- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Sustainability
- By Omega Team

In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, the concept of sustainability has emerged as a fundamental driver of organizational success. Beyond traditional profit motives, businesses are increasingly recognizing the importance of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations in their operations. Sustainability is no longer viewed as a mere checkbox on a corporate social responsibility (CSR) report but rather as a strategic imperative that drives innovation, fosters resilience, and enhances long-term value creation.
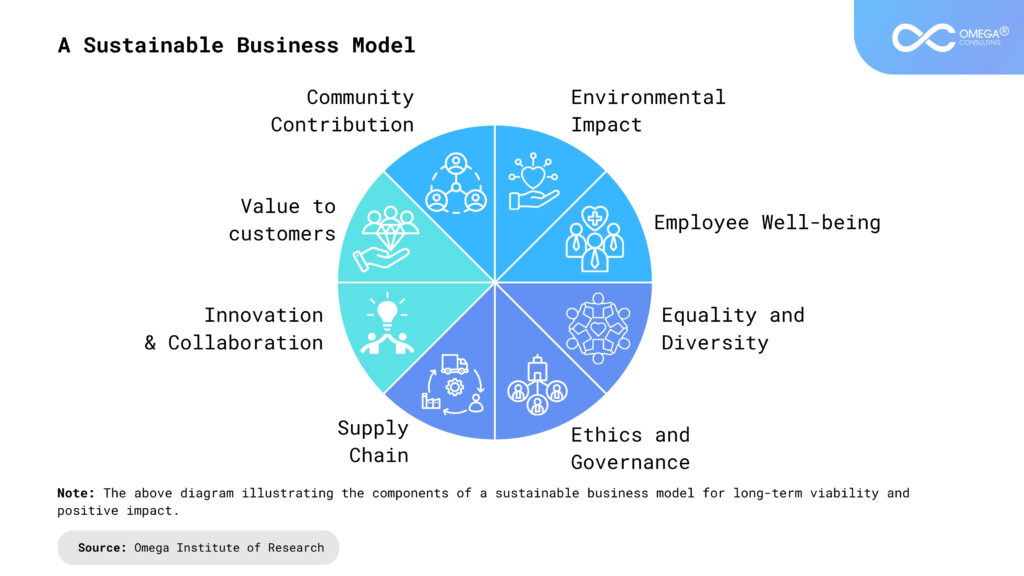
Understanding Sustainability in Business Transformation
Sustainability has transcended its traditional environmental connotations to become a multifaceted imperative for organizations worldwide. Sustainability in business transformation signifies a paradigm shift from viewing profitability as the sole measure of success to embracing a holistic approach that integrates environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and economic prosperity into every facet of an organization’s operations and strategy.
At its essence, sustainability in business transformation involves a profound reimagining of traditional business models to align with principles that foster long-term viability and resilience. It goes beyond compliance with regulations or superficial CSR initiatives to permeate the very core of an organization’s culture, values, and decision-making processes.
This transformation entails recognizing that businesses operate within complex ecosystems where the health of the environment, the well-being of communities, and the integrity of governance systems are inextricably intertwined with financial performance. It necessitates a shift towards regenerative practices that not only minimize harm but actively contribute to the restoration and preservation of natural resources, social equity, and ethical governance.
Moreover, understanding it requires organizations to adopt a systems thinking approach, recognizing the interconnectedness and interdependencies of various stakeholders, both within and beyond their immediate sphere of influence. It involves engaging in meaningful dialogue with stakeholders—from employees and customers to investors, suppliers, and local communities—to understand their expectations, concerns, and aspirations regarding sustainability issues.
Furthermore, sustainability necessitates a fundamental reevaluation of value creation, moving beyond short-term profit maximization to embrace broader notions of value that encompass social, environmental, and ethical dimensions. It entails recognizing that sustainable business practices are not only compatible with financial success but can also enhance competitiveness, foster innovation, and create shared value for all stakeholders involved.
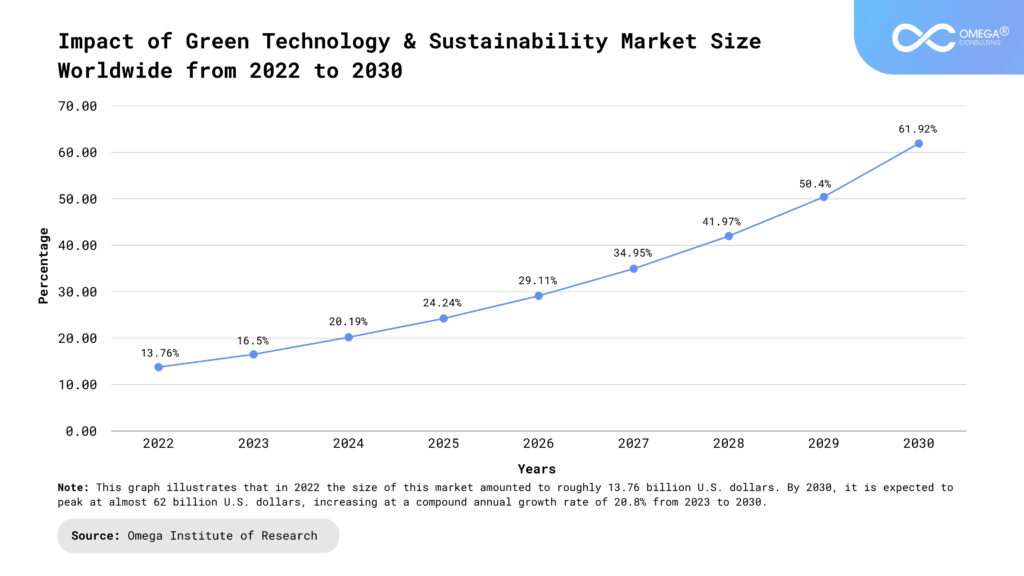
Ultimately, it requires a fundamental shift in mindset—one that recognizes the imperative of aligning business objectives with broader societal and environmental goals. It involves embracing sustainability as a strategic imperative that drives innovation, fosters resilience, and enables organizations to thrive in an increasingly complex and interconnected world. By integrating sustainability into their DNA, organizations can not only future-proof their operations but also contribute to building a more equitable, inclusive, and sustainable future for generations to come.
Key Principles for Regulating Sustainability in Business Transformation
Several key principles underpin sustainability in business transformation:
- Integration: Sustainability should be embedded across all levels of an organization, from strategic planning to day-to-day decision-making processes.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging with stakeholders, including employees, customers, investors, and communities, is essential for understanding their expectations and addressing their concerns regarding sustainability issues.
- Transparency and Accountability: Transparency in reporting and accountability for performance are critical to building trust and credibility with stakeholders.
- Continuous Improvement: Sustainability is a journey, not a destination. Organizations must commit to continuous improvement and innovation to advance their sustainability objectives over time.
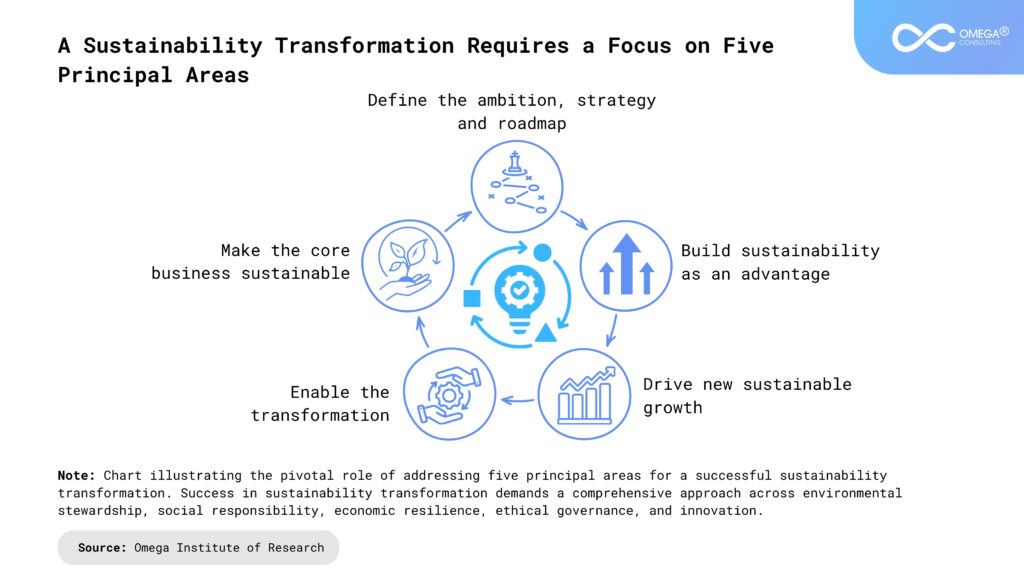
Frameworks & Practices to Implement Sustainability in Business Transformation
Various frameworks and practices can guide organizations in implementing sustainability in their business transformation efforts. These include:
- Triple Bottom Line: The triple bottom line framework evaluates business performance based on three dimensions: profit, people, and planet. It encourages organizations to measure and report their social and environmental impact alongside financial results.
- Life Cycle Assessment (LCA): LCA assesses the environmental impacts of products or services throughout their entire life cycle, from raw material extraction to disposal. It helps identify opportunities for reducing environmental footprints and optimizing resource use.
- Circular Economy: The circular economy paradigm promotes the efficient use of resources by minimizing waste and maximizing the reuse, recycling, and regeneration of materials. It offers opportunities for businesses to create value while reducing their environmental impact.
- Sustainability Reporting Standards: Frameworks such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) provide guidelines for reporting on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance. These standards help organizations transparently communicate their sustainability efforts to stakeholders and benchmark their performance against industry peers.
- Impact Assessment Tools: Impact assessment tools, such as the Social Return on Investment (SROI) and Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA), help organizations evaluate the social, environmental, and economic impacts of their activities. By quantifying and monetizing these impacts, organizations can make informed decisions that maximize positive outcomes and minimize negative consequences.
- Stakeholder Engagement Strategies: Developing robust stakeholder engagement strategies is essential for understanding and addressing the diverse needs and expectations of stakeholders. Stakeholder mapping, consultation forums, and multi-stakeholder partnerships facilitate meaningful engagement and collaboration.
- Supplier Sustainability Programs: Implementing supplier sustainability programs involves working closely with suppliers to assess and improve their sustainability performance. Initiatives such as supplier assessments, audits, capacity-building workshops, and incentivized sustainability targets help integrate sustainability principles into the supply chain.
Benefits of Planning Sustainability in Business Transformation
Embracing sustainability in business transformation offers numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Brand Reputation: Demonstrating a commitment to sustainability can enhance brand reputation, attract socially conscious consumers, and differentiate organizations in the marketplace.
- Risk Mitigation: Proactively addressing sustainability issues helps organizations mitigate risks related to regulatory compliance, supply chain disruptions, and reputational damage.
- Cost Savings: Adopting sustainable practices, such as energy efficiency measures and waste reduction initiatives, can lead to cost savings and operational efficiencies over time.
- Access to Capital: Investors increasingly consider ESG factors when making investment decisions. Embracing sustainability can improve access to capital and lower the cost of capital for organizations.
- Employee Engagement and Retention: Embracing sustainability can boost employee morale, attract top talent, and improve retention rates. Employees are more likely to be engaged and committed to organizations that prioritize social and environmental responsibility.
- Market Differentiation and Competitive Advantage: Sustainability can serve as a powerful differentiator in crowded markets, helping organizations stand out from competitors. Companies that lead in sustainability innovation and practices often enjoy a competitive advantage and capture market share.
Challenges and Considerations in ensuring Sustainability in transformation
While the benefits of sustainability are compelling, organizations may encounter several challenges in their transformation journey:
- Complexity: Integrating sustainability into business operations can be complex and require significant organizational change. It may involve overcoming resistance from stakeholders and addressing cultural barriers within the organization.
- Resource Constraints: Implementing sustainability initiatives may require upfront investment in technology, infrastructure, and talent. Organizations must carefully balance short-term costs with long-term benefits.
- Measurement and Reporting: Measuring and reporting sustainability performance can be challenging due to the lack of standardized metrics and methodologies. Organizations must invest in robust measurement systems and transparent reporting practices to accurately communicate their sustainability efforts.
- Supply Chain Complexity: Organizations with complex supply chains may face challenges in ensuring the sustainability of their entire value chain. Managing supplier relationships, monitoring compliance, and addressing sustainability risks throughout the supply chain requires collaboration and coordination across multiple stakeholders.
- Data Management and Analysis: Collecting, managing, and analyzing sustainability data can be resource-intensive and complex. Organizations must invest in robust data management systems, processes, and expertise to track performance, measure impact, and make informed decisions.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Rapidly evolving regulatory landscapes, both domestically and internationally, can pose challenges for organizations navigating sustainability requirements and compliance obligations. Staying abreast of regulatory developments and proactively addressing compliance risks is essential for mitigating regulatory uncertainty.
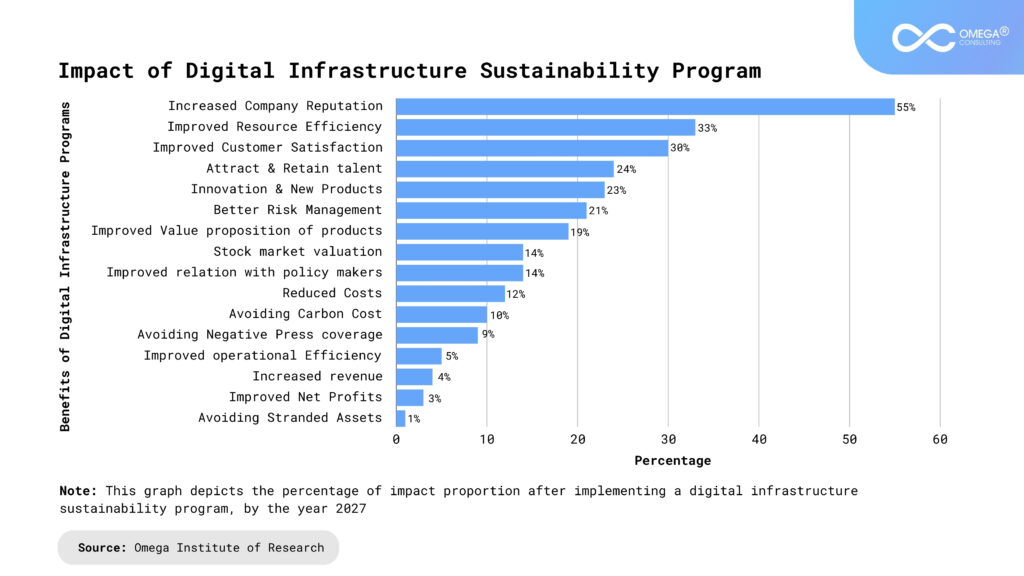
Perspective of Management Consulting in Ensuring Sustainability
Management consulting firms guide organizations through the complexities of integrating sustainability into their operations, strategies, and cultures. With their deep expertise, diverse skill sets, and strategic insights, consultants serve as trusted advisors, catalysts for change, and champions of sustainability within organizations of all sizes and industries.
One of the primary roles of management consulting in ensuring sustainability is to assist organizations in navigating the multifaceted landscape of sustainability challenges and opportunities. Consultants comprehensively assess clients’ sustainability performance, analyzing their environmental impact, social practices, governance structures, and stakeholder relationships. Through rigorous data analysis, benchmarking, and stakeholder engagement, consultants identify key areas for improvement and develop tailored strategies to drive positive change.
Moreover, they provide organizations with access to specialized knowledge and best practices in sustainability management. Consultants bring a wealth of experience from working with diverse clients across industries, allowing them to offer valuable insights, innovative solutions, and proven methodologies for addressing sustainability challenges. From designing sustainable supply chains to implementing renewable energy projects and enhancing stakeholder engagement, consultants offer practical guidance and support at every stage of the sustainability journey.
Furthermore, they help organizations integrate sustainability into their strategic planning and decision-making processes. Consultants work closely with senior leadership teams to align sustainability objectives with broader business goals, develop clear metrics for measuring progress, and embed sustainability considerations into strategic initiatives and investment decisions. By integrating sustainability into corporate strategy, organizations can create alignment, accountability, and momentum for sustainable growth and value creation.
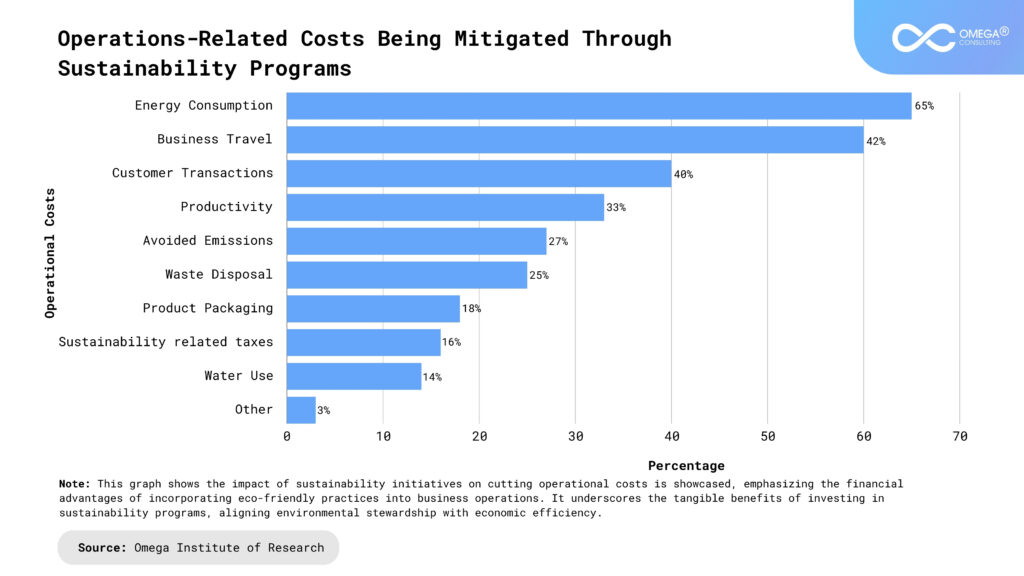
In addition, these firms support organizations in building internal capabilities and fostering a culture of sustainability across the organization. Consultants provide training, coaching, and change management support to empower employees at all levels to embrace sustainability principles, adopt best practices, and drive continuous improvement. By fostering a culture of sustainability, organizations can mobilize their workforce, unleash creativity, and unlock the full potential of their people to drive positive change.
They advocate for sustainability within the broader business community. Consultants engage with policymakers, industry associations, and other stakeholders to advocate for policies and practices that support sustainable development and create a level playing field for responsible businesses. By leveraging their expertise and influence, consultants can drive systemic change and catalyze collective action toward a more sustainable future.
Conclusion
Sustainability is no longer a choice but a necessity for businesses seeking long-term success in a rapidly changing world. By embracing sustainability in their business transformation efforts, organizations can create value for shareholders, stakeholders, and society at large while safeguarding the planet for future generations. With the right strategies, frameworks, and practices in place, businesses can thrive sustainably and responsibly, driving positive impact and innovation in the global economy.
As we look to the future, it is clear that sustainability in business transformation is not a destination but a continuous evolution—a commitment to ongoing improvement, collaboration, and responsible stewardship of our planet and society.
- http://(https://kpmg.com/xx/en/home/insights/2023/09/kpmg-global-ceo-outlook-survey.html)
- http://(https://www.wbcsd.org/)
- http://(https://integratedreporting.ifrs.org/)
- http://(https://www.fsb.org/2022/10/progress-report-on-climate-related-disclosures/)
- http://(https://www.unepfi.org/industries/banking/principles-for-responsible-banking-to-strengthen-climate-ambition-to-meet-increased-expectations/)
- http://(https://www.accenture.com/content/dam/accenture/final/corporate/corporate-initiatives/sustainability/document/360-Value-Report-2022.pdf)
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions