- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Technology
- By Omega Team
Organizations in today’s competitive hiring landscape are under increasing pressure to quickly and efficiently attract and retain top talent.. Traditional recruitment methods, often burdened by manual screening, unconscious bias, and prolonged timelines, are increasingly falling short. AI-powered recruitment tools are transforming this landscape by automating repetitive tasks, enhancing decision-making, and enabling smarter talent acquisition strategies. These tools leverage technologies like machine learning, natural language processing, and predictive analytics to streamline processes such as resume screening, candidate sourcing, interview scheduling, and skill assessment. The result is a faster, more consistent, and data-driven hiring process that benefits both recruiters and candidates. Beyond efficiency, AI helps reduce human bias and improve the overall candidate experience through personalized interactions and quicker feedback. As organizations scale and remote hiring becomes the norm, the integration of AI into recruitment workflows is shifting from a competitive edge to a strategic necessity. This article explores the key components, advantages, challenges, and emerging trends shaping the future of AI in recruitment.
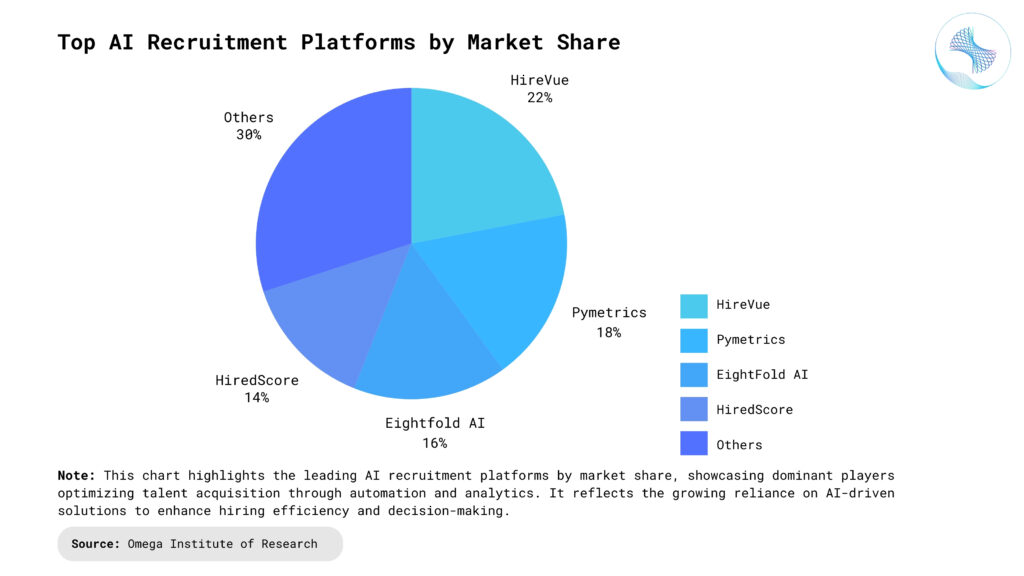
Key Features of AI Recruitment Tools
AI recruitment tools are equipped with powerful features designed to optimize and automate hiring processes. One of the most essential features is automated resume parsing, where AI scans and extracts relevant details such as skills, experience, and qualifications. This significantly reduces manual screening time and ensures consistent filtering based on job-specific criteria. Another key feature is candidate ranking, which uses machine learning algorithms to score and prioritize applicants. These systems analyze multiple data points—like previous job titles, certifications, and keyword matches—to recommend top candidates more accurately. Conversational AI in the form of chatbots enhances candidate interaction by handling FAQs, guiding users through application processes, and scheduling interviews—improving engagement while freeing up recruiters for strategic tasks. Many tools also include predictive analytics, which forecast hiring outcomes like job performance or likelihood of acceptance. Some platforms integrate with video analysis tools to evaluate speech patterns, facial expressions, and body language during virtual interviews. Collectively, these features help reduce time-to-hire, improve hiring quality, and deliver a data-driven, scalable recruitment process.
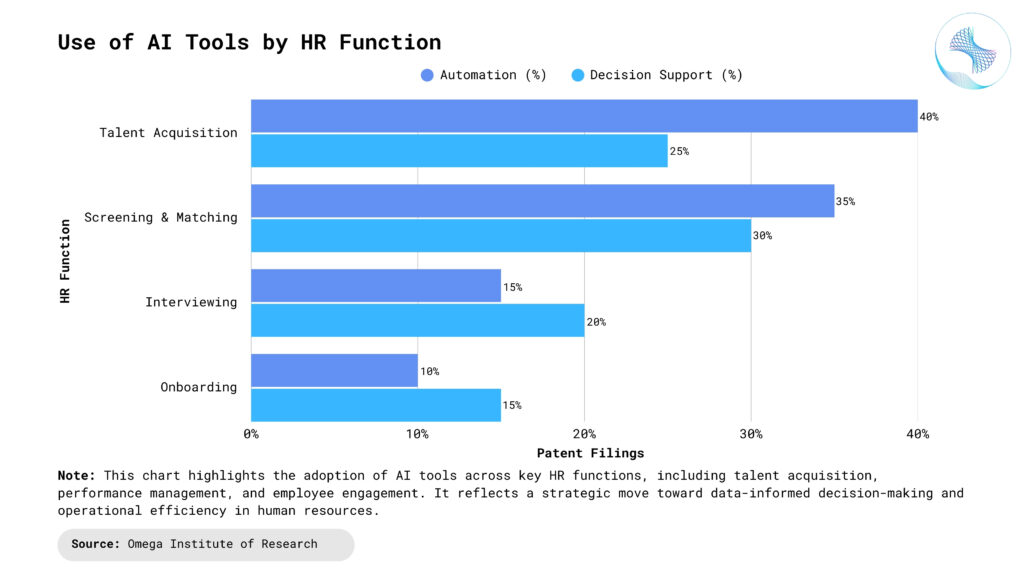
Benefits for Recruiters and HR Team
Time and Cost Efficiency: AI tools significantly reduce the time spent on repetitive tasks like resume screening, scheduling, and candidate sourcing. With automation, recruiters can process thousands of applications in a fraction of the time it would take manually, leading to quicker hiring cycles and lower operational costs. This is especially beneficial during high-volume hiring or campus recruitment drives.
Improved Hiring Accuracy: By analyzing patterns from past successful hires, AI helps match candidates more precisely with job roles. Tools powered by predictive analytics evaluate factors like skill compatibility, cultural fit, and potential for long-term retention. This reduces the chances of bad hires and boosts overall team performance.
Reduced Bias: AI recruitment tools apply objective algorithms to assess candidates, helping eliminate unconscious human bias. While not foolproof, they promote a fairer evaluation process based on data, not assumptions.
Enhanced Productivity: By offloading administrative tasks, recruiters can focus on strategic initiatives like employer branding, talent engagement, and refining hiring strategies. AI thus supports a more focused and proactive HR function.
Scalability: AI-powered systems can easily handle large volumes of applicants across multiple job openings and locations, making them ideal for rapidly growing companies or enterprises with global hiring needs.
Data-Driven Insights: AI tools provide recruiters with actionable analytics, such as talent pool trends, source effectiveness, and candidate drop-off points, enabling continuous improvement in hiring strategies.
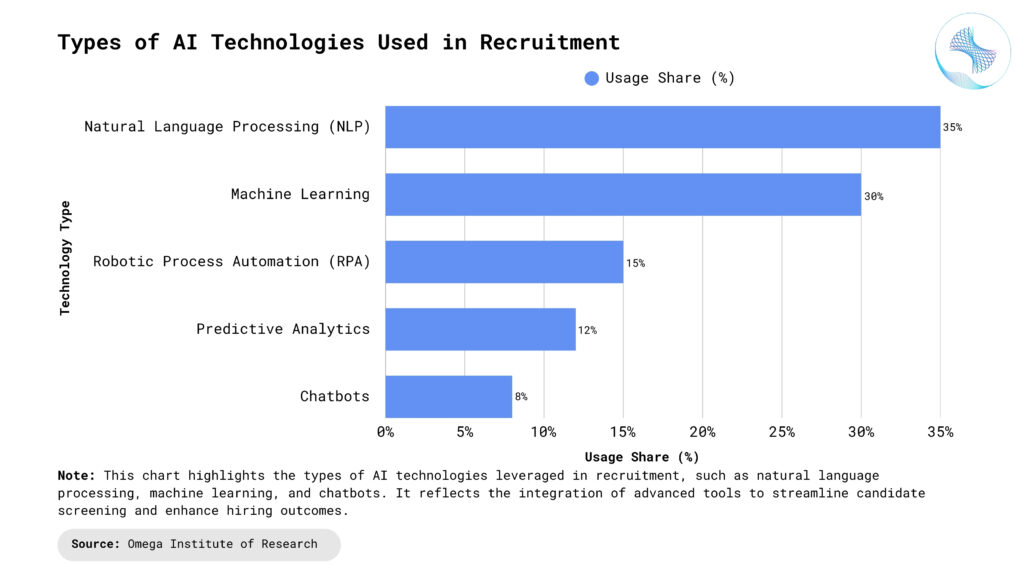
Impact on Candidate Experience
Personalized Communication: AI recruitment tools enable personalized, timely interactions through chatbots and automated emails. Candidates receive instant responses to queries, updates on application status, and tailored job recommendations. This reduces uncertainty and keeps applicants engaged throughout the process.
Faster Feedback and Decisions: Automated screening and interview scheduling shorten hiring timelines. Candidates no longer wait weeks for updates or interview calls, which improves satisfaction and reduces drop-off rates. Real-time interview feedback and faster decisions create a more transparent experience.
Accessibility and Inclusivity: AI tools can offer multilingual support and adaptive interfaces, making the application process easier for candidates from diverse backgrounds. They also help remove bias by focusing on skills and qualifications rather than demographics, promoting fairer opportunities.
Interactive Assessments: AI-driven skill tests and video interviews provide candidates with engaging and relevant challenges, giving them a chance to showcase their abilities beyond the resume. This creates a more dynamic and fair evaluation.
Consistent Experience: Automated processes ensure every candidate goes through the same structured steps, reducing variability and enhancing fairness across the hiring funnel.
Real-World Use Cases and Examples
Tech Industry: Leading tech companies like Google and IBM use AI recruitment tools to efficiently screen thousands of applications. These tools analyze resumes and online profiles to identify candidates with the best skill matches, significantly reducing recruiter workload. AI-powered chatbots handle initial candidate engagement, answering queries and scheduling interviews automatically. This speeds up hiring cycles while maintaining high candidate engagement and quality of hire.
Retail and Customer Service: Retail giants such as Walmart and Amazon employ AI-driven recruitment platforms to fill high-volume roles quickly. AI tools help screen seasonal workers by analyzing past performance data and predicting candidate success. This ensures a better fit for roles with high turnover rates. Additionally, AI assessments evaluate soft skills and personality traits, improving the quality of customer service hires and reducing attrition.
Healthcare Sector: Hospitals and healthcare providers use AI recruitment to find specialized talent like nurses and technicians more efficiently. AI algorithms assess qualifications, certifications, and experience across vast candidate pools to shortlist top candidates. During the COVID-19 pandemic, AI tools enabled faster hiring of frontline workers by automating manual screening processes, helping meet urgent staffing needs without compromising candidate quality.
Financial Services: Banks and insurance firms implement AI recruitment for compliance-heavy roles requiring specific certifications and background checks. AI systems verify credentials quickly and flag potential risks, streamlining the hiring of risk analysts and auditors. Predictive analytics help forecast candidate success, improving retention rates in highly competitive talent markets. AI also assists in creating unbiased talent pipelines to enhance workforce diversity.
Startups and SMEs: Smaller companies leverage affordable AI recruitment platforms to compete with larger firms. AI tools automate time-consuming tasks like resume screening and interview scheduling, enabling lean HR teams to focus on strategic hiring decisions. Startups benefit from AI’s ability to identify versatile candidates who fit dynamic, fast-changing roles, boosting agility and growth potential.
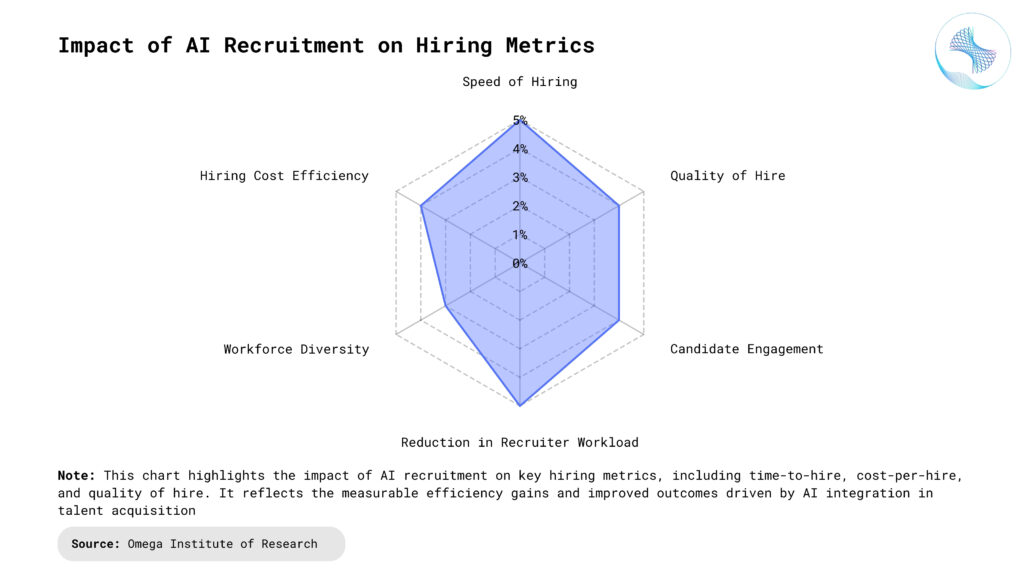
Ethical Concerns and Bias in AI
Bias in Training Data: AI recruitment tools are only as fair as the data they’re trained on. If historical hiring data contains bias—such as preferences for certain genders, ethnicities, or schools—AI models may replicate and even amplify those patterns. This can result in unfair scoring, reduced diversity, and the exclusion of qualified candidates. Companies must regularly audit their AI systems and datasets to identify and correct hidden biases. Transparent practices and inclusive datasets are essential to avoid perpetuating systemic inequalities.
Lack of Transparency: Many AI recruitment tools operate as black boxes, offering little insight into how decisions are made. Candidates may be rejected based on algorithmic judgments they cannot contest or understand. This undermines trust in the hiring process and raises concerns about accountability. Employers must ensure that AI decisions are explainable and compliant with local labor laws and data protection regulations. Providing candidates with feedback can help build credibility and transparency.
Privacy and Data Security: AI systems require access to large volumes of personal data, including resumes, social media profiles, and behavioral assessments. Mishandling or data breaches can compromise sensitive candidate information. Ensuring strong encryption, secure storage, and GDPR-compliant practices is critical to maintaining candidate trust. Organizations should also clarify what data is collected and how it’s used, giving candidates the option to opt out of automated screening.
Overreliance on Automation: Relying too heavily on AI can lead to missed opportunities. Algorithms may not fully grasp intangible traits like cultural fit, passion, or creativity, which often make a difference in hiring. Over automation may also dehumanize the candidate experience, reducing engagement. Recruiters should balance AI insights with human judgment, using technology to assist rather than replace decision-making. A hybrid approach ensures better outcomes and a more empathetic hiring process.
Future Trends in AI Recruitment
Conversational AI for Interviews: AI-driven chatbots and voice assistants are becoming more sophisticated, allowing for natural, real-time candidate interactions. These tools can conduct initial screening interviews, assess communication skills, and respond to questions using context-aware language models. Future iterations will mimic human dialogue more closely, offering personalized, unbiased interactions at scale. This will improve engagement, reduce recruiter workload, and provide candidates with an interactive, responsive experience during early hiring stages.
Emotion and Sentiment Analysis: Next-gen AI tools will incorporate emotional intelligence, analyzing facial expressions, voice tone, and language sentiment during video interviews. This will help assess soft skills such as empathy, enthusiasm, and adaptability. While still controversial, such technology could add depth to candidate evaluations if implemented ethically. It may help recruiters identify high-potential candidates who excel in human-centric roles. However, regulation and transparency will be essential to ensure fairness and prevent misuse.
Skill-Based Matching and Upskilling Guidance: AI will evolve from keyword matching to contextual skill analysis, identifying transferable capabilities and potential for growth. It will recommend personalized learning paths based on job requirements and gaps in a candidate’s profile. This future-facing approach helps companies build talent pipelines and supports applicants in improving their fit. Integrated with learning platforms, recruitment tools will guide candidates in real time, fostering a more supportive job-seeking experience.
Diversity-Aware Algorithms: Recruiters will increasingly adopt AI systems designed to enhance diversity by counteracting unconscious bias. These models will analyze job descriptions for biased language, anonymize applications, and recommend inclusive outreach strategies. They can also flag patterns that may lead to homogenous hiring. With DEI becoming a strategic priority, ethical AI will play a key role in building fairer workplaces. Transparent design and auditing will be crucial for adoption and trust.
Predictive Hiring Analytics:
AI will increasingly forecast hiring outcomes by analyzing historical data, team dynamics, and performance trends. Predictive models will help identify candidates most likely to succeed in a specific role or company culture. This allows recruiters to make proactive, data-backed decisions rather than relying solely on resumes or interviews. Over time, organizations can reduce turnover, improve role fit, and optimize hiring strategies. These insights will be integrated into dashboards for real-time, strategic talent planning.Conclusion
AI in recruitment isn’t just a process improvement—it’s a paradigm shift in how organizations connect with talent. By integrating machine learning into hiring workflows, businesses can make faster, smarter, and fairer decisions. From resume screening to candidate engagement and predictive analytics, AI reduces manual effort and helps uncover hidden talent that traditional methods might overlook. It empowers recruiters to focus on strategic, human-centric aspects of hiring, while technology handles the repetitive tasks. As AI tools continue to evolve, we can expect more personalized candidate experiences, reduced biases, and data-driven workforce planning. In the long run, AI will not only streamline recruitment but also elevate it—making hiring more insightful, inclusive, and impactful across industries.
- https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/4-trends-shaping-the-future-of-hr-technology
- https://www.bbc.com/worklife/article/20210928-how-ai-is-changing-the-way-we-hire
- https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/hr-topics/technology/pages/ai-in-recruitment.aspx
- https://hbr.org/2019/10/using-ai-to-eliminate-bias-in-hiring
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions