- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Information Technology
- By Omega Team

A blockchain is a new type of digital record-keeping or database that organizes how information and value move across the internet. The technology stores transactional records called blocks that are chained together thus, the name blockchain. The information is encrypted to ensure that the privacy of the user and the data shared is not compromised and cannot be altered. This creates trust in the network through the shared database which is distributed across vast peer-to-peer computer networks. The information on a blockchain network is not controlled by a centralized authority. This means that the participants of the network maintain the data and they hold the democratic authority to approve any transactions carried out on the network. In a nutshell, a blockchain network cannot be individually owned, neither can any individual entity modify the data stored in it without the consensus of their peers.
Unique Attributes of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain has injected a new wave of establishing trust among business partners in the digital market and is redefining online transactions in the following ways:
Network Decentralization: Blockchain networks focus on decentralized networks where there is no single owner of the network. Everyone on the network stores a copy of the ledgers and of every block. This further eliminates the need for middlemen and trust authorities.
Transparency: Blockchain follows a distributed Peer-to-Peer (P2P) network protocol where files are shared directly between systems on the network without network protocol where files are shared directly between systems on the network without the need of a central server. This in turn allows all participants in the network to have an entire copy of the Blockchain, enabling them to view all transactions on the network in real-time.
Immutability: Immutability is the ability of a blockchain transaction to remain unchanged. The technology uses a principle known as the Hash value which creates a digital signature for every block. This functionality of the blockchain technology ensures that no one can intrude into the system or alter the data saved to the block. This makes the blockchain a reliable and permanent record-keeping system.
Security: Blockchain security is ensured through the principle of cryptography where each block in the blockchain is time-stamped, uniquely hashed and copied across all nodes in the network. This makes it highly impossible to alter or destroy any data across the network. For instance, blockchain networks use consensus mechanisms such as proof of work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) to mitigate cyber-attacks from hackers.
Functionality of Blockchain
Every blockchain consists of three basic elements namely Data, Hash and Hash of the previous Block.
Data: In a blockchain, each computer in the network also known as the node has a full record of the data that has been stored on the blockchain since its inception. Data stored in a block depends on the type of blockchain. For instance, a Bitcoin blockchain contains information about the receiver, sender, transaction date and the number or number of Bitcoins transferred.
Hash: A hash is a function that meets the encrypted demands needed to solve a blockchain computation. The Hash is like a fingerprint unique to each block. For instance, when a transaction has been verified and needs to be added to a block in a chain, it is put through an algorithm that converts it into a set of unique numbers and letters using all the content the block holds. Once the block is created, any changes were done to the contents of the block will result in changes to the hash. The figure below illustrates how blocks are cryptographically linked through the hash. The first block of every blockchain is called the Genesis Block. It has no previous hash and there is no block preceding it. The second block contains the hash of the first block and the chain continues by matching a block’s hash with the previous hash value of the next block. This is mandatory if the blockchain must be considered valid.
Figure 1: Genesis Block
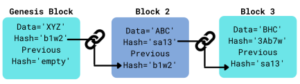
If for instance, an attacker tampers with the content of the block, a different hash is created which will eventually break the chain, making the blockchain invalid. Even though blockchains are difficult to hack, today’s high-speed computing power gives the attackers the ability to calculate hundred thousand hashes per second. This can give the attacker room to tamper with a block within a few minutes. The attacker can then recalculate the hashes of the subsequent blocks to make them a valid blockchain again. To mitigate this threat, blockchain uses two different concepts namely, Proof of Work and Distributed P2P Network.
Proof of Work: Proof-of-Work (PoW) is the original consensus algorithm in a blockchain network which requires that a computational problem needs to be solved and verified before a new block is added to the blockchain network. This means that, if an attacker intends to tamper with one block, he or she must do proof- of- Work for that block and all the subsequent blocks, making the tampering task much tougher for the attacker.
Distributed P2P Network: Distributed P2P Network is based on the principle of decentralization. It, therefore, eliminates the need for a central server or intermediaries within the network. All computers within the network are connected in a way that each of them maintains a complete copy of the ledger and compares it to other devices to ensure the accuracy of the data. For instance, when any user creates a new block, the new block is sent to all users on the network. Each node then verifies the block to ensure that it has not been altered. After complete checking, each node adds this block to their blockchain. All the nodes in the network then create a consensus. They agree on blocks that are valid and those that are not valid. Those that are not valid will be rejected by all the nodes in the network. The figures below illustrate how a blockchain is distributed across all nodes in the network to ensure it is tamperproof.
Global Growth Opportunities
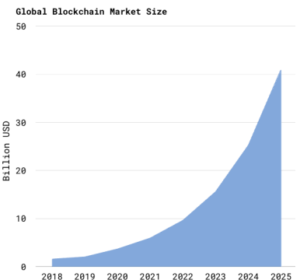
The global market for Blockchain Technology is projected to reach USD 30.67 billion by the year 2027 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 43% over the analysis period of 2020 through 2027. In the year 2019, USD 2.7 Billion was spent on blockchain solutions and it is projected to reach USD 11.2 billion in the year 2022. On the other hand, a massive growth opportunity was witnessed in North America as it dominated the global market size for the year 2020 after making a huge investment in blockchain technology during 2016-2017.
Figure 2: Distributed P2P Network
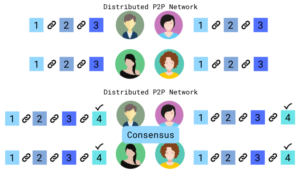
Figure 3: Global Market Size
Finance Industry: The global cryptocurrency market was estimated at USD 792.53 million in 2019 and is expected to reach USD 5,190.62 million by 2026. Growth is facilitated by smart contracts, international Payments, Syndicate loans, P2P lending, remittance, and many other complex financial products.
Retail Market: Growth in the retail market characterized by the need for safe and secure data transmission in the supply chain. Application in the retail market that contribute to this growth include Compliance Management, Identity Management, Loyalty and Rewards Management, Payments, and Supply Chain Management.
Insurance Market: The growth of this market has been fueled by fraudulent insurance claims, which has necessitated the need for transparent and trustworthy systems such as the blockchain. The need to reduce the total cost of ownership has also fueled the growth in this market. This kind of growth has been witnessed in the recent past in the Asia-Pacific region where opportunities for low-cost innovations have taken the center stage.
Manufacturing Industry: The global manufacturing output is stabilizing with a blockchain solution. Manufacturers now have a living dossier of activity logs and can keep tabs on the flow of goods between companies. The demand for blockchain in logistics and supply chain management, counterfeit, quality control, and compliance from large-scale operators are reasons for growth.
Agricultural Industry: Blockchain technology enables the key players of this industry to use data-driven innovations for smart farming and smart index-based agriculture for agricultural insurance. The technology enables the traceability of information in the food supply chain thus improving food safety. The world’s largest food suppliers like Walmart and Nestle have implemented blockchain technology to improve traceability. According to 451 Alliance, enterprise use of blockchain has remained strong over time. To understand different phases of blockchain adoption, 451 Alliance collected data from different organizations across the world. The figure below illustrates the rate of blockchain adoption among different industries. The figure below indicates that the financial service industry holds a much stronger foothold with over 60% of the firms considering blockchain technology while 25% of the firms have already implemented blockchain because of its high potential in vast use cases. In the manufacturing industry, 52% of the organizations are considering the implementation of blockchain to enhance transparency and trust within every stage of the industry value chain.
Figure 4: Adoption of Blockchain
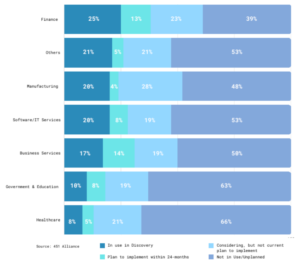
Latest Trends
Federated blockchain: In a federated Blockchain network, participants from different authorities make use of the network instead of following a single secure, trusted node. This provides a more customized outlook to the private blockchain. It further provides access control to multiple authorities for the pre-selected nodes intended to validate a new block to further process the transactions.
Blockchain as-a-service: The Blockchain as a service model allows customers to leverage cloud-based solutions to build, host and operate advanced blockchain operations ranging from Ethereum network and Hyperledger fabric to provide the creation of smart digital products. Using cloud-based services enables users to develop their products by working on the blockchain without any predefined setup requirements. Companies developing the Blockchain as a service model include Amazon, IBM, and Microsoft.
The rise of NFTs: Non-fungible tokens are units of data stored on a blockchain that certifies a digital asset to be unique and therefore not interchangeable. They are also called digital collectibles and are unique digital files because they cannot be duplicated, copied, or tampered with. The NFTs can be used to represent items such as photos, videos, audio, and other types of digital files. While copies of these digital items are made available for anyone to obtain, NFTs are tracked on blockchains to provide the owner with a Proof of Ownership that is separate from copyright. For instance, the musician, Grimes sold an artwork as an NFT for $ 6.6 million while the NBA has generated $230 million in sales of video clips across its Top Shot marketplace.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology has shown tremendous potential in various industries across the globe. The main driver for this growth being industry-wide adoption. As companies discover the real value of blockchain technology, many have begun to invest exponentially across all sectors. The Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) sector have posted greater adoption and higher returns in terms of cost-saving and value creation. The decentralized nature of blockchain technology tremendously reduces transactional and ownership costs. This is serving as a major attraction for companies in the BFSI sector. The increasing adoption of blockchain technology by organizations in the region is driving regional market growth with North America leading the pack. As companies adopt this groundbreaking technology, they are bound to face some technological challenges since blockchain technology is still in the development phase. Technology has an intrinsic property of evolving and can always find a way through any challenges. Therefore, it is not a matter of “whether” legacy businesses will adopt blockchain technology, is a question of “when” they will do so.
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions