- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Information Technology
- By Omega Team

As the digital landscape evolves, so too does the complexity of associated risks. Digital risk now extends beyond cybersecurity threats, encompassing a wide range of challenges that can disrupt operations, damage reputations, and result in significant financial losses. With the increasing interconnectedness of technology, vulnerabilities can spread rapidly, affecting entire industries. This exploration will examine the multifaceted nature of digital risk, including cyberattacks, data breaches, compliance issues, and emerging technologies like AI and blockchain. Understanding why digital risk matters is crucial for organizations to protect their assets and operations. We will discuss strategies to identify, mitigate, and manage these risks effectively. By doing so, businesses can build resilience and thrive in a digitally driven world. This guide offers insights on how to navigate digital risk and leverage opportunities for growth.
What is Digital Risk?
Digital risk refers to the potential for harm arising from the use of digital technologies, encompassing everything from cybersecurity vulnerabilities to compliance failures, operational disruptions, and reputational damage. It is a broad concept that encapsulates risks across multiple domains, including:
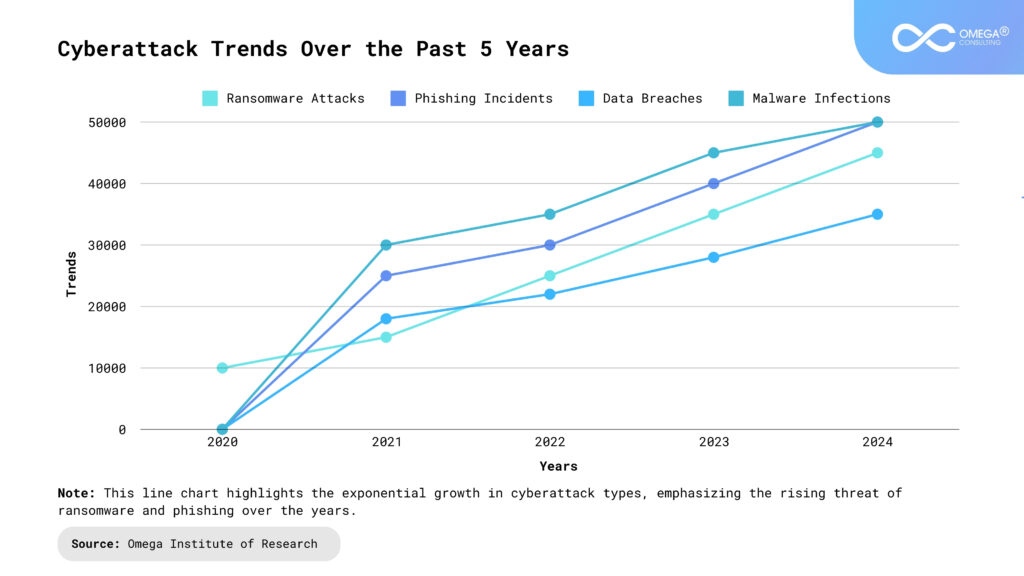
Cybersecurity Threats: These include data breaches, ransomware attacks, phishing schemes, and other malicious activities that target digital assets. For instance, the 2021 Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack highlighted how cyber threats can disrupt critical infrastructure and lead to significant financial and operational consequences. Such incidents showcase the importance of robust security measures to protect digital assets and ensure business continuity.
Data Privacy Risks: Mismanagement of sensitive information can lead to regulatory fines and loss of customer trust. The Facebook-Cambridge Analytica scandal is a prime example of how mishandling user data can result in reputational damage and legal repercussions. Ensuring transparent data practices and compliance with privacy laws is crucial for maintaining stakeholder confidence.
Third-Party Risks: Vendors and supply chain partners can introduce vulnerabilities into an organization’s ecosystem. The 2020 SolarWinds attack demonstrated how third-party software can be exploited to infiltrate multiple organizations. This incident underscores the need for stringent vendor assessments and continuous monitoring of third-party activities.
Operational Risks: Failures in critical digital systems can disrupt business continuity. For example, prolonged outages in cloud services like AWS have caused widespread disruptions across industries. Organizations must have contingency plans and redundancy mechanisms to minimize the impact of such failures.
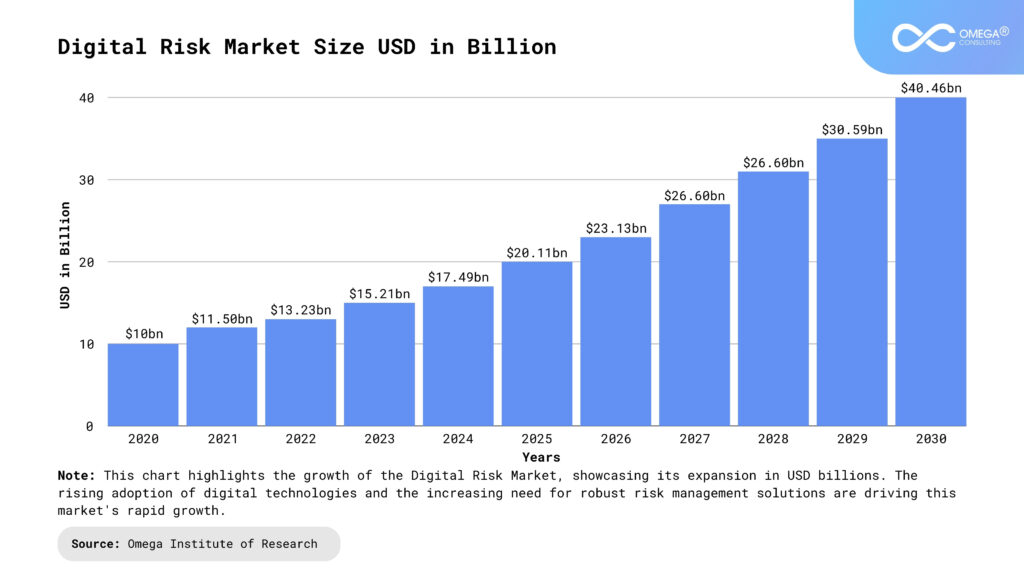
The Expanding Digital Risk Landscape
The rapid pace of digital transformation has exponentially increased the exposure of organizations to digital risks. Key factors contributing to this expansion include:
Proliferation of Connected Devices: The Internet of Things (IoT) has introduced billions of devices into the digital ecosystem, each a potential entry point for cyber threats. In industries like healthcare, connected medical devices such as pacemakers and infusion pumps are critical for patient care but can be exploited if not properly secured. This highlights the importance of device-level security and continuous monitoring.
Remote Work and Hybrid Models: The shift to decentralized work environments has broadened attack surfaces and introduced new vulnerabilities. For instance, in the finance sector, remote access to sensitive financial systems requires stringent security measures to prevent unauthorized access. Organizations must adopt secure access solutions and educate employees on best practices for remote work.
Cloud Adoption: While cloud computing offers scalability and efficiency, it also brings unique security and compliance challenges. Retailers using cloud platforms to manage e-commerce operations face risks of data breaches that could compromise customer payment information. Implementing robust encryption and access controls is essential to mitigate these risks.
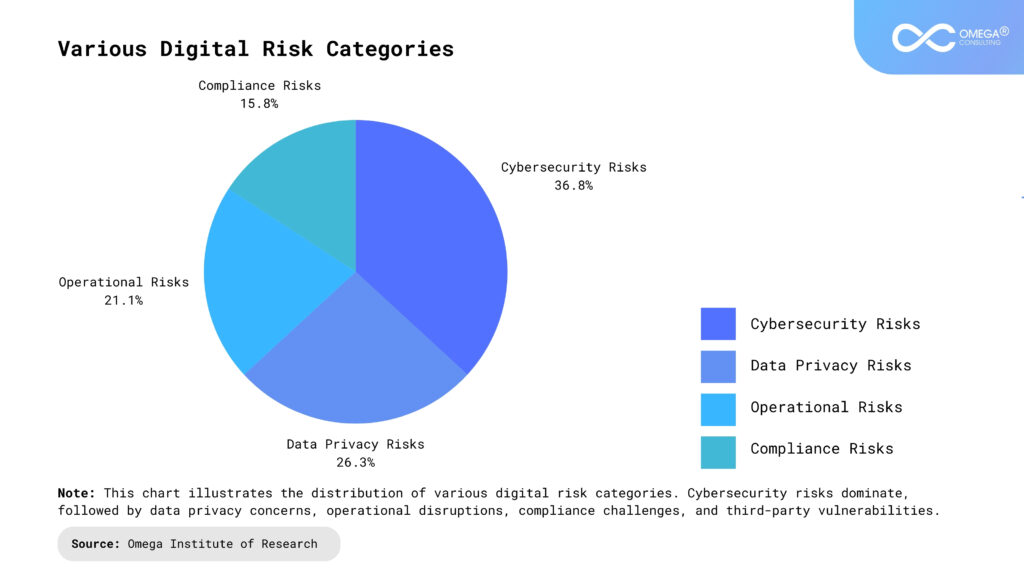
Dimensions of Digital Risk
Digital risk can be categorized into several dimensions, each requiring tailored strategies for mitigation. Below, we explore these dimensions with real-world examples to illustrate their impact:
Strategic Risks: These arise from poorly planned digital initiatives that fail to deliver value or expose the organization to unnecessary vulnerabilities. For instance, the failed launch of Quibi, a short-form streaming platform, serves as a cautionary tale. Despite significant investment, the platform faced challenges with its business model and audience engagement, ultimately leading to its shutdown within six months. This highlights the importance of aligning digital strategies with clear business objectives and market needs.
Operational Risks: System outages, software failures, and process inefficiencies can disrupt business operations. A notable example is the 2021 Facebook outage, which not only affected the platform but also disrupted businesses relying on Facebook’s services for marketing and communication. This incident underscores the need for robust operational resilience and disaster recovery plans.
Compliance Risks: Non-adherence to regulatory requirements, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA, can lead to severe penalties. In 2020, British Airways was fined £20 million under GDPR for failing to protect customer data, emphasizing the importance of compliance in mitigating financial and reputational damage. Regular compliance audits and employee training are critical in addressing these risks.
Reputational Risks: Incidents that damage public perception, such as data breaches or unethical data usage, fall into this category. The 2017 Equifax data breach, which exposed sensitive information of 147 million people, caused significant reputational harm and eroded consumer trust. Transparent communication and swift corrective actions are essential for managing reputational risks effectively.
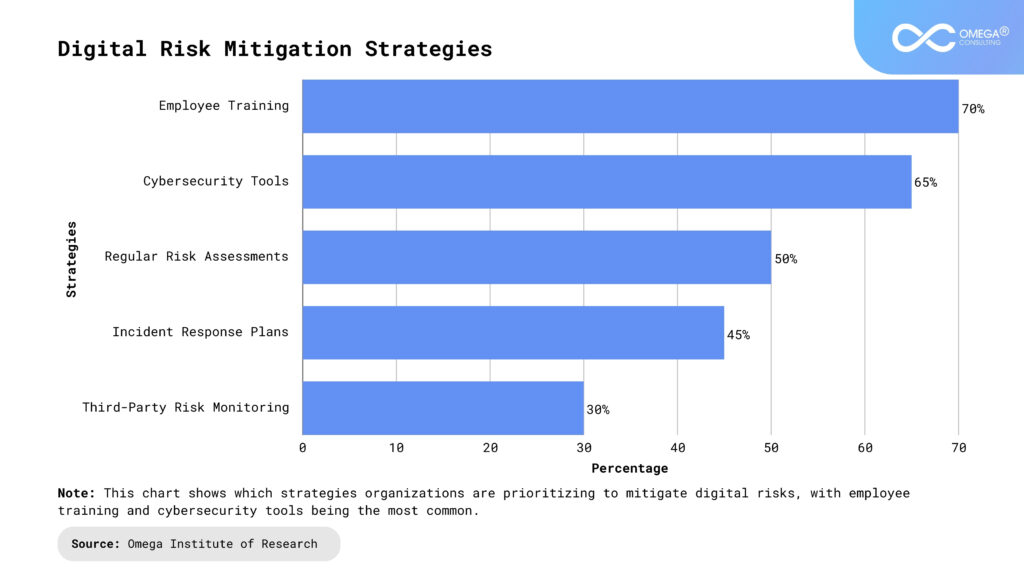
Strategies for Mitigating Digital Risk
To effectively address digital risk, organizations must adopt a holistic approach that combines technology, processes, and people. Here are some key strategies with real-world examples:
Comprehensive Risk Assessment: Conduct regular audits to identify vulnerabilities across systems and processes. For example, a global manufacturing company implemented a risk-scoring framework, which helped them prioritize and mitigate risks in their supply chain, reducing potential downtime by 30%. Risk assessments provide actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
Strengthening Cybersecurity Posture: Implement multi-layered security measures, including firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems. After experiencing a phishing attack, a financial services firm adopted advanced email filtering and multi-factor authentication, reducing incidents by 80% within a year. Regular updates and threat intelligence integration are vital components.
Enhancing Data Governance: Establish clear policies for data classification, storage, and access control. A healthcare provider implemented a data governance platform, ensuring compliance with HIPAA and preventing unauthorized access to patient records. Effective governance minimizes risks and enhances operational efficiency.
Future Trends in Digital Risk
Increased Threats from AI-Driven Attacks: As artificial intelligence (AI) becomes more accessible, cybercriminals are leveraging AI to automate and scale attacks. These attacks include advanced phishing campaigns, AI-generated deepfake videos, and automated vulnerability scanning. Organizations will need to invest in AI-driven defense systems that can detect these sophisticated threats. Real-time threat detection and mitigation will be essential to stay ahead of evolving cybercriminal tactics. Companies must also train their workforce to recognize AI-based scams and attacks.
Regulation and Compliance Evolution: As data privacy concerns continue to rise, governments worldwide are introducing stricter regulations. Laws like GDPR in Europe and similar frameworks globally are setting higher standards for data protection. Organizations will need to stay updated on these regulations to avoid hefty fines and reputational damage. The evolving compliance landscape will require businesses to adopt more stringent data management practices. Failure to comply with these regulations will expose companies to significant legal and financial risks.
Zero-Trust Security Models: The traditional perimeter-based security approach is no longer sufficient in a hyperconnected world. The zero-trust model assumes that no one, whether inside or outside the organization, should be trusted by default. Every user and device must be verified before being granted access to critical resources. This approach reduces the risk of insider threats and unauthorized access to sensitive data. Implementing zero-trust security requires investment in advanced authentication methods and continuous monitoring systems.
Conclusion
Organizations need to implement proactive risk management strategies, which should encompass routine threat evaluations and security audits, to effectively address the ever-changing landscape of digital risks. Cultivating a security-first mindset throughout all organizational levels is vital for successful risk reduction. Enhanced collaboration among industries, government entities, and cybersecurity professionals will facilitate quicker responses to new threats. It is essential to adjust strategies in line with emerging technologies such as AI, quantum computing, and blockchain to mitigate potential vulnerabilities. Leadership must emphasize the importance of cybersecurity, allocate appropriate resources, and promote ongoing education and awareness. A holistic approach to digital risk management is essential for navigating the complexities of today’s cybersecurity environment and ensuring sustained security.
- https://www.centraleyes.com/glossary/digital-risk-management/
- https://www.adb.org/publications/managing-digital-risks-primer
- https://www.proofpoint.com/au/threat-reference/digital-risk
- https://www.zengrc.com/blog/what-is-digital-risk-management/
- https://www.upguard.com/glossary/digital-risk
- https://www.bcg.com/capabilities/digital-technology-data/cybersecurity-digital-risk-management
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions