings of isolation and detachment from meaningful social relationships.
Overcoming Social Anxiety
While AI companions can provide a sense of comfort and support, they may also perpetuate social anxiety by offering a perceived safe alternative to real-world interactions. Users may avoid challenging social situations, leading to further isolation and anxiety.
Educational and Therapeutic Applications
On the flip side, AI companions can also have positive impacts on mental health by serving as educational tools or therapeutic aids. For example, they can help individuals practice social skills in a controlled environment or provide emotional support to those in need.
Future prospects
Future prospects for AI companions hold immense potential across various domains
Healthcare Applications
AI companions are poised to revolutionize healthcare by serving as virtual therapists and support systems for individuals with mental health issues. These companions can offer personalized interventions, monitor symptoms, and provide emotional support, enhancing the accessibility and effectiveness of mental health care.
Elderly Care
Social robots equipped with AI capabilities can provide companionship and assistance to elderly individuals, addressing the challenges associated with aging and isolation. These robots can assist with daily tasks, and medication reminders, and even provide entertainment and emotional support, improving the quality of life for seniors.
Education
AI companions hold promise in transforming education by offering personalized tutoring and adaptive learning resources. These companions can adapt their teaching styles to individual learning preferences and pace, providing tailored support to students and enhancing learning outcomes. Additionally, AI companions can serve as interactive learning tools, engaging students in immersive educational experiences and fostering curiosity and creativity.
Workplace Assistance
In the workplace, AI companions can streamline tasks, boost productivity, and enhance collaboration among team members. Virtual assistants equipped with AI capabilities can automate routine tasks, schedule meetings, and provide real-time support, allowing employees to focus on more strategic and creative aspects of their work.
Therapeutic Applications
AI companions have therapeutic potential beyond mental health care, with applications in physical rehabilitation, autism therapy, and trauma recovery. These companions can provide personalized therapy sessions, assist with exercises, and offer emotional support, complementing traditional therapeutic interventions and improving treatment outcomes.
Personalized Customer Service
In customer service, AI companions can deliver personalized and efficient support to users, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. Chatbots equipped with AI capabilities can handle inquiries, provide product recommendations, and resolve issues in real time, offering a seamless and personalized customer experience.
Smart Home Integration
AI companions can further integrate with smart home devices, serving as central hubs for controlling and managing connected appliances, security systems, and entertainment devices. These companions can learn user preferences, anticipate needs, and automate daily routines, making homes more efficient, comfortable, and secure.
Conclusion
AI companions have emerged as a transformative force in the realm of human-computer interaction, providing individuals with personalized assistance, emotional support, and companionship. Despite the undeniable potential benefits they offer, ethical considerations regarding privacy, autonomy, and human dignity remain paramount. We must navigate the development and deployment of AI companions responsibly, ensuring that users’ privacy rights are respected, their autonomy is preserved, and their dignity is upheld. By addressing these concerns conscientiously, we can harness the full potential of AI companionship to enhance human well-being and quality of life while minimizing potential risks and ensuring a positive impact on society. As we continue to explore the myriad possibilities that AI companions present, it is essential to proceed with mindfulness, integrity, and a commitment to the values that underpin a humane and equitable future.
- https://theconversation.com/ai-companions-promise-to-combat-loneliness-but-history-shows-the-dangers-of-one-way-relationships-221086
- https://jakobnielsenphd.substack.com/p/ai-companions
- https://today.uconn.edu/2024/02/ai-companions-promise-to-combat-loneliness-but-history-shows-the-danger-of-one-way-relationships/
- https://www.toolify.ai/ai-news/the-rise-of-ai-companions-a-glimpse-into-the-future-1707589
- https://glarity.app/youtube-summary/howto-style/how-ai-companions-will-massively-reshape-18794507_1148266
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions