- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Healthcare
- By Omega Team

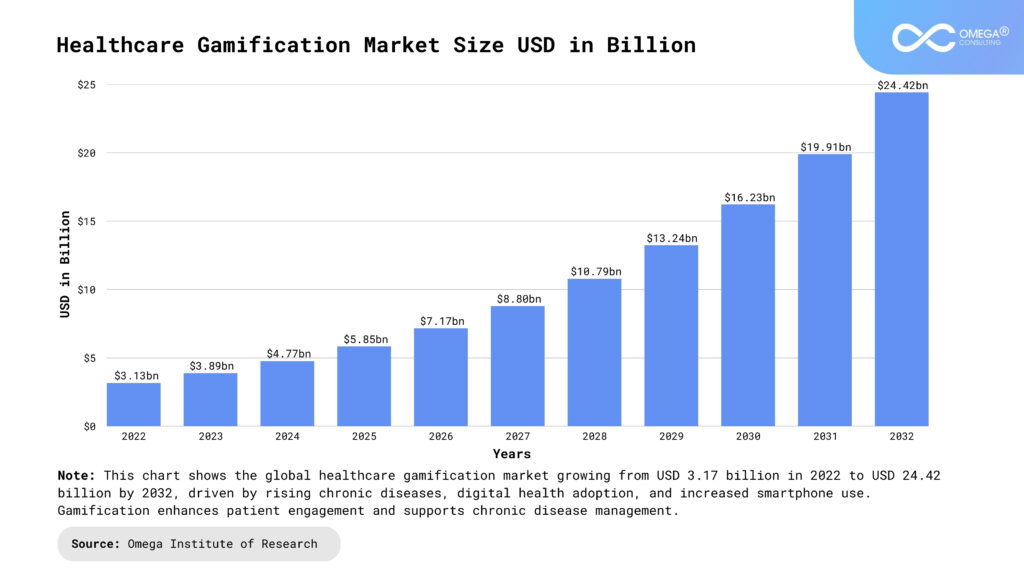
The healthcare industry is undergoing a remarkable transformation, with technology playing a pivotal role in reshaping how care is delivered and experienced. Among the most exciting and promising innovations is health gamification, the integration of game mechanics into non-game contexts to enhance patient experiences and outcomes. By embedding game-like elements into health and wellness programs, gamification is proving to be a powerful strategy to drive patient engagement, improve compliance with treatment plans, foster healthier behaviors, and ultimately enhance overall health outcomes. This article explores the concept of health gamification, its benefits, and its growing impact on patient engagement.
What is Health Gamification?
Gamification in healthcare is rapidly emerging as a patient-centric approach to transform habits, drive compliance, and improve health outcomes by motivating individuals to engage consistently in personal care activities. Far beyond just “playing games,” gamification applies game design principles such as rewards, challenges, leaderboards, and progress tracking — to healthcare contexts, making health-related activities more interactive, enjoyable, and effective. Popularized initially through devices like Fitbits, Apple Watches, and fitness apps, gamification has already proven its ability to encourage physical activity and wellness; now, the healthcare industry is advancing these concepts to support deeper management of chronic diseases. By tapping into the human desire for competition, achievement, and recognition, gamified healthcare solutions not only boost patient engagement and build loyalty but also empower individuals to take an active role in managing various aspects of their health, including medication adherence, healthy eating, physical fitness, and mental well-being.
Features of Health Gamification
Leaderboards: Leaderboards rank users according to milestones, points, or challenges they’ve completed. Seeing how they fare against other users invokes a sense of competitiveness. Naturally, this reinforces the behavior that they demonstrate and helps them to sustain positive practices.
Badges: Badges are tokens of recognition that users can proudly showcase with their friends. Usually, users receive badges when they’ve collected enough points, completed challenges, or participated in special events.
Feedback: Feedbacks in gamification is about providing users with real-time information about how they’re doing. It’s like a progress report. Feedback helps users see where they stand, whether they’re improving or need to do more. It can be shown through things like progress bars, notifications, and status updates. This keeps them motivated and engaged.
Rewards: Rewards encourage people to keep participating and completing tasks. Think of them as incentives. Rewards can come in different forms, like earning virtual money, unlocking achievements (such as badges or trophies), leveling up, or getting access to unique content. These rewards make the experience more fun and give users something to work toward.
Progression: Progression refers to the growth and advancement users feel as they interact with the system. It’s like leveling up in a game. As users complete tasks, face challenges, or go through stages, they unlock new levels, rewards, or opportunities. This gives them a feeling of accomplishment and keeps them returning to improve and master the system.
Healthcare Challenges that Games can Solve
Data Security and Privacy: Gamification is regularly used to help gather personal information of various kinds. Reputable gamification brands such as BeeLiked ensure Audience Data is strictly protected, processed, and stored in accordance with relevant legislation.
Poor Patient Experience: When a gamified healthcare application is designed well, it engages patients and improves their overall experience of a healthcare setting.
An effective health game engages patients to reach their goals in a fun and enjoyable way. Features might also be of a competitive nature because it allows them to challenge others and enter competitions.
Long Waiting Times: Gamification in healthcare can help to reduce patient wait times. Games that promote healthy behaviors also increase the likelihood of patients being seen on time. Gamification-based digital health apps can help patients automatically schedule their appointments. Other gamification strategies can also engage patients before they arrive for their appointments, thereby lowering any anxiety they might feel.
Overemphasizing Rewards and Points: A significant challenge for gamification in healthcare is to find the right balance of rewards and points. There is always the risk that gamification will become a novelty and lose its effectiveness over time. To reduce the risk of this happening, gamification is always being updated and improved. In particular, research determines which specific game mechanics and design features are the most effective for different patients and health conditions.
Costly Solutions for Health Providers: Health providers tend to have a budget, often a tight one. Gamification is a low-cost solution and is effective because it helps patients manage their conditions and avoid complications. Tools are available to enable patients to customize their treatment plans, adhere to discharge summaries, and much more. The end result is that less money is wasted.
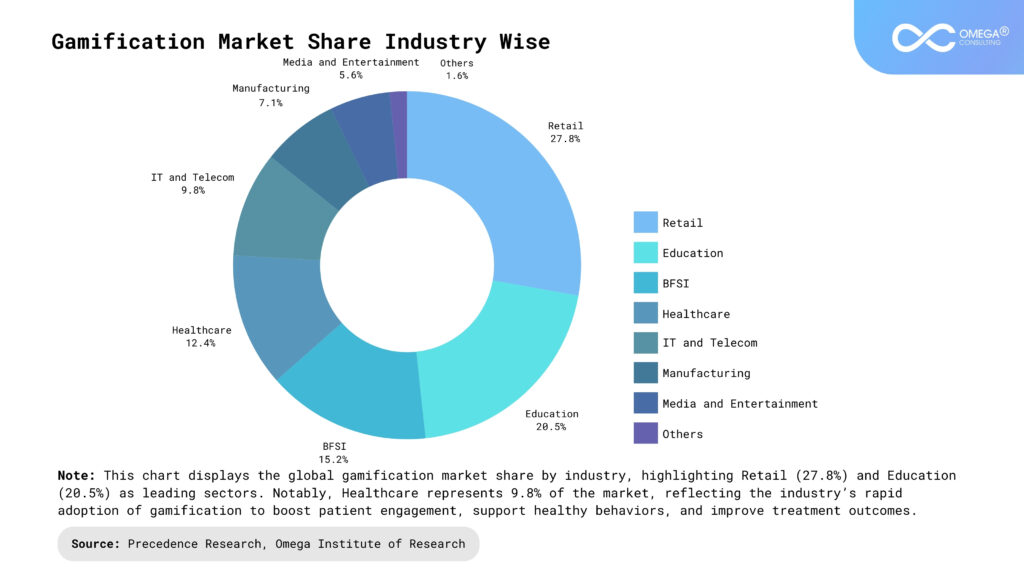
Importance of Health Gamification
Increased Patient Engagement: One of the most significant advantages of gamification is its ability to increase patient engagement. Traditional healthcare interventions often struggle to keep patients motivated and committed to their treatment plans. Gamification, by contrast, leverages intrinsic and extrinsic motivators to keep patients actively involved in their care. By transforming mundane health tasks into enjoyable and rewarding activities, patients are more likely to adhere to their treatment regimens and make healthier lifestyle choices.
Improved Health Outcomes: The ultimate goal of any healthcare intervention is to improve patient outcomes, and gamification has demonstrated its potential to achieve this. For example, gamified platforms encouraging regular physical activity have reduced the risk of chronic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular conditions. Similarly, gamification can enhance medication adherence, leading to better management of chronic conditions and reducing the likelihood of hospital readmissions.
Enhanced Patient Education: Education is critical to effective healthcare, and gamification offers a novel way to deliver health-related information. Presenting educational content in an interactive and engaging format makes patients more likely to absorb and retain important information about their condition, treatment options, and self-care practices, ensuring they feel informed and knowledgeable about their health.
Behavioral Change: Gamification is particularly effective at driving behavioral change, a key factor in preventing and managing chronic diseases. By breaking down complex health goals into smaller, achievable tasks and rewarding progress, gamification helps patients develop healthier habits over time. For example, a gamified app might encourage users to gradually increase their daily water intake, reduce sugar consumption, or incorporate mindfulness practices into their routine.
Social Support and Community Building: Many gamified health platforms incorporate social features that allow patients to connect with others who have similar health goals. This sense of community can provide valuable support, encouragement, and accountability, making it easier for patients to stay on track with their health objectives.
Healthcare Gamification Strategy: Key Steps
Identify Your Consumers’ Pain Points: To begin with, set clear business goals that you want to achieve. Identify the challenge areas that you want to address through gamification. For instance, the lack of focus of patients while practicing their yoga or meditation, non-adherence to medications and prescribed food & lifestyle changes or other pre and post-surgical challenges faced by the patients in adhering to their care plans and recovery processes.
Determine the Right Mix of Gaming Strategy: Once your goals are set, design a unique gaming strategy aligned with them. Plan your care coordination app carefully, integrating gaming components that fit best. Focus on two key elements: mechanics to drive engagement and dynamics to shape user behavior.
Design Your Game: You can use a creative combination of gaming types including storytelling, levels, challenges, leaderboards, rewards, avatars and other gaming formats. One or more of the above combinations can be used to create immersive gaming experiences, while seamlessly engaging patients in your care plans to enable cohesive, coordinated and hyper-personalized PX.Actively Seek Feedback: The major reason behind adopting gamification for patients is to drive better patient outcomes. Without constantly monitoring the progress of patients, the gamification of health and wellness apps will remain just games for patients and will not achieve its intended purpose. It is critical to obtain feedback from patients and monitor the positive effect of gamification on their overall health.
Applications of Health Gamification
Mobile Apps for Chronic Disease Management: Several mobile apps have been developed to help patients manage chronic conditions such as diabetes, asthma, and hypertension. These apps often include gamified features such as daily challenges, progress tracking, and rewards for meeting health goals. By making self-management more engaging, these apps encourage patients to monitor their condition and adhere to treatment plans actively.
Fitness and Wellness Platforms: Fitness and wellness platforms like MyFitnessPal and Noom have embraced gamification to help users achieve their weight loss and fitness goals. These platforms offer calorie tracking, workout challenges, and social sharing features to make the journey toward better health more enjoyable and motivating.
Mental Health Interventions: Mental health apps like Headspace and Happify use gamification to promote mental well-being. These apps offer guided meditation sessions, mood tracking, and daily challenges, encouraging users to develop mindfulness and resilience. Making mental health care more accessible and engaging, these apps help users build positive mental health habits.
Rehabilitation Programs: Gamification is also used in rehabilitation programs to help patients recover from injuries or surgeries. For example, virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) platforms can create immersive, gamified environments that motivate patients to complete physical therapy exercises. These platforms often include progress tracking and rewards to keep patients engaged throughout their recovery.
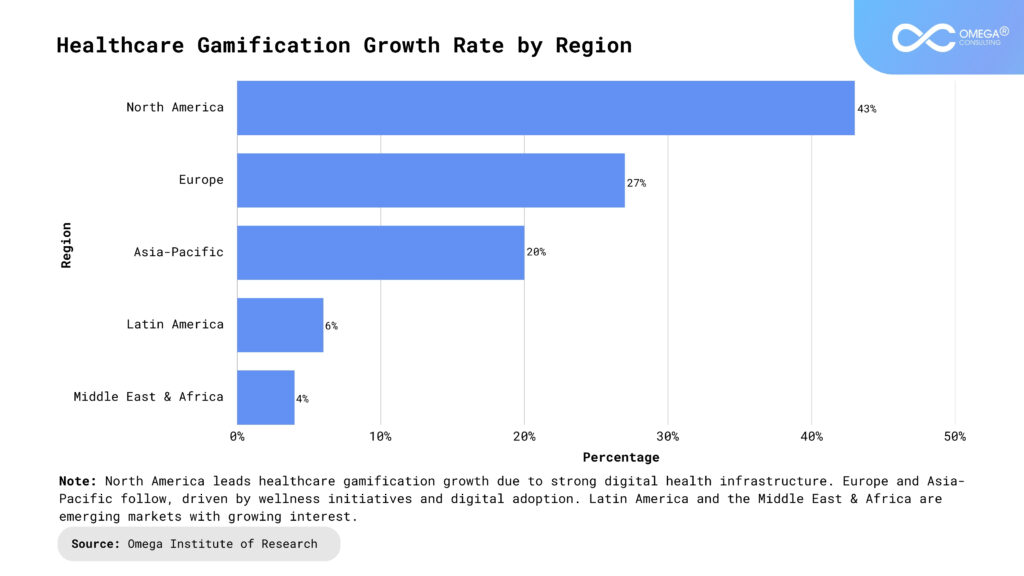
Trends in Health Gamification
Game-based treatments: Gamification can be used to remind people to take their medication. It can also be used by patients with diabetes to control their intake and calculate insulin doses. These treatments use point systems, rewards, and challenges to keep users engaged and consistent. They can be tailored to individual conditions, making treatment more interactive and motivating.
Wearables and remote monitoring devices: These devices seek to improve patients’ physical conditions by recording steps and distances traveled, heartbeat, sleep patterns, and many other things. They provide real-time data to both patients and healthcare providers, enabling proactive health management. Over time, this data can reveal trends that help in early diagnosis and preventive care.
Gamified healthcare apps: These can be used to help people reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases by encouraging them to maintain a healthier diet, move and walk more, hydrate, and much more. Progress tracking, badges, and friendly competition often increase long-term user engagement. They also integrate with other health tools to provide a comprehensive wellness experience.
Telehealth: This is a way of getting personal care from a healthcare provider without an in-person office visit. It increases accessibility, especially for patients in remote or underserved areas. With secure platforms, it also allows for continuity of care through virtual follow-ups and consultations.
AI and machine learning: Artificial intelligence and machine learning are currently being used for disease prevention, diagnosis, treatment plans, and to enhance public health and safety. They can analyze massive datasets quickly to uncover patterns invisible to human doctors. Additionally, AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are improving patient interaction and triage.
Conclusion
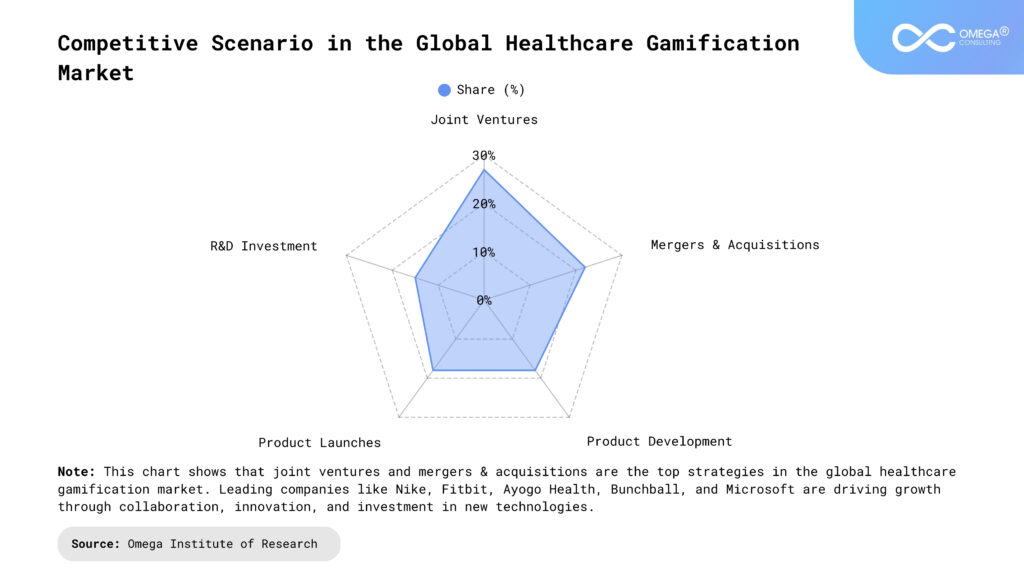
Gamification can be a powerful tool for improving patient engagement, education, adherence to treatment, and reducing healthcare costs.By leveraging game elements such as rewards, competition, and social influence, healthcare providers can create more enjoyable and effective treatment experiences for patients. However, challenges such as privacy concerns and a lack of consensus on effective game design must be addressed to ensure maximum benefits. Lastly, healthcare providers are encouraged to consider integrating gamification into their practices to improve patient outcomes and reduce costs.
- https://www.hurix.com/blogs/benefits-of-gamification-in-healthcare-engaging-patients-and-improving-outcomes/
- https://www.mylanguageconnection.com/gamification-in-healthcare/
- https://digitalhealth.folio3.com/blog/what-ways-can-gamification-be-used-in-the-healthcare-industry/
- https://www.solvedge.com/Healthcare-Gamification
- https://www.beeliked.com/blog/gamification-in-healthcare
- https://www.grgonline.com/post/the-rise-of-health-gamification-and-its-impact-on-patient-engagement
- https://lightit.io/blog/gamification-in-healthcare-basics-and-examples/
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions