- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Information Technology
- By Omega Team
In today’s digital landscape, data is the backbone of every organization. From customer information to operational analytics, enterprises rely on structured and unstructured data to drive decisions, optimize operations, and create value. However, as data grows in volume, variety, and velocity, businesses face increasing challenges in managing, securing, and leveraging it effectively. Effective data management is essential for maintaining data integrity, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, and improving business intelligence. Organizations must implement robust strategies to store, process, and analyze data efficiently while mitigating risks related to data breaches and inconsistencies. Without a structured approach, businesses may struggle with data silos, duplication, and quality issues, leading to inefficiencies and missed opportunities. This article explores the critical aspects of data management in IT, including its importance, key components, best practices, and future trends.
What is Data Management?
Data management encompasses the processes, policies, and technologies used to collect, store, organize, and protect data. It ensures that data is accurate, accessible, and secure, allowing organizations to maximize its value for strategic decision-making and compliance. Effective data management involves data governance, quality control, integration, and lifecycle management, ensuring consistency and reliability across business operations. As organizations generate vast amounts of data from multiple sources, a well-structured data management framework helps prevent data silos, enhances collaboration, and supports real-time analytics. Additionally, adopting modern data management solutions, such as cloud-based storage, AI-driven analytics, and automated data pipelines, enables businesses to scale efficiently while maintaining security and regulatory compliance. Without a strong data management strategy, organizations risk inefficiencies, poor decision-making, and exposure to cyber threats. Investing in robust data management practices fosters innovation, operational agility, and a competitive advantage in the digital era.
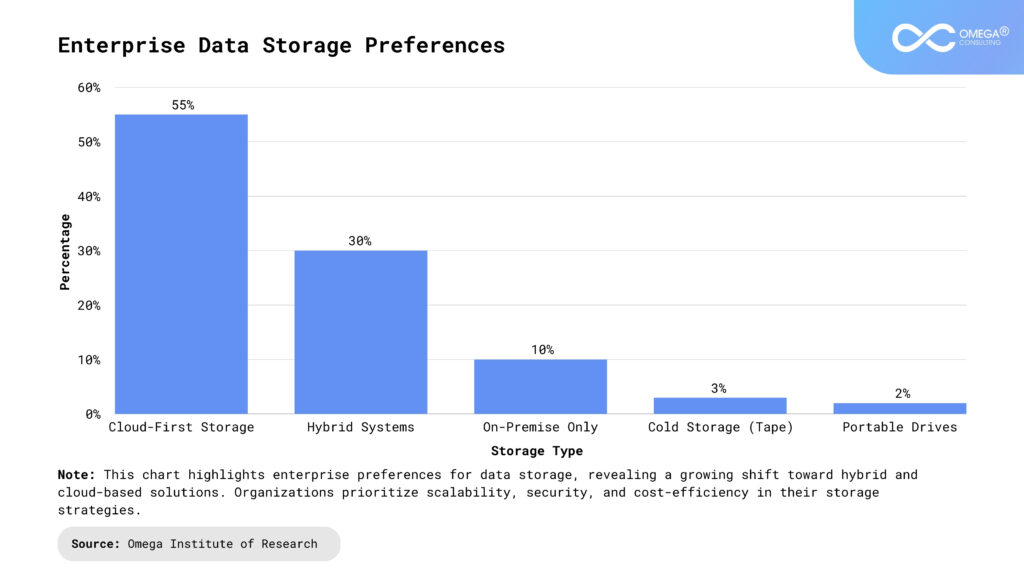
The Importance of Data Management
Effective data management offers several benefits:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: High-quality data supports analytics and business intelligence, enabling informed decision-making. Reliable data allows businesses to identify trends, predict market changes, and optimize strategies with confidence. Without accurate data, organizations risk making poor choices that could impact revenue and customer satisfaction. Well-managed data also enhances AI and machine learning models, leading to more precise insights and automation.
- Regulatory Compliance: Organizations must adhere to data regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA. Compliance with these standards ensures that sensitive information is protected and reduces the risk of legal penalties. A strong data management framework helps organizations maintain audit trails, implement proper access controls, and ensure that data-handling practices align with industry regulations. Failing to comply can result in hefty fines, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlined data processes reduce redundancy and improve productivity. Efficient data management eliminates duplicate records, enhances workflow automation, and minimizes time spent searching for critical information. By integrating data across departments, businesses can improve collaboration and accelerate decision-making processes. This efficiency allows employees to focus on strategic initiatives rather than wasting time on data inconsistencies.
- Security and Risk Mitigation: Proper data governance helps prevent breaches and cyber threats. Implementing encryption, access controls, and real-time monitoring can protect sensitive data from unauthorized access. Additionally, a well-defined data security strategy reduces the likelihood of insider threats, ransomware attacks, and data loss incidents. Proactive risk management not only safeguards assets but also builds trust among customers and stakeholders.
- Cost Reduction: Effective storage and retrieval reduce operational expenses. By optimizing data storage solutions, such as cloud computing and data archiving, businesses can lower infrastructure costs while maintaining accessibility. Reducing data redundancy and automating processes further decreases the need for manual intervention, improving overall cost efficiency. A well-structured data management approach also minimizes costly downtime caused by data-related errors or system failures.
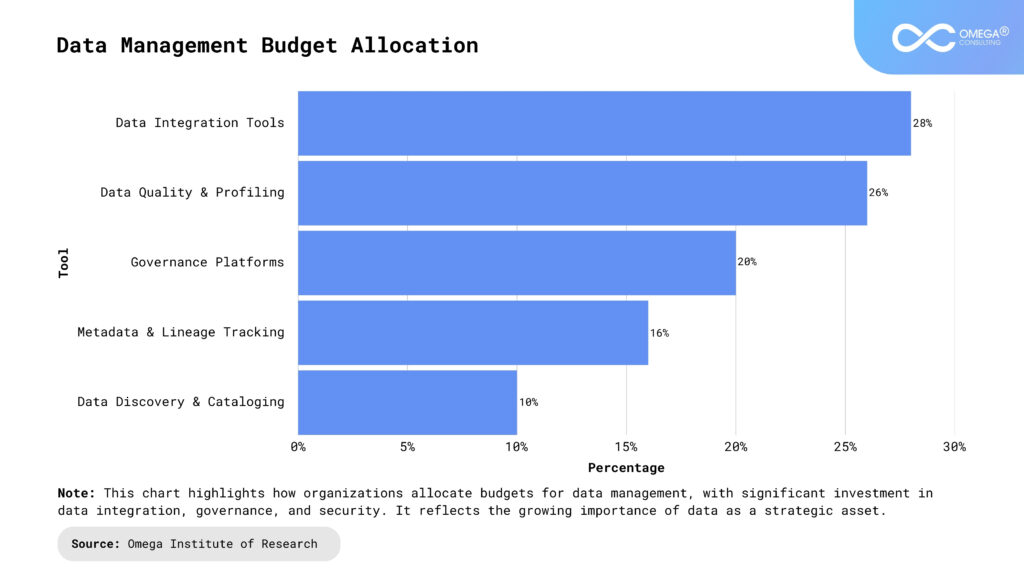
Key Components of Data Management
- Data Governance: Data governance refers to the policies, standards, and roles that guide data management. It ensures accountability, integrity, and compliance within an organization. A strong governance framework establishes data ownership, policies for data access, and mechanisms to enforce data consistency across systems. It also includes regulatory compliance measures, ensuring organizations meet industry standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA. Effective data governance fosters transparency, improves collaboration, and minimizes the risk of data misuse or unauthorized modifications. Additionally, businesses leveraging governance frameworks can enhance decision-making and establish trust in data-driven processes.
- Data Architecture: Data architecture defines how data is collected, stored, and accessed. A well-structured architecture supports scalability and performance. It includes defining logical and physical structures for databases, warehouses, and cloud environments to optimize data flow. A strong architecture framework enables seamless data integration between on-premise, cloud, and hybrid environments, ensuring high availability and redundancy. Organizations must also consider future scalability needs, designing architectures that support growing data volumes and emerging technologies like AI and IoT. Additionally, adopting modern architectural approaches, such as data fabric and data mesh, enhances agility and adaptability in an evolving digital landscape.
- Data Storage and Integration: Organizations use various storage solutions, including on-premise databases, cloud storage, and hybrid models. Integration strategies like ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and data lakes help unify disparate data sources. Choosing the right storage solution depends on factors such as security, compliance, and accessibility requirements. Cloud-based storage provides flexibility and cost-efficiency, while on-premise storage offers more control over data security. Integration tools, including API-based data sharing and real-time data streaming, facilitate seamless communication between applications. Businesses leveraging effective storage and integration strategies can improve workflow efficiency, reduce operational costs, and enable data-driven decision-making across all departments.
- Data Quality Management: Data quality management ensures accuracy, consistency, and reliability. It involves data cleansing, deduplication, and validation. Poor data quality can lead to incorrect analytics, flawed business strategies, and regulatory compliance issues. Implementing data profiling and automated error detection mechanisms helps maintain data integrity. Regular audits and validation rules ensure that data remains up to date, preventing outdated or redundant information from influencing critical decisions. Organizations with high data quality standards experience improved customer satisfaction, enhanced reporting accuracy, and better risk management. Additionally, AI-powered data quality tools can further automate processes and enhance data reliability.
- Data Security and Privacy: Protecting data from unauthorized access and breaches is critical. Encryption, access controls, and multi-factor authentication are key security measures. Organizations must implement robust cybersecurity frameworks that include intrusion detection systems (IDS) and firewalls to safeguard sensitive data. Regular security audits and penetration testing help identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Compliance with global privacy laws requires businesses to enforce data anonymization and encryption protocols, reducing the risk of exposure in case of a breach. A strong data security posture not only protects an organization’s assets but also builds trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders.
- Data Lifecycle Management: Data has a lifecycle—from creation to archiving or deletion. Proper lifecycle management ensures efficiency and compliance. Organizations must establish clear retention policies, ensuring that essential data is preserved while obsolete information is securely removed. Automated data lifecycle management (DLM) tools help categorize, archive, and delete data based on business and legal requirements. Implementing a structured approach to data lifecycle management enhances system performance, reduces storage costs, and improves compliance with data protection regulations. Additionally, lifecycle management supports business continuity by ensuring that critical data is always accessible when needed while preventing data overload.
- Master Data Management (MDM): MDM creates a single, consistent source of truth across systems, reducing inconsistencies in customer and operational data. By centralizing key business data, MDM eliminates duplication and ensures accuracy across departments. A well-implemented MDM strategy enhances reporting, analytics, and business intelligence by providing reliable, high-quality data. Organizations benefit from improved customer relationship management (CRM) and supply chain efficiency due to standardized data definitions. AI-powered MDM solutions further enhance data harmonization, ensuring that businesses can adapt to evolving market demands. Additionally, MDM plays a crucial role in digital transformation by enabling seamless interoperability between legacy systems and modern applications.
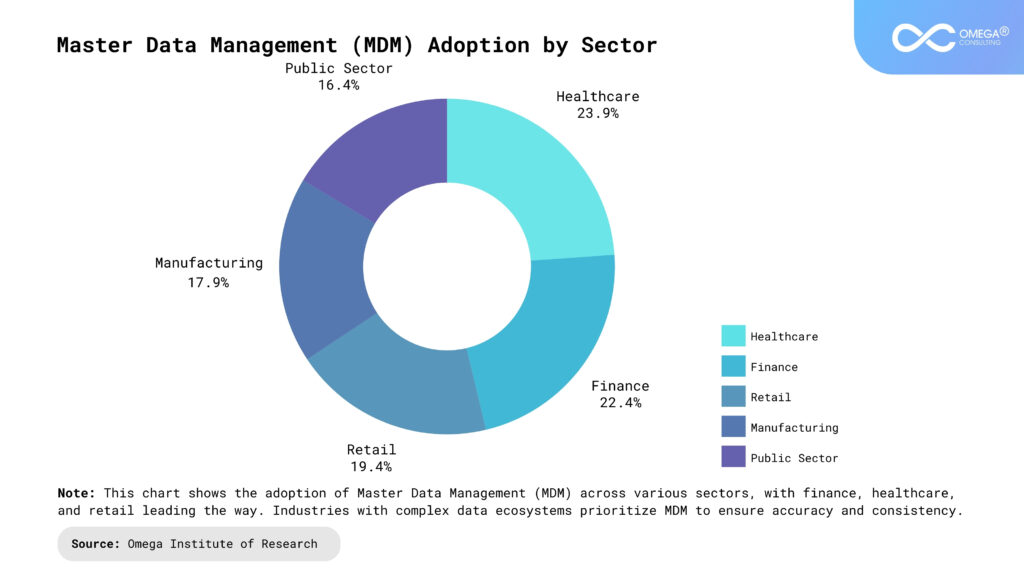
Best Practices for Effective Data Management
- Establish a Data Governance Framework: Define roles and responsibilities for data ownership to ensure accountability and consistency in data management. Assigning data stewards and governance teams helps enforce policies and maintain compliance. Implement data policies and compliance measures to align with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA. Regular audits and monitoring ensure that governance frameworks remain effective and adapt to evolving business needs. Additionally, fostering a data-driven culture within the organization promotes transparency and responsible data handling.
- Adopt Cloud-Based Data Solutions: Leverage cloud platforms for scalability and cost-effectiveness, allowing organizations to manage growing data volumes efficiently. Cloud solutions offer pay-as-you-go pricing models, reducing infrastructure costs while ensuring high availability. Utilize hybrid cloud strategies for flexibility, enabling seamless data movement between on-premise and cloud environments. Implement cloud security best practices, such as encryption and access controls, to protect sensitive data. Additionally, leveraging cloud-native analytics and AI-driven automation can optimize resource utilization and enhance business intelligence capabilities.
- Ensure Data Security: Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit to safeguard it from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Encryption protocols such as AES and TLS help maintain data confidentiality. Implement access control and user authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC), to prevent unauthorized data access. Regular security audits, penetration testing, and threat intelligence monitoring help identify vulnerabilities and mitigate potential risks. Additionally, establishing an incident response plan ensures a rapid and effective recovery from security breaches, minimizing downtime and reputational damage.
- Maintain Data Quality: Use automated tools for data validation and cleansing to ensure accuracy, consistency, and reliability. AI-powered data profiling can detect anomalies and suggest corrective actions. Standardize data entry procedures by enforcing predefined formats, drop-down selections, and validation rules to minimize human errors. Conduct regular data audits and deduplication processes to eliminate inconsistencies and outdated records. Additionally, integrating real-time data monitoring systems ensures that data remains up to date, supporting more accurate analytics and decision-making.
- Utilize AI and Machine Learning for Data Analytics: AI-driven analytics can uncover insights from structured and unstructured data, providing organizations with valuable business intelligence. Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques can extract meaning from text-based data sources, enhancing customer sentiment analysis. Machine learning algorithms help in predictive analytics and anomaly detection, enabling proactive decision-making. Implementing AI-driven automation in data classification and processing can reduce manual efforts and improve efficiency. Additionally, leveraging deep learning techniques for advanced analytics can help businesses uncover hidden patterns and trends within vast datasets.
- Implement Robust Backup and Recovery Strategies: Regularly back up critical data using automated and scheduled backup solutions to prevent data loss from system failures or cyber incidents. Cloud-based backup solutions provide redundancy and quick recovery capabilities. Develop a disaster recovery plan to ensure business continuity, including data replication across multiple locations and failover systems. Regularly test recovery procedures to validate the effectiveness of backup strategies and identify potential weaknesses. Additionally, implementing versioning and immutable storage options helps protect against ransomware attacks by maintaining secure copies of critical data.
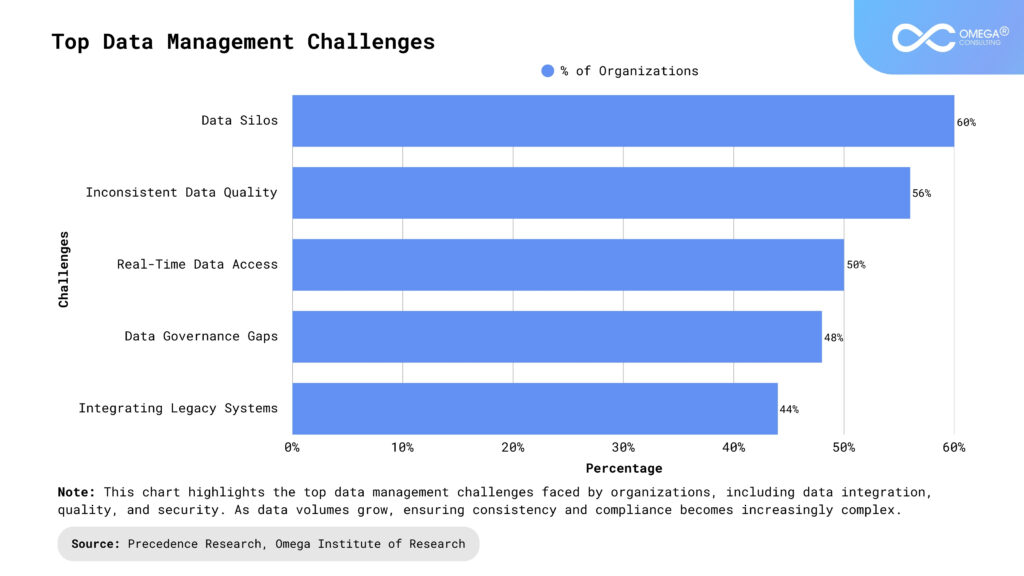
Future Trends in Data Management
AI-Driven Data Management: Artificial intelligence is enhancing data management by automating processes like data cleansing, categorization, and predictive analytics. AI-driven tools can identify anomalies, optimize storage, and improve data governance. Machine learning algorithms are also being integrated into data management platforms to enhance real-time decision-making. Additionally, AI-powered automation is reducing manual data processing, improving efficiency, and enabling organizations to focus on strategic initiatives.
Edge Computing: With IoT proliferation, edge computing is reducing latency by processing data closer to its source. This minimizes reliance on centralized cloud infrastructure, reducing bandwidth costs and improving real-time analytics. Edge computing is crucial for applications in industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and autonomous vehicles where low-latency processing is critical. Additionally, advancements in 5G technology are further accelerating the adoption of edge computing by enabling faster and more reliable data transmission.
Blockchain for Data Security: Blockchain offers enhanced security and transparency in data transactions, particularly for sensitive and financial data. It provides an immutable ledger that ensures data integrity and prevents unauthorized alterations. Smart contracts are also being leveraged to enforce data access controls and automate compliance with regulatory standards. Additionally, decentralized identity management solutions using blockchain technology are enhancing privacy and security in digital interactions.
Data Fabric Architecture: This emerging architecture connects various data sources across environments, improving accessibility and integration. It enables seamless data sharing between on-premise, cloud, and hybrid environments while maintaining security and compliance. Data fabric reduces data silos, allowing organizations to derive insights from disparate data sources efficiently. Additionally, AI-driven data fabric solutions are streamlining data discovery, metadata management, and governance across the enterprise.
Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs): New privacy-focused tools, such as homomorphic encryption and differential privacy, are improving data security while enabling analytics. These technologies allow organizations to analyze data without exposing sensitive information, enhancing regulatory compliance. PETs are particularly valuable in industries like healthcare and finance, where data confidentiality is paramount. Additionally, federated learning is emerging as a key privacy-enhancing technique, enabling machine learning models to be trained on decentralized data without sharing raw information.
Conclusion
Data management is no longer just an IT function—it is a strategic asset that drives innovation and efficiency. Organizations that prioritize data governance, security, and analytics will gain a competitive edge in the digital era. By adopting best practices and staying ahead of emerging trends, businesses can unlock the full potential of their data and achieve long-term success. A well-structured data management strategy ensures compliance with evolving regulations, mitigates risks, and enhances operational efficiency. As AI, automation, and cloud computing continue to reshape data ecosystems, companies must embrace a data-driven culture to remain agile and competitive. Investing in scalable and secure data management frameworks will empower organizations to make informed decisions, improve customer experiences, and drive sustained growth in an increasingly digital world.
- https://www.techtarget.com/searchdatamanagement/definition/data-management
- https://www.oracle.com/in/database/what-is-data-management/
- https://hbr.org/topic/subject/data-management
- https://www.tableau.com/learn/articles/what-is-data-management
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8371066/
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions