- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Technology
- By Omega Team
Digital banking has revolutionized finance, moving from a niche to the primary mode of interaction in the banking landscape for millions. Leveraging online and mobile platforms, it offers a vast range of services beyond traditional branch limitations, impacting everything from basic transactions to complex investments with unprecedented convenience. This shift reshapes customer expectations, compels traditional banks to innovate, and enables fintech growth. Digital banking fosters financial inclusion, enhances efficiency, and drives personalized products such as personalized financial insights, and customized advice by leveraging AI and other technologies. As technology advances, it will further integrate into daily life, blurring finance and tech boundaries and setting new standards for accessibility and customer experience globally. This article examines digital banking’s components, benefits, challenges, and future trends.
What is Digital Banking?
Digital banking refers to the digitization of virtually all traditional banking activities and programs that were historically only available to customers when physically inside a bank branch. It involves providing banking services and products through electronic channels, primarily via the internet and mobile devices, rather than through physical branches. This encompasses a wide spectrum of functionalities, moving beyond simple online banking (which often focused on basic tasks like viewing balances and statements) to include a comprehensive suite of services such as money transfers, bill payments, loan applications and approvals, account opening, investment management, and personalized financial advice.
At its core, digital banking is about leveraging technology – including online platforms, mobile applications, APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), cloud computing, data analytics, and artificial intelligence – to create a seamless, integrated, and customer-centric banking experience. It aims to make financial services accessible anytime, anywhere, reducing reliance on physical infrastructure and manual processes. This involves not only digitizing existing services but also reimagining banking processes to be inherently digital-first. For financial institutions, this means transforming backend operations, adopting agile methodologies, and fostering a culture of continuous innovation to meet the evolving demands of digitally savvy customers. It represents a fundamental shift from a product-centric model to a customer-centric one, where services are tailored to individual needs and delivered through the customer’s preferred digital channel.
Key Characteristics of Digital Banking
Digital banking is defined by several key characteristics that differentiate it from traditional banking models and even basic online banking:
Omnichannel Accessibility: Digital banking provides a consistent and integrated experience across multiple devices and platforms – including web browsers on desktops/laptops, dedicated mobile apps on smartphones and tablets, and sometimes even wearables or voice assistants. Customers can start a transaction on one device and seamlessly continue it on another.
24/7 Availability: Digital banking offers 24/7 access, a key advantage over traditional branches with limited hours. Customers can manage finances anytime, anywhere with internet, transcending time zones and physical locations. This constant availability provides unparalleled convenience and flexibility for modern financial management.
Automation and Efficiency: Digital platforms automate many routine banking tasks, such as transfers, bill payments (often through scheduled or recurring payments), and account reconciliation. This reduces manual effort for both the customer and the bank, leading to faster processing times and lower operational costs.
Personalization and Data Analytics: Digital banks leverage customer data (transaction history, spending patterns, financial goals) and analytics, often powered by AI, to offer personalized insights, product recommendations, budgeting tools, and tailored financial advice, enhancing customer engagement and value.
Enhanced Security Measures: While digital channels introduce new security challenges, they also enable sophisticated security protocols beyond traditional methods. This includes multi-factor authentication (MFA), biometric verification, real-time fraud detection algorithms, encryption, and secure tokenization for payments.
Real-Time Processing: Enables near real-time processing for transactions like P2P payments and balance updates. This immediacy offers customers instant feedback and accurate insights into their financial standing. This speed enhances user experience by providing up-to-the-minute information and facilitating quicker financial management.
Integration Capabilities (APIs): Digital banking platforms leverage APIs for seamless integration with diverse financial services (investment, budgeting apps) and non-financial applications. This fosters Open Banking and embedded finance, allowing users to connect various services within a unified digital experience.
Reduced Reliance on Physical Infrastructure: Digital banking cuts the need for extensive physical branches by offering services online. This shift saves costs for banks and provides greater convenience for customers who prefer remote access. Online platforms deliver banking services directly, eliminating the necessity of visiting a physical location for many transactions.
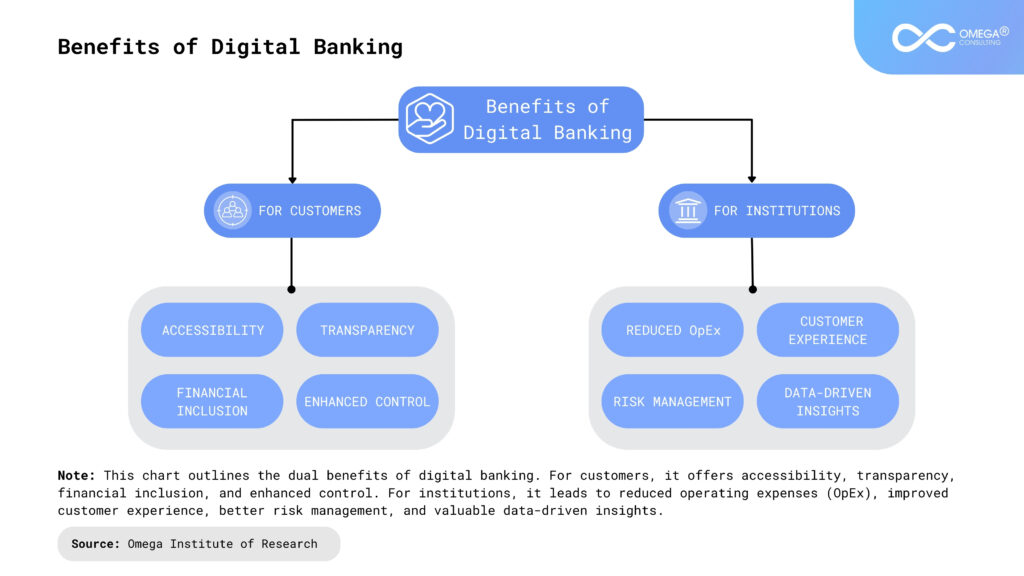
Benefits of Digital Banking
Digital banking offers significant advantages for both customers and the financial institutions serving them, making it a critical component of the modern financial ecosystem.
For Customers
Convenience and Accessibility: Digital banking’s prime advantage is its anytime, anywhere accessibility. Customers bypass branch visits and fixed hours, managing finances at their convenience. This saves valuable time and effort, seamlessly integrating banking into today’s fast-paced lifestyles, making financial management more flexible and user-friendly.
Improved Speed and Efficiency: Digital channels significantly accelerate banking processes. Transfers, payments, and loan applications are often completed much faster than traditional methods. Real-time updates offer immediate clarity on account balances and transaction statuses, enhancing efficiency and providing users with timely financial information.
Enhanced Control and Transparency: Digital platforms empower users with greater financial control. Easy access to account details, transaction history, spending analysis, and budgeting tools promotes understanding. Timely alerts and notifications keep customers informed about their account activity, fostering transparency and proactive financial management.
Lower Costs: Opting for digital banking often translates to reduced or eliminated transaction fees compared to branch services. Additionally, customers save on time and travel expenses associated with physical branch visits, making digital channels a more cost-effective and efficient way to manage finances.
Increased Financial Inclusion: Digital banking extends financial services to underserved populations, particularly in remote areas lacking physical branches. Requiring only internet access and a device, it breaks down geographical barriers, promoting greater financial inclusion and accessibility for a wider range of individuals.
For Financial Institutions
Reduced Operational Costs: Shifting operations to digital platforms drastically cuts expenses related to physical branches, including rent, utilities, and staffing. Automating processes further boosts efficiency, leading to significant cost savings for financial institutions by streamlining workflows and minimizing manual intervention.
Improved Customer Experience and Retention: Providing convenient, fast, and personalized digital services is key to enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty in today’s competitive landscape. A seamless and positive digital experience is now essential for retaining tech-savvy customers and building long-term relationships.
Broader Reach and Customer Acquisition: Digital channels enable banks to expand their reach beyond traditional geographical limits, facilitating entry into new markets and demographics without the need for physical infrastructure. This broadens their potential customer base and supports scalable growth strategies.
Data-Driven Insights: Digital interactions generate extensive customer data, offering valuable insights. Analyzing this information allows banks to gain a deeper understanding of customer behavior, identify emerging market trends, improve risk management strategies, and develop more effective, targeted products and marketing campaigns.
Improved Risk Management and Security: While introducing new security concerns, digital platforms also facilitate the implementation of advanced, real-time fraud detection and security protocols. These sophisticated measures can often be more effective in mitigating risks compared to traditional, manual security approaches.
Core Services & Applications
Digital banking offers a constantly growing suite of services and applications that go beyond basic balance checks. Core features usually consist of:
Account Management: Digital platforms enable users to effortlessly view their financial standing across diverse accounts, including checking, savings, credit cards, and loans. Accessing detailed transaction records and downloading statements is straightforward. Furthermore, updating personal details and initiating requests for new checks or cards can be conveniently managed online, enhancing user autonomy.
Payments and Transfers: Electronic fund transfers between a user’s own accounts are easily executed. Sending money to others via P2P services or direct account transfers is simplified, including international transactions and recurring payment setups. Paying bills to various merchants electronically, with options for one-time or recurring payments and receiving e-bills, offers significant convenience.
Mobile Banking Apps: Tailored applications for smartphones and tablets provide optimized access to essential banking functions. Features often include mobile check deposit via camera capture, secure biometric login for enhanced security, and location-based services to locate nearby ATMs or bank branches, catering to on-the-go financial management needs.
Digital Account Opening: New customers can conveniently apply for and open various accounts, such as checking, savings, or credit cards, entirely through online platforms or mobile applications. This process frequently incorporates digital identity verification methods, streamlining the onboarding experience and eliminating the need for physical branch visits.
Online Lending: Applying for personal loans, mortgages, or lines of credit is facilitated through digital channels, often resulting in quicker decision times, especially for smaller loan amounts. Existing loan accounts can be efficiently managed online, allowing borrowers to track balances, make payments, and access relevant loan information conveniently.
Personal Finance Management (PFM) Tools: Integrated within digital banking platforms, PFM tools offer functionalities for budgeting, expense tracking, setting savings targets, and analyzing spending patterns. Visual dashboards and insights aid in net worth calculation. Access to brokerage accounts for trading and monitoring investments, along with research and market data, is often provided, sometimes including robo-advisory services.
Card Management and Digital Wallets: Users can activate new cards, report lost or stolen ones, and temporarily freeze or unfreeze cards directly through the digital interface. Setting spending limits and travel notifications adds a layer of control. Linking cards to digital wallets like Apple Pay and Google Pay enables seamless contactless transactions for enhanced payment convenience.

Challenges in Digital Banking
Despite its numerous benefits, the transition to and operation of digital banking presents significant challenges for financial institutions and regulators:
Cybersecurity Threats: Digital platforms are prime targets for cyberattacks, including phishing, malware, ransomware, account takeover fraud, and data breaches. Ensuring robust security measures to protect sensitive customer data and financial assets is a constant and evolving challenge, requiring significant investment in technology and expertise.
Regulatory Compliance: The financial industry is heavily regulated. Digital banking introduces complexities related to data privacy (like GDPR, CCPA), anti-money laundering (AML), know-your-customer (KYC) requirements, cross-border data flows, and ensuring fair access. Banks must navigate these complex and often changing regulations across different jurisdictions.
Technology Infrastructure and Integration: Implementing and maintaining sophisticated digital platforms requires substantial investment in technology infrastructure, including core banking system modernization, cloud adoption, API development, and integration with legacy systems. Ensuring reliability, scalability, and performance is crucial.
Customer Adoption and Digital Literacy: While many customers embrace digital channels, some segments (e.g., older populations, those in areas with poor internet connectivity, or those with low digital literacy) may be hesitant or unable to use digital banking services, potentially leading to a “digital divide” and exclusion. Banks need strategies to support these customers.
Maintaining the Human Touch: Over-reliance on digital channels can sometimes lead to a less personal customer experience. Banks face the challenge of balancing digital efficiency with the need for human interaction and personalized support, especially for complex financial advice or resolving sensitive issues. Integrating human support within digital journeys (e.g., video banking, co-browsing) is key.
Operational Risks: Digital banking faces threats from system outages, software errors, and integration problems, which can interrupt services. Such disruptions erode customer trust and may lead to financial losses or regulatory fines. Therefore, establishing strong operational resilience and comprehensive disaster recovery strategies is of paramount importance for maintaining stability and customer confidence.
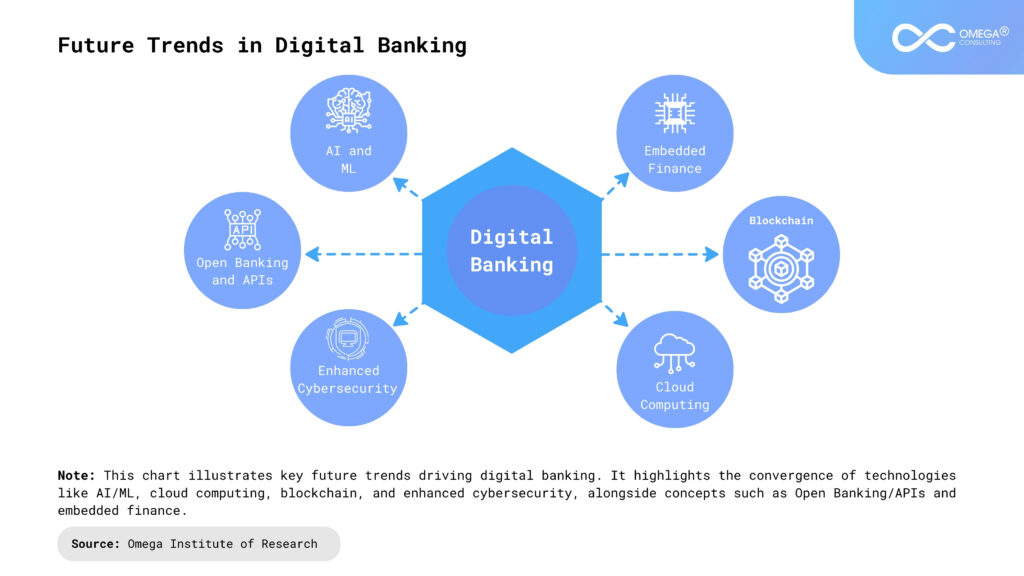
Future Trends in Digital Banking
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI/ML will become even more integral, powering hyper-personalized customer experiences, sophisticated fraud detection, predictive analytics for credit scoring and risk management, AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants for customer service, and process automation (Robotic Process Automation – RPA) in backend operations.
Open Banking and APIs: Driven by regulations (like PSD2 in Europe) and market demand, Open Banking allows third-party financial service providers to access customer banking data (with consent) through secure APIs. This fosters innovation, enabling aggregation services, comparison tools, and new integrated financial products, leading towards a more interconnected financial ecosystem.
Embedded Finance: Banking services will increasingly be integrated directly into non-financial platforms and customer journeys. Examples include “Buy Now, Pay Later” (BNPL) options at e-commerce checkouts, insurance offered during travel booking, or accounting software seamlessly integrating with business bank accounts. Banking becomes a contextual feature rather than a separate destination.
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT): While still evolving, blockchain holds potential for applications in areas like cross-border payments (reducing cost and time), trade finance (improving transparency and efficiency), digital identity verification, and potentially central bank digital currencies (CBDCs).
Cloud Computing: The trend of banks migrating to cloud environments will intensify. This move offers significant advantages, including enhanced scalability to handle fluctuating demands, improved cost-efficiency by optimizing resource utilization, and seamless access to advanced analytics and artificial intelligence tools provided by cloud vendors, ultimately accelerating the pace of innovation within the financial sector.
Enhanced Cybersecurity Focus: As threats evolve, there will be an increased focus on next-generation security measures, including advanced threat intelligence, zero-trust architectures, sophisticated biometric authentication, and AI-powered anomaly detection to protect against increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks.
Sustainability and ESG Integration: Digital platforms will increasingly incorporate features related to Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors, allowing customers to track the carbon footprint of their spending, invest in sustainable funds, or access green loans.
Conclusion
Digital banking has undoubtedly transformed the financial services industry, shifting the paradigm from physical branches and limited hours to ubiquitous, 24/7 access via electronic channels. Driven by technological advancements and evolving customer expectations, it offers unparalleled convenience, speed, and control to users while enabling financial institutions to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and reach broader markets. Key features like omnichannel accessibility, mobile-first design, automation, personalization, and real-time processing define the modern digital banking experience. However, this transformation is not without its hurdles; significant challenges remain in cybersecurity, regulatory compliance, ensuring digital inclusion, and managing intense competition. Looking ahead, trends like AI, Open Banking, embedded finance, and blockchain promise to further revolutionize how we interact with financial services, making banking even more integrated, personalized, and intelligent. As digital banking continues its rapid evolution, it will remain a critical engine of innovation, shaping the future of finance and redefining the relationship between customers and their money.
- https://neontri.com/blog/digital-banking-transformation/
- https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/pages/financial-services/articles/digital-banking-landscape.html
- https://innowise.com/blog/digital-banking-trends/
- https://www.bankdirector.com/article/made-for-you-personalization-in-digital-banking/
- https://www.bankofbaroda.in/banking-mantra/digital/articles/cybersecurity-in-banking
- https://www.rgcms.edu.in/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/The-impact-of-fintech-on-traditional-banking-models.pdf
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions