- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Technology
- By Omega Team

Change management is no longer just a corporate buzzword, it’s a vital organizational function. In today’s dynamic business environment, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into the workplace is ushering in unprecedented shifts, not just in tools and processes but also in workforce roles, cultural dynamics, and strategic priorities. Human-AI collaboration has become a defining characteristic of modern enterprises, demanding a reevaluation of how we manage change. Organizations are now navigating a dual transformation adapting to digital innovation while also redefining human work. This evolution requires more than updating workflows; it involves reshaping mindsets, building digital confidence, and fostering an adaptive culture. As AI systems become decision-making partners rather than mere tools, leaders must craft change strategies that are inclusive, transparent, and responsive. The future of work hinges on our ability to manage this synergy effectively.
The Evolution of Work: From Human-Centric to Hybrid Intelligence
Traditional Workspaces: Historically, workplaces were built around human capabilities, structured hierarchies, and linear workflows. Change management in these environments focused on process improvements, employee training, and structural reorganizations. These systems emphasized compliance, efficiency, and predictability, where decisions often followed a top-down approach. Communication channels were formal, and innovation was typically incremental. The pace of change was manageable, and employees had clear, well-defined roles within stable systems.
The Advent of AI Workspaces: AI is changing this narrative. From automating routine tasks to augmenting decision-making with predictive analytics, AI tools are becoming co-workers rather than mere tools. Intelligent systems now participate in operations, HR, finance, marketing, and even creative domains. These technologies bring speed, scalability, and real-time insights, reshaping how work is performed and decisions are made. AI introduces new capabilities such as natural language processing, image recognition, and cognitive automation. As a result, organizations must adapt not only structurally but also culturally to fully integrate these digital collaborators.
Hybrid Workspaces: The result is a hybrid workspace, where humans and AI systems collaborate. In this environment, humans focus on tasks requiring creativity, empathy, and strategic thinking, while AI handles data-driven, repetitive, or predictive tasks. This evolution demands a reimagined approach to change management. It involves fostering trust in AI systems and equipping employees with digital literacy to work alongside intelligent tools. Leadership must redefine roles, establish ethical AI frameworks, and promote continuous learning. Hybrid workspaces blur traditional boundaries, requiring adaptive models for performance, collaboration, and communication.
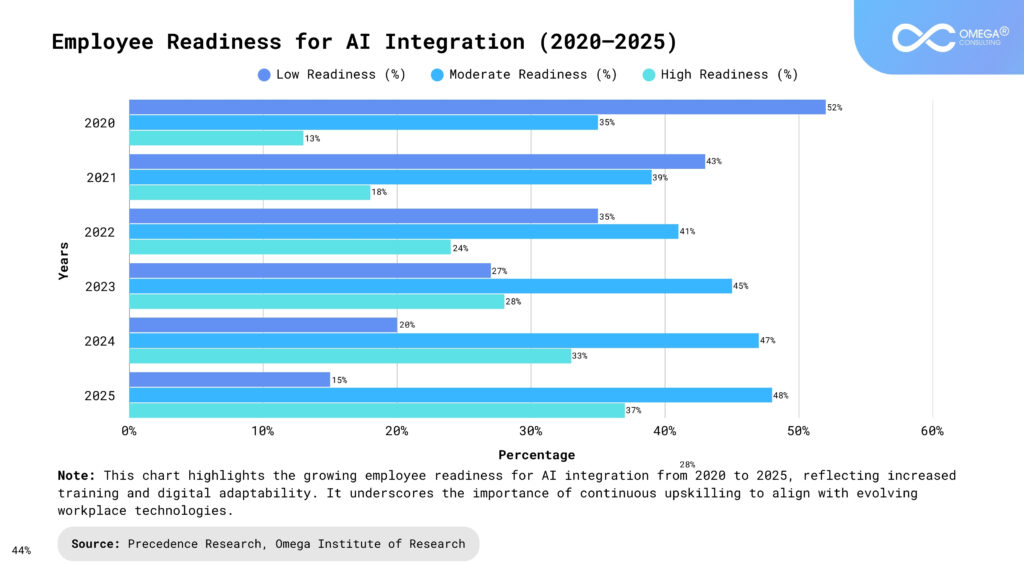
Why Change Management Is Crucial in AI-Integrated Workspaces
Technological Adoption Alone Isn’t Enough: Successful AI integration depends on people embracing the change not just adopting the tools, but reshaping their workflows and mindsets. Without proper guidance, AI initiatives can face resistance or fail to deliver value. Change management ensures alignment between technology and business goals. It also cultivates a shared vision that motivates employees to engage with AI meaningfully.
Reskilling and Role Redefinition: AI transforms job roles. Change management supports employees through the anxiety and uncertainty of learning new skills or transitioning to new roles. This involves not only upskilling but also redefining career paths and performance metrics. Leaders must identify gaps early and create personalized development plans. A strong support system fosters resilience and encourages growth in the face of disruption.
Organizational Agility: The pace of AI innovation requires organizations to become agile, making continuous adaptation a necessity. Change management provides frameworks to support this agility. It enables faster decision-making, smoother transitions, and iterative experimentation. Agile change models promote responsiveness over rigidity. This flexibility helps companies evolve in real-time with technological shifts and market demands.
Maintaining Trust and Transparency: Employees often mistrust AI decisions or fear job displacement. A robust change management plan addresses these concerns head-on through clear communication. Open dialogue, training, and involvement in AI implementation build confidence. Transparency about how AI works and why it’s being used reduces uncertainty. Creating feedback loops ensures employees feel heard and empowered in the transformation.
Ethics and Compliance: AI raises new ethical issues—from data privacy to bias. Change management helps embed governance mechanisms into everyday practices. It ensures that ethical guidelines are understood, followed, and regularly updated. Change leaders play a critical role in reinforcing accountability across departments. A values-driven approach safeguards both organizational integrity and public trust.
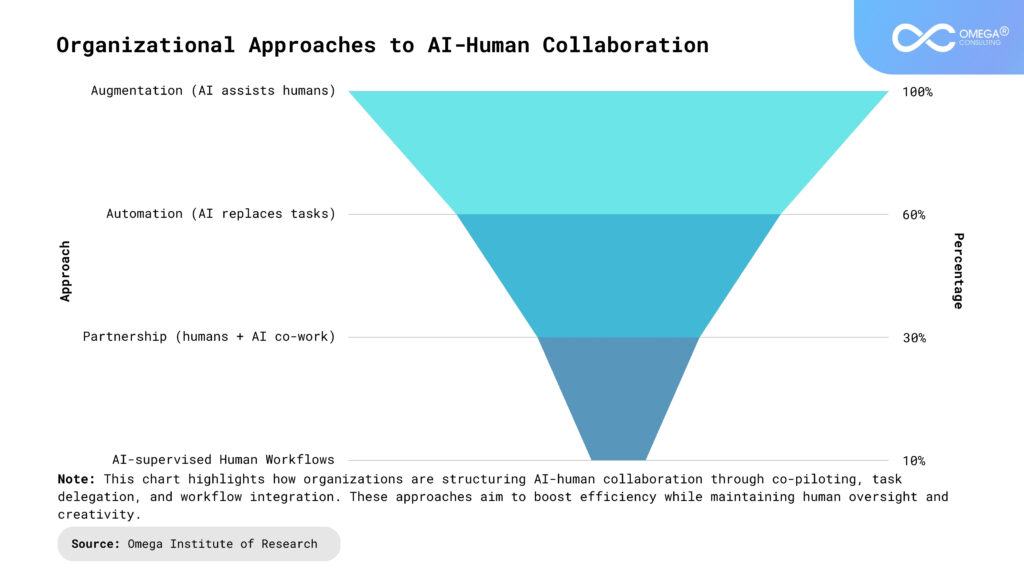
Key Components of Change Management in Human-AI Workspaces
Clear Vision and Strategy: Establish a clear purpose and strategic direction for integrating AI into the workspace. This includes defining the expected benefits, such as increased efficiency and accuracy, while aligning AI initiatives with broader organizational goals like growth or innovation. A well-articulated strategy helps in gaining buy-in from all stakeholders, guiding the entire change process, and ensuring everyone is working towards the same objectives. Moreover, a solid roadmap outlines actionable milestones and timelines, making the implementation process more structured and less overwhelming.
Leadership and Sponsorship: Strong leadership support is essential for successful AI integration. Executives and change champions should advocate for the change, address concerns, and provide guidance throughout the process, demonstrating the organization’s commitment to the new direction. Their visible support encourages trust and buy-in from employees at all levels. Leadership should also actively engage with teams to gather insights and feedback, showing that AI is not just a top-down initiative, but one that is shaped with input from across the organization.
Training and Development: Invest in training programs to ensure employees have the necessary skills to collaborate effectively with AI tools. This includes both technical skills, such as learning to use AI-powered software, and soft skills, like problem-solving, decision-making, and adaptability. By equipping the workforce with the right capabilities, organizations can empower their employees to work alongside AI systems efficiently, ensuring they view the technology as an enhancement, not a threat. Continuous learning opportunities should also be provided to keep employees updated as AI evolves, fostering a culture of lifelong learning.
Cultural Transformation: Cultivate a culture that embraces change, innovation, and human-AI collaboration. Encouraging an open mindset, fostering curiosity, and promoting trust in AI tools ensures that employees are more receptive to the changes. A culture that values collaboration and adaptability makes it easier for employees to adjust to new ways of working, rather than feeling overwhelmed. Furthermore, leadership should actively promote these cultural values by integrating them into daily operations, making the shift to an AI-enabled environment feel like a natural progression for employees.
Managing Resistance: Resistance to AI can arise from concerns about job displacement or distrust in the technology. Address these concerns through clear, transparent communication, and involve employees early in the change process. By actively managing resistance and emphasizing the complementary nature of AI, organizations can reduce fear and build confidence in the new systems. It’s crucial to reassure employees that AI will augment their work rather than replace it, and to highlight examples where AI has improved productivity and job satisfaction in similar settings. Additionally, providing avenues for ongoing dialogue can help employees voice their concerns and feel heard throughout the transition.
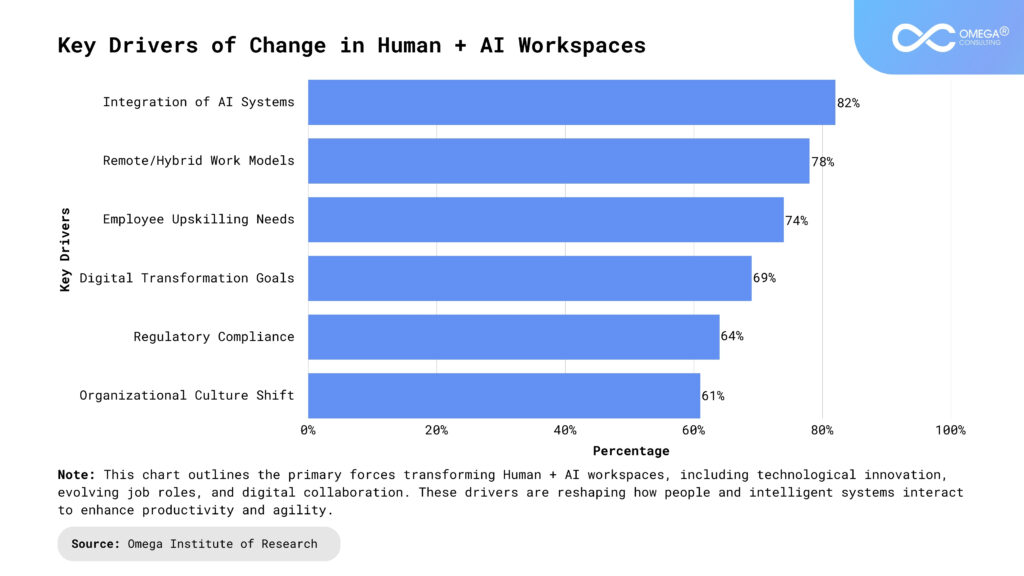
Common Challenges in Managing Change for AI Integration
Resistance to Change: Fear of job loss or the unknown can create significant pushback when introducing AI technologies. Employees may feel that AI is a threat to their roles or that it will replace their jobs entirely. To reduce resistance, involve employees early in the process by sharing the vision, purpose, and expected outcomes of AI integration. Engaging them through workshops, discussions, and feedback channels helps them feel included and more in control of the transition. Additionally, showing how AI will enhance their roles rather than replace them, and providing reassurances regarding job security, can alleviate anxiety and foster acceptance.
Skill Gaps: Not all employees have the baseline skills necessary to work alongside AI systems effectively. Many workers may lack technical knowledge or experience with AI tools and platforms. Tailored training programs are crucial to address these gaps, ensuring employees acquire the specific skills required for their roles. Additionally, providing digital mentorship and on-the-job learning opportunities can help employees bridge knowledge gaps. Organizations should also consider upskilling initiatives that focus on soft skills like problem-solving, adaptability, and communication, which are essential for collaborating with AI technologies in dynamic environments.
Poor Communication: Vague or inconsistent messaging about the AI integration process can undermine trust and breed confusion among employees. Clear communication is essential to ensure everyone understands the goals, benefits, and challenges of AI adoption. Communications must be continuous, transparent, and two-way, providing ample opportunities for feedback and addressing concerns. Regular updates, town hall meetings, and open forums allow employees to ask questions and share their thoughts. Ensuring that key messages are consistent across all levels of the organization and that there is alignment between leadership and teams is essential for maintaining trust throughout the change process.
Cultural Inertia: Organizational cultures rooted in hierarchical thinking or risk aversion may struggle to embrace the agility and flexibility required for AI integration. Employees accustomed to traditional, structured ways of working may feel uncomfortable with the disruptive nature of AI. To overcome cultural inertia, organizations must foster a culture of innovation and continuous learning. Leaders should model the behaviors they want to see by embracing change, encouraging experimentation, and supporting AI-driven initiatives. Creating an environment where failure is seen as a learning opportunity rather than something to be avoided will help shift the culture toward one that is more open to innovation and agility.
Unclear Governance: Without clear policies for data use, algorithmic decisions, and accountability, AI adoption can lead to ethical and operational issues, such as biased outcomes or misuse of sensitive information. Organizations must establish robust governance frameworks to ensure that AI systems are used responsibly and ethically. This includes defining clear policies on data privacy, transparency, and fairness in algorithmic decision-making. Regular audits and oversight of AI systems should be implemented to monitor compliance and identify potential risks. Moreover, organizations must assign accountability for AI decisions to specific roles, ensuring there is transparency and responsibility at every level of the process.
Best Practices for Effective Change Management
Adopt a Human-Centric Approach: AI should augment human work, not replace it. Center the change strategy on enhancing employee experience, satisfaction, and productivity by ensuring AI tools are user-friendly and align with human skills. Focus on how AI can relieve employees from mundane tasks, allowing them to engage in more meaningful, creative, and strategic activities. Additionally, involve employees in the design and implementation phases, soliciting feedback on how AI tools can better serve their needs and improve their work environments. This inclusion fosters a sense of ownership and reduces resistance to the change process.
Create Cross-Functional Change Teams: Involve experts from IT, HR, operations, and legal to ensure a balanced and holistic approach to change. These cross-functional teams provide diverse perspectives and ensure that all aspects of AI integration—technical, organizational, and legal—are carefully considered. Collaboration between these departments enables smooth coordination and prevents gaps in the planning and execution stages. HR can manage the human elements of change, IT ensures seamless technological integration, and legal departments focus on compliance and risk management. This comprehensive approach results in a more effective and sustainable change process.
Champion Ethical AI: Promote fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI use by establishing an ethics board or appointing AI ethics officers to oversee compliance. Ensuring ethical AI implementation is not just a regulatory necessity but also a key factor in building trust with employees and customers. This includes addressing biases in AI algorithms, safeguarding data privacy, and being transparent about how AI decisions are made. Ethical considerations should be integrated into every stage of the AI deployment process, from development to implementation and ongoing monitoring, ensuring AI systems are used responsibly and equitably.
Leverage AI for Change Itself: Use AI for sentiment analysis, chatbot-based employee support, or personalized training pathways to improve the change journey. AI tools can help identify areas where employees are struggling with the transition and offer personalized solutions. Sentiment analysis, for instance, can provide real-time feedback on employee reactions, allowing leaders to address concerns quickly. AI-powered chatbots can serve as accessible, 24/7 support channels, answering employee queries and offering guidance during the change process. Additionally, personalized training pathways powered by AI ensure that each employee receives the specific training they need to adapt successfully, improving both efficiency and engagement.
Celebrate Small Wins: Recognize teams and individuals who adapt successfully. Success stories humanize the change and inspire others by showing tangible examples of how AI can improve workflows and outcomes. Celebrating small wins not only boosts morale but also reinforces the value of change and the benefits of AI integration. Acknowledging these successes publicly through newsletters, team meetings, or internal social platforms can create positive momentum, motivate hesitant employees, and encourage further participation in the change process. Over time, these incremental victories build confidence and trust in AI, gradually leading to broader adoption.
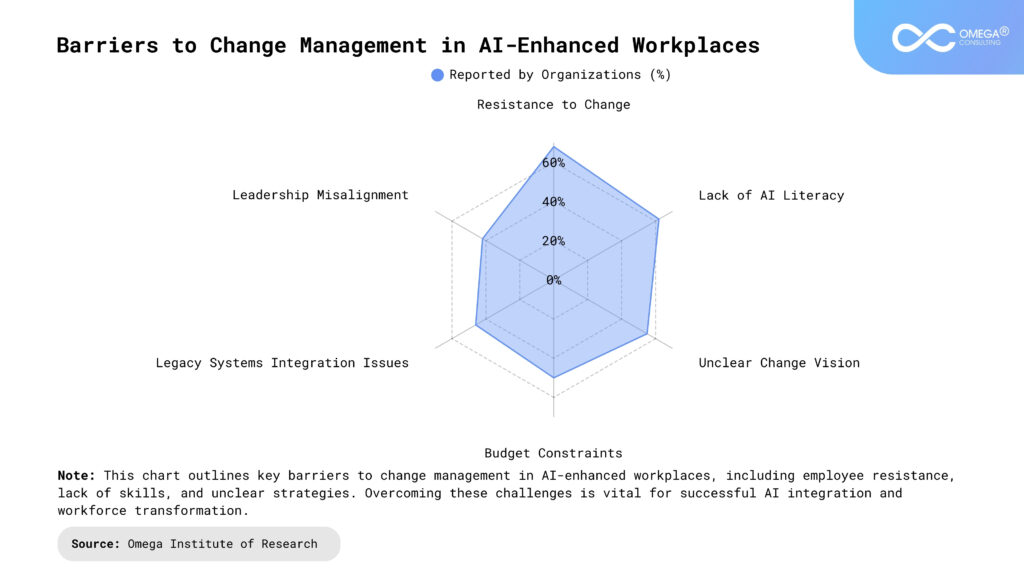
The Future of Change Management: What to Expect
From Change Events to Continuous Change: As AI becomes more autonomous and embedded in decision-making, change management will evolve to embrace agility and flexibility. Rather than being limited to discrete change events, the process will become continuous, with organizations adapting in near real-time. This will require organizations to adopt agile change management principles, enabling them to pivot quickly in response to new challenges, technological advancements, or evolving business needs. A continuous change model will help organizations remain competitive and resilient, ensuring they can leverage AI and other innovations without significant disruptions to day-to-day operations.
Emphasis on Emotional Intelligence: Leaders will need empathy, cultural fluency, and psychological insight to manage human-AI dynamics effectively. As AI systems take on more decision-making roles, leaders must be attuned to the emotional and psychological impact these changes may have on employees. Emotional intelligence will become a critical leadership skill, as leaders will need to understand and address employee concerns, fears, and motivations. Additionally, cultural fluency will be crucial in managing global teams, as different regions may have varying attitudes toward AI and automation. Leaders who can navigate these complexities will foster trust, collaboration, and a smoother integration of AI technologies.
Personalized Change Journeys: AI will enable hyper-personalized change plans based on each employee’s role, skill level, and learning style. Instead of a one-size-fits-all approach, AI-driven systems will tailor training, communication, and support to individual needs, ensuring that each employee receives the right resources at the right time. This personalization will enhance engagement and reduce resistance by making the change process more relevant and accessible. AI tools will continuously track progress, identify knowledge gaps, and adjust training pathways, ensuring that employees are equipped to thrive in an AI-enhanced workplace.
AI Governance Integration: Change management will work closely with compliance and risk teams to ensure AI use aligns with ethical and legal standards. As AI continues to influence decision-making, organizations will need robust governance frameworks to ensure that AI systems are transparent, accountable, and aligned with company values. This will involve the integration of AI governance into the change management process, ensuring that AI policies, data security measures, and ethical guidelines are part of every stage of the change journey. Regular audits and monitoring will be essential to maintain trust and ensure that AI technologies operate within legal and ethical boundaries.
Conclusion
The integration of AI into the workplace marks a fundamental shift—not just in technology, but in the integration of AI into the workplace is not just a technological shift but a fundamental transformation of organizational structures, cultures, and roles. Successful change management in AI-integrated workspaces requires more than just adopting new tools; it demands a strategic, inclusive, and transparent approach that prioritizes reskilling, leadership, and a culture of continuous learning. By addressing the challenges of resistance, skill gaps, and poor communication, organizations can navigate this change effectively. Embracing AI as a partner rather than a replacement, fostering trust, and embedding ethical frameworks will be key to ensuring a smooth transition. As AI continues to reshape the future of work, organizations that cultivate agility, emotional intelligence in leadership, and personalized change management strategies will be better equipped to thrive in a rapidly evolving environment.
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00146-024-02136-2
- https://www.dpublication.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/57-202364.pdf
- https://www.peoplemattersglobal.com/site/interstitial?return_to=%2Farticle%2Fhr-technology%2Fhow-ai-is-changing-the-dynamics-of-change-management-42490
- https://www.rolandberger.com/en/Insights/Publications/Change-management-and-AI.html
- https://www.innovativehumancapital.com/article/embracing-ai-in-change-management
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions