- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Sustainability
- By Omega Team

The convergence of Generation Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) and sustainability represents a watershed moment in human history, where cutting-edge technology intersects with the imperative to build a more sustainable and equitable world. GenAI, the latest iteration of artificial intelligence, encompasses a suite of advanced technologies such as machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and robotics, which exhibit human-like cognitive abilities and unprecedented efficiency in processing and analyzing data. On the other hand, sustainability encompasses a broad spectrum of principles and practices to ensure the long-term health and vitality of our planet and society. It encompasses environmental stewardship, social equity, economic prosperity, and ethical governance.
Understanding the integration of GenAI and Sustainability
The integration of GenAI and sustainability holds immense promise for addressing complex global challenges, including climate change, resource depletion, social inequality, and ethical business practices. By leveraging the power of AI, organizations can analyze vast amounts of data to extract actionable insights, predict future trends and outcomes, automate processes, optimize resource utilization, and enhance transparency and accountability in decision-making. From climate modeling and energy optimization to supply chain management and social impact assessment, the applications of GenAI in sustainability are diverse and far-reaching.
GenAI represents a culmination of decades of research and development in the field of artificial intelligence. Recent breakthroughs in deep learning, neural networks, and natural language processing have propelled AI capabilities to unprecedented levels. Generative AI models, such as OpenAI’s GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) series, have demonstrated remarkable proficiency in generating human-like text, images, and even code. These advancements hold immense potential for applications in sustainability, ranging from climate modeling and energy optimization to social impact assessment and ethical decision-making.
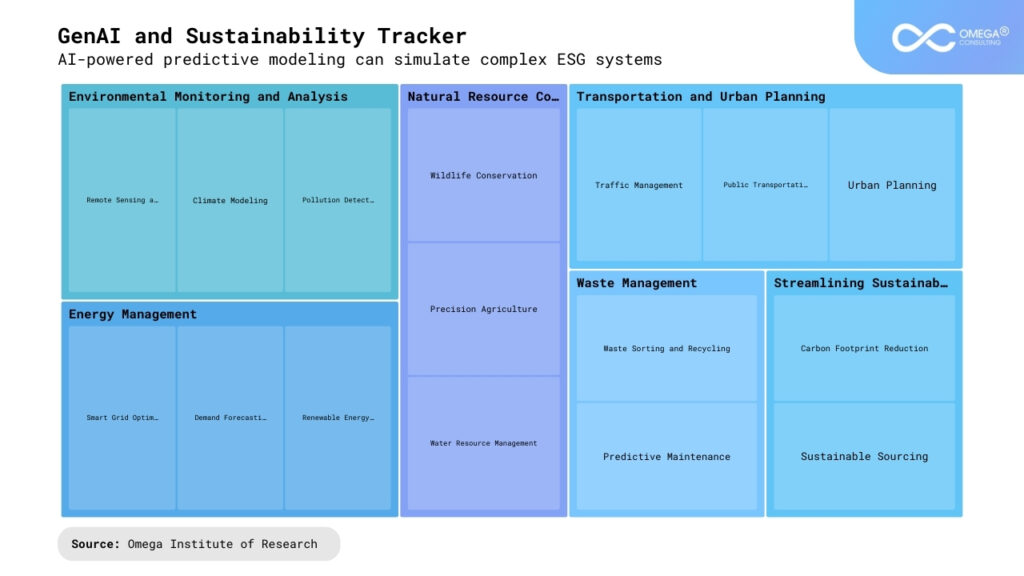
Applications in Environmental Sustainability
In environmental sustainability, GenAI offers innovative solutions for mitigating climate change, conserving biodiversity, and managing natural resources. AI-powered predictive modeling can simulate complex environmental systems, such as weather patterns and ecosystem dynamics, to forecast the impacts of climate change and inform adaptation strategies. AI algorithms can also analyze satellite imagery and sensor data to monitor deforestation, pollution, and habitat loss in real time, enabling proactive conservation efforts and ecosystem restoration initiatives.
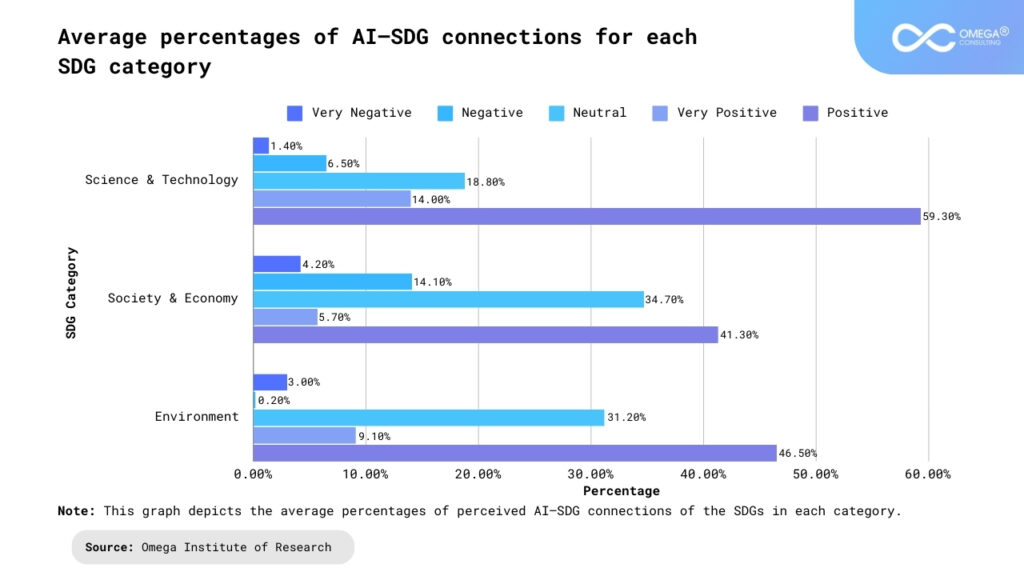
Social Impact of GenAI and Sustainability Intersection:
GenAI has the potential to address social inequalities and promote inclusive development by leveraging data-driven insights and automation to enhance access to essential services, such as healthcare, education, and financial services. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide personalized support and information to underserved communities, bridging the digital divide and empowering individuals with knowledge and resources to improve their livelihoods. Furthermore, AI algorithms can identify patterns of discrimination and bias in decision-making processes, such as hiring and lending, enabling organizations to mitigate biases and promote fairness and diversity.
Governance and Ethical Considerations:
As GenAI becomes increasingly integrated into our daily lives and decision-making processes, it raises important governance and ethical considerations. The responsible development and deployment of AI systems require robust frameworks for accountability, transparency, and oversight to ensure that AI technologies uphold ethical principles and respect human rights. Organizations must prioritize ethical AI design principles, such as fairness, transparency, accountability, and inclusivity, throughout the AI lifecycle, from data collection and model training to deployment and evaluation. Moreover, stakeholders must engage in dialogue and collaboration to develop regulatory frameworks and standards that promote the responsible use of AI and protect against potential risks and harms.
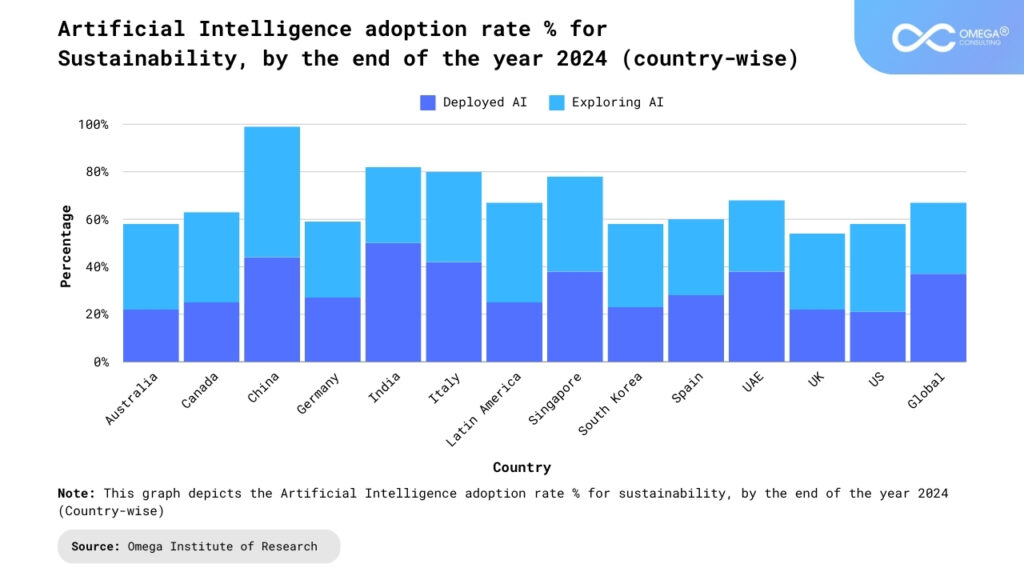
Cross-sector Collaboration and Partnerships:
Addressing complex sustainability challenges requires collaboration and partnerships across sectors, disciplines, and stakeholders. Governments, businesses, academia, civil society organizations, and the tech industry must work together to harness the full potential of GenAI for sustainable development. Collaborative initiatives, such as AI for Good and the Partnership on AI, bring together diverse stakeholders to explore innovative solutions to pressing global challenges, including poverty, inequality, and environmental degradation. By fostering open dialogue, knowledge sharing, and collective action, these partnerships can catalyze transformative change and create a more sustainable and equitable future for all.
Key Principles
At the heart of the integration of GenAI and sustainability lie several key principles:
- Data-driven Insights: GenAI empowers organizations to harness the power of big data to gain deeper insights into complex environmental, social, and economic systems. By analyzing diverse datasets, ranging from satellite imagery and sensor data to social media feeds and financial records, AI algorithms can uncover patterns, correlations, and insights that facilitate more informed decision-making and strategic planning.
- Predictive Modeling: AI algorithms enable organizations to forecast future trends and anticipate potential risks and opportunities in areas such as climate change, resource management, and social impact. By analyzing historical data and identifying patterns, AI systems can generate accurate predictions and scenarios that inform proactive interventions and adaptive strategies.
- Automation and Optimization: By leveraging AI-driven automation, organizations can streamline processes, reduce inefficiencies, and optimize resource utilization across various operations. From energy management and supply chain optimization to waste reduction and emissions monitoring, AI technologies can significantly improve operational efficiency and sustainability performance.
- Transparency and Accountability: GenAI facilitates greater transparency and accountability in ESG reporting by providing stakeholders with real-time access to relevant data, metrics, and performance indicators. By integrating AI-powered analytics and reporting tools, organizations can enhance transparency, build trust, and demonstrate their commitment to sustainable and responsible business practices.
Frameworks & Practices
Numerous frameworks and best practices have emerged to guide organizations in integrating GenAI and sustainability:
- ESG Integration Frameworks: Standards such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) provide structured guidelines for incorporating ESG factors into corporate strategies, governance, and reporting. These frameworks help organizations identify material ESG issues, set targets and metrics, and communicate their sustainability performance to stakeholders effectively.
- AI for ESG Analytics: Advanced analytics platforms powered by AI enable organizations to measure, monitor, and analyze ESG performance metrics in real time, facilitating data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement. By leveraging machine learning algorithms and predictive analytics, organizations can identify trends, patterns, and anomalies in ESG data, enabling them to assess risks, identify opportunities, and optimize performance.
- Supply Chain Optimization: AI-driven supply chain management systems optimize sourcing, production, distribution, and logistics processes, enhancing efficiency, reducing emissions, and ensuring ethical and sustainable practices. By analyzing data from multiple sources, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and customers, AI algorithms can identify inefficiencies, optimize routes, and minimize environmental impact throughout the supply chain.
- Renewable Energy Management: AI algorithms optimize the integration and utilization of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, by predicting demand patterns, optimizing grid operations, and maximizing energy efficiency. By analyzing weather data, energy consumption patterns, and grid performance metrics, AI systems can optimize the deployment and operation of renewable energy systems, enabling organizations to reduce costs, increase resilience, and minimize environmental impact.
Benefits of the intersection of GenAI and Sustainability
The integration of GenAI and sustainability offers a wide range of benefits to organizations:
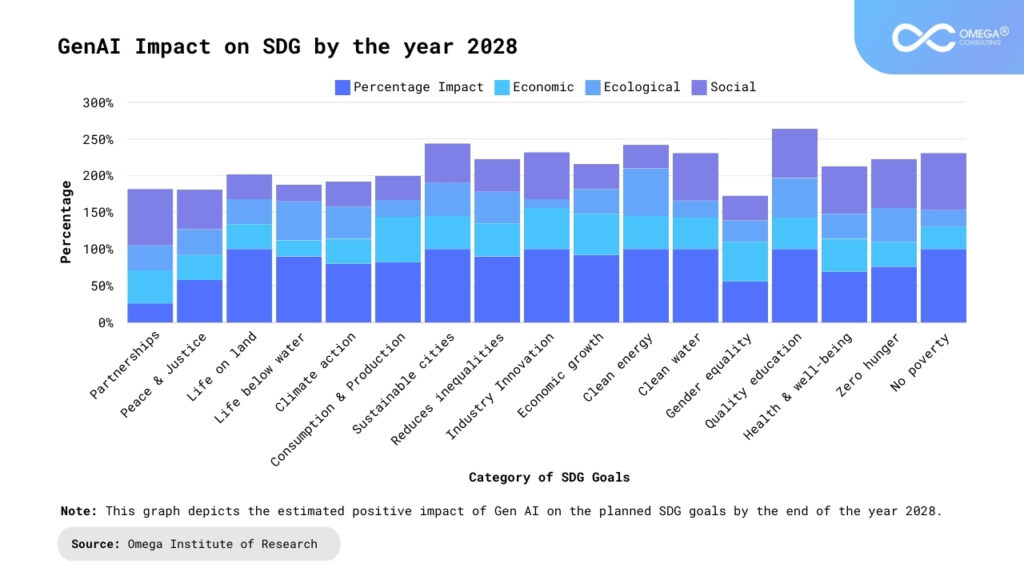
- Enhanced Efficiency: AI-driven automation streamlines workflows, reduces operational costs, and improves resource efficiency, leading to significant savings and productivity gains. By automating repetitive tasks, analyzing data at scale, and optimizing processes, organizations can achieve higher levels of efficiency and competitiveness while minimizing waste and inefficiency.
- Risk Mitigation: Predictive analytics powered by AI help organizations identify and mitigate environmental risks, supply chain disruptions, and other sustainability-related challenges before they escalate, enhancing resilience and risk management capabilities. By analyzing historical data, simulating future scenarios, and identifying potential risks and vulnerabilities, AI systems can help organizations anticipate threats, implement proactive measures, and build adaptive capacity to respond to changing conditions.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies that leverage GenAI for sustainability gain a competitive edge by innovating new products, services, and business models that meet evolving consumer preferences for ethical, eco-friendly, and socially responsible brands. By embedding sustainability into their core business strategies and operations, organizations can differentiate themselves in the market, attract new customers, and drive growth and profitability in a rapidly changing business environment.
- Long-term Value Creation: Sustainable practices driven by AI contribute to long-term value creation by enhancing brand reputation, fostering customer loyalty, and attracting investment capital from socially conscious investors. By aligning their business models with sustainability principles and leveraging AI technologies to drive innovation and impact, organizations can create shared value for shareholders, employees, customers, and society at large, thereby securing their long-term viability and success.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its promise, the integration of GenAI and sustainability presents several challenges and considerations:
- Ethical Implications: The development and deployment of AI systems raise important ethical questions related to fairness, transparency, accountability, and bias. AI algorithms can perpetuate and amplify existing biases and inequalities if not designed and implemented responsibly. Organizations must prioritize ethical AI design principles, such as fairness, transparency, accountability, and inclusivity, throughout the AI lifecycle, from data collection and model training to deployment and evaluation.
- Data Privacy: The use of big data in sustainability initiatives raises concerns about data privacy, security, and ownership. Organizations must ensure that they collect, store, and use data responsibly and in compliance with applicable regulations and privacy standards, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). By implementing robust data protection measures, encryption protocols, and access controls, organizations can safeguard sensitive information and maintain trust with stakeholders.
- Digital Divide: The digital divide refers to the gap between those who have access to digital technologies and those who do not. In the context of AI and sustainability, the digital divide may exacerbate social inequalities, as communities lacking access to AI technologies may be disproportionately affected by environmental degradation, economic disparities, and lack of access to critical services and resources. Organizations must ensure that AI-driven solutions are inclusive, accessible, and equitable and that they prioritize the needs and concerns of marginalized communities.
- Regulatory Compliance: Evolving regulatory landscapes and standards governing AI and sustainability require organizations to navigate complex legal frameworks, comply with reporting requirements, and uphold ethical and governance standards to avoid regulatory fines, litigation, and reputational damage. Organizations must stay abreast of emerging regulations and guidelines related to AI, data privacy, and sustainability reporting, and ensure that they have robust compliance mechanisms and internal controls in place to mitigate legal and regulatory risks.
Perspective & Role of Omega Consulting
Omega consulting plays a pivotal role in guiding organizations through the integration of GenAI and sustainability. They provide strategic advice, technical expertise, and implementation support to help companies:
- Strategy Development: Omega Consulting assists organizations in developing comprehensive ESG strategies aligned with their values, goals, and stakeholder expectations. By conducting stakeholder engagement, materiality assessments, and scenario analysis, we help organizations identify key sustainability issues, set ambitious targets, and develop action plans to drive meaningful change.
- Technology Adoption: Omega Consulting helps organizations identify, evaluate, and implement AI solutions tailored to their sustainability needs, leveraging technologies such as machine learning, predictive analytics, IoT, and blockchain to drive innovation, efficiency, and impact. By conducting technology assessments, pilot projects, and implementation roadmaps, we help organizations harness the full potential of GenAI to address sustainability challenges and achieve their strategic objectives.
- Risk Management: Omega Consulting advises on identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with AI deployment, including ethical risks, cybersecurity threats, regulatory compliance, and reputational risks. By conducting risk assessments, gap analyses, and scenario planning exercises, we help organizations anticipate and mitigate potential risks and vulnerabilities, ensuring that AI-driven solutions are implemented responsibly and sustainably.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Omega Consulting facilitates stakeholder engagement initiatives to build trust, transparency, and accountability in ESG reporting and communication. By conducting stakeholder mapping, materiality workshops, and engagement campaigns, we help organizations communicate their sustainability goals, progress, and impact to internal and external stakeholders, fostering dialogue, collaboration, and collective action.
Conclusion
The integration of GenAI and sustainability represents a transformative opportunity to address pressing global challenges and build a more sustainable and equitable world. By leveraging the power of AI to drive innovation, efficiency, and impact, organizations can unlock new opportunities for growth, resilience, and value creation. However, realizing the full potential of this convergence requires a holistic approach that addresses technological, ethical, regulatory, and societal considerations. With strategic vision, responsible leadership, and collective action, we can harness the transformative power of GenAI to create a brighter and more sustainable future for all.
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/339630437_Artificial_Intelligence_for_Sustainability_Challenges_Opportunities_and_a_Research_Agenda
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0268401220300967
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/9781119771524.ch1
- https://techbullion.com/generative-ai-and-sustainability-green-tech-innovations-in-2024/
- https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/services/sustainability/publications/accelerating-sustainable-development.html
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/1446248/worldwide-artificial-intelligence-impact-industry-revenues-by-industry/
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions