- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Technology
- By Omega Team

AI Strategies for Modern Businesses
Artificial Intelligence is a term you have heard a lot lately. This is not just a concept from science fiction movies, it’s genuine, and changing the way businesses operate. With the data, report analysis, and contribution of Omega experts we will explore: what AI is, how it works, and implications that provide value for growing businesses. This field of computer science focuses on creating algorithms that can learn from data, adapt to new situations, and make decisions.
AI’s Integration for Business Owners
Artificial Intelligence offers benefits and opportunities for business owners. AI empowers business owners by providing data-driven insights, enhancing operational efficiency, improving customer experiences, enabling innovation and success in the highly competitive business landscape and AI holds importance for business owners due to its potential to revolutionize operations, decision-making, and overall business strategies.
Artificial Intelligence has various subfields like machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and robotics. Machine learning is a subset of AI that enables systems to improve their performance on a task by learning from data without being explicitly programmed. This is achieved through algorithms that allow machines to recognize patterns and relationships in data, and subsequently make informed decisions based on that information.
Natural language enables us to understand computers, interpret, and generate human language. This technology underlies applications such as chatbots, and language translations. Computer vision, on the other hand, focuses on giving machines the ability to interpret and understand visual information from the world, enabling them to identify objects, recognize faces, and even drive autonomous vehicles.
As AI continues to evolve, striking a balance between innovation and ethical safeguards will be crucial in shaping the role of AI in our society.
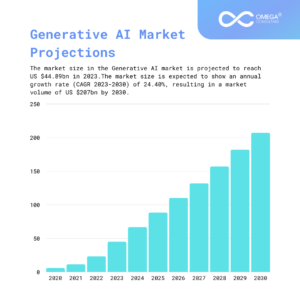
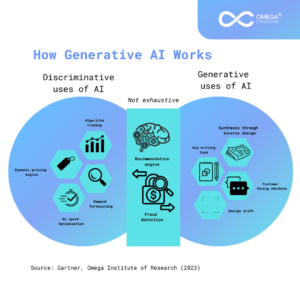
Generative AI
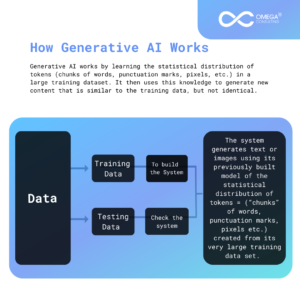
Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence that can create new content, such as text, images, audio, and video. It does this by learning the patterns and structure of its input training data and then generating new data that has similar characteristics.
Generative AI models are trained on massive datasets of existing data. For example, a generative AI model that can generate text might be trained on a dataset of books, articles, and other written materials. Once the model is trained, it can be used to generate new text, such as news articles, poems, or even code.
Generative AI is still a relatively new field, but it has the potential to revolutionize many industries. For instance, generative AI can be used to create new product designs, develop new marketing campaigns, and even produce new forms of art and entertainment.
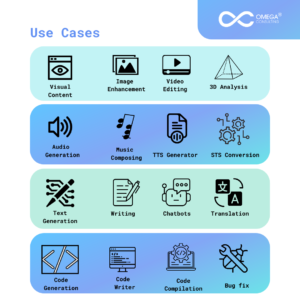
Harnessing the Power of Generative AI in Business
Automated Content Creation: For use in marketing materials, blogs, social media, websites, and other online media, generative AI can create excellent written content. Businesses may do this to save time and money while assuring constant and interesting content.
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: Generative AI is used by virtual assistants and AI-powered chatbots to handle common requests, respond to frequently asked queries, and offer 24/7 customer service, increasing productivity and satisfaction.
Idea Generation: Businesses may utilize generative AI to produce creative product ideas based on consumer preferences and market trends.
Recommendation Engines: Generative AI improves user experiences in e-commerce, streaming services, and other areas by assisting firms in personalizing suggestions for clients.
Multilingual Communication: Generative AI can help with content translation and localization for various markets, enabling companies to go worldwide.
The AI Business Revolution
We now know what AI is, and how it works, let’s dive into how it’s impacting business.
Automation: One of the biggest changes AI is bringing to business is automation. This means that AI can take over repetitive tasks that used to be done by humans. In a factory, robots powered by AI can assemble products faster and more accurately than human workers.
Example: AI-powered robots in manufacturing assembly lines automate repetitive tasks like welding and quality checks.
Data Privacy: To make AI work, you need lots of data. This raises concerns about how businesses handle and protect customer data. It’s crucial to ensure that data privacy laws and ethical practices are in place to safeguard sensitive information.
Example: AI-driven encryption and tokenization systems protect sensitive customer data in e-commerce transactions.
Job Displacement: AI is becoming more widespread; some jobs may disappear or change. Businesses need to support employees who might be affected by these changes through retraining.
Example: Retail stores use self-checkout kiosks with AI to reduce cashier positions but create jobs for kiosk maintenance and customer support.
Customer Service: Nowadays AI-powered chatbots can answer customer questions, help with troubleshooting, and even process orders. This saves business time and money by providing round-the-clock support without the need for human staff.
Example: Airlines use AI-powered chatbots to provide passengers with real-time flight updates and answer common queries.
Personalization: AI can analyze amounts of data to understand customer preferences better than ever before. For instance, when you shop online, AI systems can recommend products based on your past purchases and browsing history.
Example: Streaming platforms such as Netflix use AI algorithms to recommend personalized movie and TV show suggestions based on user viewing history.
Fraud Detection: AI is excellent at spotting unusual patterns in data. In the world of finance, AI can detect fraudulent transactions by analyzing millions of transactions in real time. This protects businesses and their customers from financial losses.
Example: Banks employ AI to analyze transaction data in real time, identifying suspicious activities and preventing fraudulent transactions.
Personalization at Scale: AI-powered personalization is changing how businesses interact with customers by analyzing customer behavior and preferences. Companies can tailor their products, services, and marketing campaigns to individual needs.
Example: For instance, streaming platforms use AI to recommend content based on the user’s viewing history.
Competitive Advantages of AI for Business
Better decision-making: AI can assist organizations in improving decision-making by analyzing massive volumes of data and seeing patterns and trends that are hard to see with the naked eye. For instance, AI may be used to better efficiently manage resources and forecast consumer attrition.
Greater effectiveness and productivity: AI can automate a number of laborious and repetitive jobs, freeing up staff members to concentrate on more strategic work. For instance, AI may be used to automate data input, fraud detection, and customer assistance. AI may be used to gather and analyze customer data to develop personalized customer experiences that are more likely to result in sales and customer loyalty. AI may be used, for instance, to make product recommendations, deliver personalized marketing messages, and offer customer care.
Lower expenses: AI may lower costs for organizations by automating jobs, increasing productivity, and making wiser judgments. AI may be used, for instance, to optimize supply chains, lower expenses in some sectors, and reduce the volume of customer support calls.
Better risk management: Threats like fraud, cyberattacks, and product recalls may be identified and reduced. AI may be used, for instance, to examine financial transactions for fraud, keep an eye on client behavior for indications of questionable conduct, and test items for flaws.
Business Evolution with the help of AI Implementation
Amazon: Amazon is a pioneer in the use of AI, and it has used AI to improve its operations in many ways. For example, Amazon uses AI to recommend products to customers, optimize its warehouses, and personalize its search results. As a result of its AI adoption, Amazon has been able to increase its sales, improve its customer experience, and reduce its costs.
Netflix: Netflix uses AI to recommend movies and TV shows to its users. This has helped Netflix to personalize its offerings and keep its users engaged. Netflix also uses AI to optimize its content library and to improve its search results. As a result of its AI adoption, Netflix has been able to grow its subscriber base and increase its revenue.
Spotify: Spotify uses AI to recommend music to its users. This has helped Spotify to create a personalized listening experience for its users. Spotify also uses AI to improve its discovery features and to personalize its marketing campaigns. As a result of its AI adoption, Spotify has been able to increase its user engagement and revenue.
Walmart: Walmart is using AI to improve its supply chain management. For example, Walmart is using AI to predict demand for products, optimize its inventory levels, and improve its delivery routes. As a result of its AI adoption, Walmart has been able to reduce its costs and improve its customer service.
Siemens: Siemens is using AI to improve its manufacturing processes. For example, Siemens is using AI to identify defects in products, optimize its production lines, and improve its energy efficiency. As a result of its AI adoption, Siemens has been able to improve its quality, productivity, and profitability.
Compliance Essentials
The compliance requirements for AI vary depending on the industry and the specific application.
Data protection: Organizations that use AI to process personal data must comply with data protection laws, such as the GDPR and HIPAA. This includes ensuring that the data is collected and used fairly and lawfully and that it is protected from unauthorized access and misuse.
Privacy protection: Organizations that use AI to collect or process personal data must comply with privacy laws, such as the GDPR and CCPA. This includes ensuring that individuals have the right to access their personal data, to correct it if it is inaccurate, and to object to its processing.
Transparency: Organizations that use AI must be transparent about how their AI systems work. This includes providing information about the data that is used to train the systems, the algorithms that are used, and the decisions that are made by the systems.
Non-discrimination: Organizations that use AI to make decisions that affect individuals must comply with non-discrimination laws, such as the Equal Employment Opportunity Act (EEOA) and the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). This means that AI systems must not be biased against individuals on the basis of their race, gender, religion, or other protected characteristics.
Accountability: Organizations that use AI must be accountable for the decisions that are made by their AI systems. This means that they must be able to explain how the decisions were made and to take steps to correct any errors.
Compliance Scope
Regulatory compliance: For example, AI can be used to help businesses comply with anti-money laundering regulations by analyzing financial transactions for suspicious activity.
Customer due diligence: For example, AI can be used to help businesses comply with Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations by collecting and analyzing data about customers to assess their risk of being involved in financial crimes.
Automation Revolution: AI’s 48% Task Takeover by 2025
Enhanced Customer Experience: Virtual assistants and chatbots driven by AI have already greatly enhanced customer service. But there’s a lot more in store for the future. Businesses will be able to offer more personalized client experiences because of AI. AI can forecast client wants, provide specialized product suggestions, and even foresee when a customer might require assistance by analyzing enormous volumes of data.
For instance, e-commerce platforms will use AI in around 1-2 years to create virtual shopping assistants that know a customer’s style, preferences, and shopping history, making online shopping as convenient and personalized as in-store experiences. Data-Driven Decision Making: In the future, businesses will rely even more on AI to harness the power of big data. Advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms will help organizations extract valuable insights from their data.
Automation of Repetitive Task: Automating repetitive and time-consuming operations across several sectors will continue to be accomplished through the integration of AI into business applications. In addition to increasing productivity, this will free up human resources for more imaginative and strategic responsibilities. Robots controlled by AI, for instance, would do repetitive assembly line labor while human workers concentrate on innovation and quality assurance in the manufacturing industry.
Supply Chain Optimization: Supply chain optimization will greatly benefit from AI’s predictive powers. Businesses will estimate demand, manage inventory, and improve logistics using AI-driven algorithms. This will result in lower prices, quicker delivery times, and less waste.
Security and Fraud Prevention: AI will be essential to improving cybersecurity. It will continually scan network traffic for threats and abnormalities and take immediate action to protect critical data.
Use of AI tools in sales
Improved Customer Service: Chatbots are increasingly used to provide customer support 24/7. AI-driven chatbots can answer queries, resolve issues, and offer personalized recommendations to enhance customer satisfaction while reducing customer service costs.
Cost Reduction: AI-driven automation not only saves time but also reduces operational costs. Businesses can use AI to streamline processes from automating data entry to optimizing logistics routes. Cost savings contribute to improved profitability and competitiveness.
Market Insights: AI tools can analyze market trends, competitor strategies, and customer sentiment. This information is invaluable for businesses seeking a competitive edge as it informs product development, pricing strategies, and marketing campaigns.
Alive AI
AI is not alive in the traditional sense of the word, it can copy many of the functions of living beings, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. It is important to remember that AI is still a tool that is created and controlled by humans, and it does not have consciousness or feelings.
Reinforcement Learning: Reinforcement learning is a type of machine learning where the AI learns by trial and error. The AI is given a reward for taking actions that lead to desired outcomes, and it is penalized for taking actions that lead to undesired outcomes. This allows the AI to learn how to behave in a way that maximizes its rewards.
Neural Networks: Neural networks are a type of machine learning algorithm that is inspired by the structure of the human brain. Neural networks can learn to recognize patterns and make predictions, and they are often used in AI applications.
Benefits of Alive AI:
- It could be used to develop more efficient and effective ways to solve complex problems.
- It could be used to improve our understanding of the world around us.
- It could be used to create new products and services that improve our lives.
Potential risks associated with Alive AI:
- It could be used to create autonomous weapons systems that could harm people.
- It could be used to create AI systems that are biased or discriminatory.
- It could be used to create AI systems that are hacked or controlled by malicious actors.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is a game-changer for businesses across industries. Its implications include enhanced data analysis, automation of repetitive tasks, personalization, improved customer service, predictive analytics, cost reduction, market insights, and enhanced security. Incorporating AI into business strategies is no longer an option, it’s a necessity for staying competitive and meeting evolving customer demands. Successful integration requires a holistic approach that considers both the opportunities and responsibilities that AI brings to the modern business landscape. For businesses to thrive in this AI-driven world, it’s essential to embrace AI responsibly. This means prioritizing data privacy, investing in employee training, addressing biases, and fortifying cybersecurity. AI is a powerful tool that can drive success, but it must be used wisely and ethically to benefit both businesses and society as a whole.
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions