- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Information Technology
- By Omega Team
The digital age demands a robust foundation for businesses to thrive, and a digital core provides precisely that. It is the essential infrastructure and interconnected framework that empowers organizations to innovate, adapt, and drive continuous digital transformation. By strategically combining technology with operational functions, a digital core enables companies to streamline processes, enhance customer experiences, and stay agile in an ever-changing market landscape.
What is a Digital Core?
The digital core represents a central ecosystem within an organization, encompassing critical digital technologies like enterprise resource planning (ERP), customer relationship management (CRM), and advanced data analytics platforms. It is a unified, data-centric foundation that interlinks processes across departments, ensuring a consistent and real-time flow of information. This foundation enables data-driven decision-making and fosters a highly integrated business environment where efficiency, transparency, and cross-functional collaboration flourish. With a digital core, organizations can break down silos, optimize resource use, and respond more effectively to market changes.
Key Components of the Digital Core
Building an effective digital core requires a well-integrated set of foundational elements, each serving a distinct purpose in supporting a modern, data-driven organization. This digital core is not merely a set of technologies but a strategic infrastructure designed to foster agility, enhance decision-making, and drive business growth in an increasingly complex environment. The core elements include robust data infrastructure, advanced analytics, and automation, all of which must be aligned with the organization’s goals and culture.
Data Infrastructure: A solid data infrastructure is essential to manage vast amounts of information reliably. This infrastructure includes cloud storage, data lakes, and real-time data processing tools that collectively serve as a centralized “source of truth” for the organization. With such infrastructure, businesses can generate accurate, actionable insights that fuel more informed decision-making. A well-established data infrastructure allows teams to access and leverage data seamlessly, ensuring accuracy and consistency across all departments.
Automation and AI: Automation and artificial intelligence are pivotal to the digital core, enabling organizations to optimize workflows by handling repetitive tasks with precision. Automation tools free up time, reduce human error, and allow teams to shift focus toward strategic, high-impact activities. AI capabilities, such as predictive analytics and machine learning, offer deeper insights into customer behavior, demand forecasting, and operational efficiencies. Together, these technologies allow organizations to operate at a higher efficiency level, with reduced costs and improved decision-making.
ERP and CRM Systems: ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems serve as foundational components that unify business operations. ERP systems help manage internal processes, such as finance, supply chain, and production, by consolidating data and promoting a single source of operational truth. CRM systems, on the other hand, centralize customer data, allowing for better customer relationship management and more personalized marketing efforts. With integrated ERP and CRM solutions, organizations can improve overall efficiency while delivering a seamless customer experience.
Cybersecurity Framework: As businesses digitize core functions, safeguarding digital assets becomes increasingly critical. A strong cybersecurity framework protects against data breaches, cyber threats, and unauthorized access, ensuring the safety and integrity of organizational data. This framework typically includes advanced security measures such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring. A resilient cybersecurity strategy helps companies maintain trust with customers, comply with regulatory standards, and protect both customer and corporate data from cyber risks.
Cloud Computing: Cloud technology forms a core part of the digital infrastructure by offering scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency. It allows organizations to expand their digital footprint without investing in extensive physical infrastructure. Cloud computing also facilitates remote access to data and applications, promoting real-time collaboration and supporting flexible work arrangements. By leveraging cloud-based solutions, businesses can enhance operational agility and quickly respond to changing market demands.
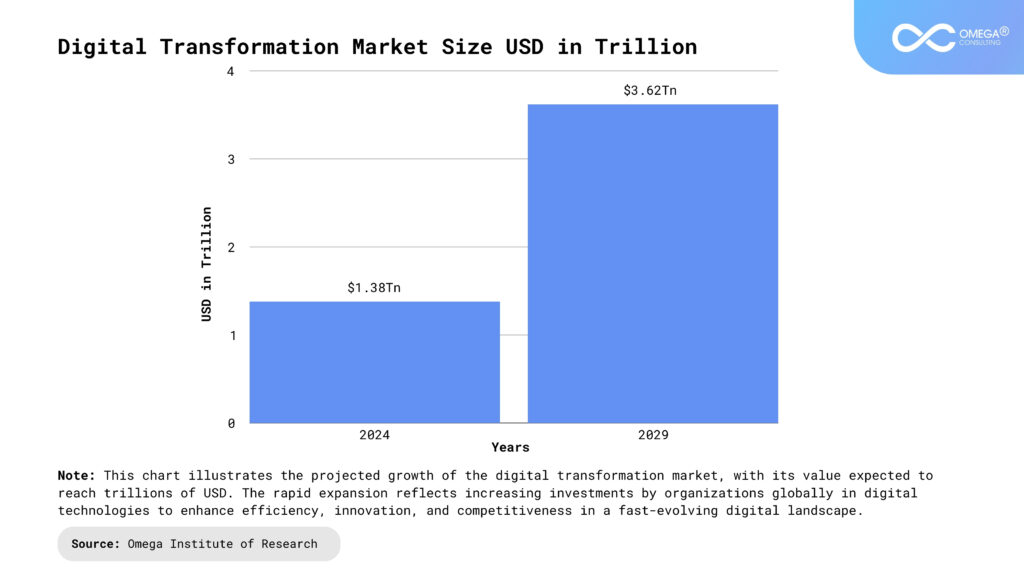
Benefits of a Digital Core
Establishing a digital core provides a multitude of benefits, each of which contributes significantly to a company’s ability to remain competitive and thrive in today’s fast-paced, technology-driven business environment. By developing a well-structured digital foundation, organizations can leverage data more effectively, streamline operations, and foster a culture of agility and innovation. These advantages not only drive operational efficiency but also enable the company to respond proactively to emerging trends and evolving customer expectations.
Operational Efficiency: By centralizing data and enabling automation, a digital core significantly enhances operational efficiency. Redundant manual processes can be minimized or eliminated, freeing up resources and reducing operational costs. Teams can access real-time information, which improves cross-departmental collaboration and streamlines workflows. This enhanced efficiency allows the organization to allocate resources more strategically and focus on innovation and growth.
Enhanced Customer Experience: The digital core helps businesses personalize and improve customer interactions by providing a unified view of customer data across touchpoints. With CRM systems and analytics tools integrated into the core, companies can track customer preferences and behaviors, enabling more tailored engagement strategies. This improved customer experience not only increases satisfaction and loyalty but also strengthens the brand’s reputation in a competitive market.
Agility and Innovation: The digital core enables businesses to adapt rapidly to market changes, scale operations easily, and experiment with new technologies without significant disruption. By establishing a responsive and agile core infrastructure, organizations can introduce innovative products and services faster, leveraging their data and digital assets to stay ahead of competitors. This flexibility also allows businesses to pivot in response to emerging trends and explore new revenue streams more effectively.
Data-Driven Decisions: A centralized data infrastructure within the digital core allows decision-makers to access up-to-date, accurate information in real time. This ability to base decisions on reliable data leads to more strategic planning, better performance tracking, and improved financial forecasting. With comprehensive insights readily available, executives and teams can make informed choices that align with organizational goals and enhance competitive positioning.

Implementing the Digital Core
Building a digital core requires meticulous planning, strategic alignment, and disciplined execution, as it signifies a transformative shift in an organization’s structure, culture, and operations. This process is not simply about adopting new technologies but involves a comprehensive redesign of workflows, data management, and decision-making practices to create a foundation that supports a truly digital-first mindset. Developing a digital core is a multi-step journey that demands leadership commitment, stakeholder buy-in, and the readiness to embrace continuous change. Here are the key considerations for constructing a digital core effectively:
Assessment and Planning: Begin by assessing existing processes and identifying gaps that a digital core could address. This phase involves understanding both business objectives and digital needs, conducting an internal audit of technology capabilities, and engaging stakeholders to align on goals. Developing a clear roadmap for digital core implementation, with timelines, KPIs, and milestones, ensures that all team members are aligned and prepared for the transformation journey.
Technology Integration: Select the most suitable technology solutions that meet the organization’s current and future needs. This phase involves implementing core systems such as ERP, CRM, data analytics platforms, and AI-powered tools. Additionally, integration should ensure compatibility with existing tools and systems while allowing for scalability. By choosing the right technology partners and conducting pilot tests, companies can minimize potential disruptions and maximize the digital core’s effectiveness.
Employee Training and Cultural Alignment: A successful digital transformation requires both technological and cultural change. Employees must be equipped to work with new tools and adapt to a data-driven environment. Comprehensive training sessions, workshops, and open communication can ease the transition. Encouraging a culture that values innovation, collaboration, and continuous learning will also help ensure the digital core’s adoption and success across departments.
Continuous Optimization: The digital core should be viewed as an evolving asset. After implementation, regularly monitoring performance, gathering user feedback, and conducting system updates is essential to ensure that the core aligns with organizational needs. As technology and market demands evolve, continuous optimization allows organizations to refine their digital core, implement the latest advancements, and stay responsive to new business challenges.
Digital Core is Relevance for Businesses
The relevance of a digital core for businesses in today’s digital-first world is profound. A digital core serves as the technological backbone of an organization, creating a cohesive foundation that integrates all critical processes, data, and systems. This integration allows businesses to operate more efficiently, make faster and smarter decisions, and stay agile in a rapidly evolving marketplace. Here are the key reasons why a digital core is vital for businesses today:
Operational Efficiency and Streamlined Processes
A digital core integrates key business functions—like finance, supply chain, and customer service—into a unified framework, reducing redundancy and improving cross-departmental collaboration. This streamlining leads to faster execution, cost savings, and greater productivity, helping businesses operate efficiently and competitively.
Enhanced Customer Experiences
By centralizing customer data, a digital core enables personalized, seamless interactions across touchpoints. Companies can deliver tailored experiences, fostering stronger customer loyalty and satisfaction, which are essential in today’s experience-driven market.
Data-Driven Decision-Making
With real-time access to comprehensive data, organizations can make informed, strategic decisions. Integrated analytics within the digital core provide insights on trends, customer behavior, and market changes, enabling businesses to respond proactively and stay agile.
Increased Agility and Adaptability
A digital core gives businesses the flexibility to quickly adjust to market shifts, scale operations, or introduce new products. This adaptability is crucial for responding to disruptions, capitalizing on opportunities, and staying resilient in a fast-evolving environment.
Foundation for Innovation and Sustainability
Supporting technologies like AI and IoT, a digital core enables companies to innovate continuously while also tracking and improving their sustainability practices. This foundation not only helps businesses differentiate but also align with growing demands for corporate social responsibility.
The Future of the Digital Core
As emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and advanced automation tools become more accessible, the capabilities of the digital core will continue to expand. Organizations that invest in refining and strengthening their digital core will be better equipped to navigate future challenges, remain competitive, and capitalize on opportunities for innovation. In the digital era, a well-developed digital core will be a critical component of sustainable growth and long-term business success.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Siemens
Siemens, a global leader in industrial manufacturing, embarked on a digital transformation journey to enhance operational efficiency and customer engagement through the implementation of a digital core. The company introduced a cloud-based Internet of Things (IoT) platform called MindSphere, which integrated data from various manufacturing processes, supply chains, and customer interactions. By leveraging advanced analytics and machine learning capabilities, Siemens enabled real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance of its machinery. This digital transformation led to significant improvements in production efficiency, with a reported 30% reduction in downtime. Moreover, the establishment of a digital core allowed Siemens to offer new data-driven services to its customers, thereby increasing revenue streams and enhancing overall customer satisfaction through predictive insights.
Case Study 2: Unilever
Unilever, a multinational consumer goods company, focused on establishing a digital core to streamline its global operations and enhance customer insights. The organization adopted a robust data infrastructure supported by a unified Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system, which integrated all aspects of its supply chain, finance, and sales functions. Additionally, Unilever deployed AI-driven analytics tools to process consumer data collected from various channels. As a result of this digital transformation, the company achieved a 15% reduction in operational costs and significantly improved demand forecasting accuracy. By gaining a deeper understanding of consumer behavior, Unilever was able to personalize its marketing campaigns, resulting in a 20% increase in sales for targeted products, showcasing the effectiveness of its digital core.
Case Study 3: Starbucks
Starbucks sought to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency by creating a comprehensive digital core that would streamline its services. The coffee giant integrated its mobile app with a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system, enabling customers to place orders, make payments, and collect rewards seamlessly. The app also collects valuable data on customer preferences and behaviors, which Starbucks uses to tailor marketing strategies and product offerings. The integration of this digital core led to a remarkable 25% increase in mobile orders, significantly boosting revenue while improving overall customer engagement. With the ability to analyze data more effectively, Starbucks can refine its menu and promotional strategies, thereby creating a more personalized experience for its customers and solidifying its position in the competitive coffee market.
Conclusion
In conclusion, establishing a digital core is essential for organizations aiming to succeed in the digital age. This comprehensive foundation enables companies to streamline operations, enhance customer interactions, and adapt quickly to an ever-changing business landscape. By integrating processes and data, organizations can eliminate inefficiencies and make informed decisions faster, driving productivity and innovation. Moreover, a robust digital core allows for personalized customer experiences, fostering loyalty and trust. As businesses continue to embrace digital transformation, those that prioritize a strong digital core will be better positioned to navigate challenges, capitalize on new opportunities, and sustain growth in an increasingly competitive environment.
- https://www.techtarget.com/searcherp/definition/digital-core
- https://www.accenture.com/in-en/insights/digital-core
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/digital-core
- https://www.capgemini.com/in-en/industries/retail/connected-digital-core/
- https://www.technology1.com/resources/articles/elements-of-a-digital-core
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions