- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Healthcare
- By Omega Team
The U.S. healthcare system is experiencing significant economic challenges, with spending surpassing $4.3 trillion in 2021. As healthcare costs continue to rise in 2024, driven by factors such as an aging population, technological advancements, administrative complexities, and labor shortages, providers must seek innovative solutions to maintain care quality while managing expenses. Outsourcing and digital transformation have emerged as strategic approaches to addressing these pressures, offering cost-saving opportunities and operational efficiencies without compromising patient care.
Economic Pressures in U.S. Healthcare: A 2024 Perspective
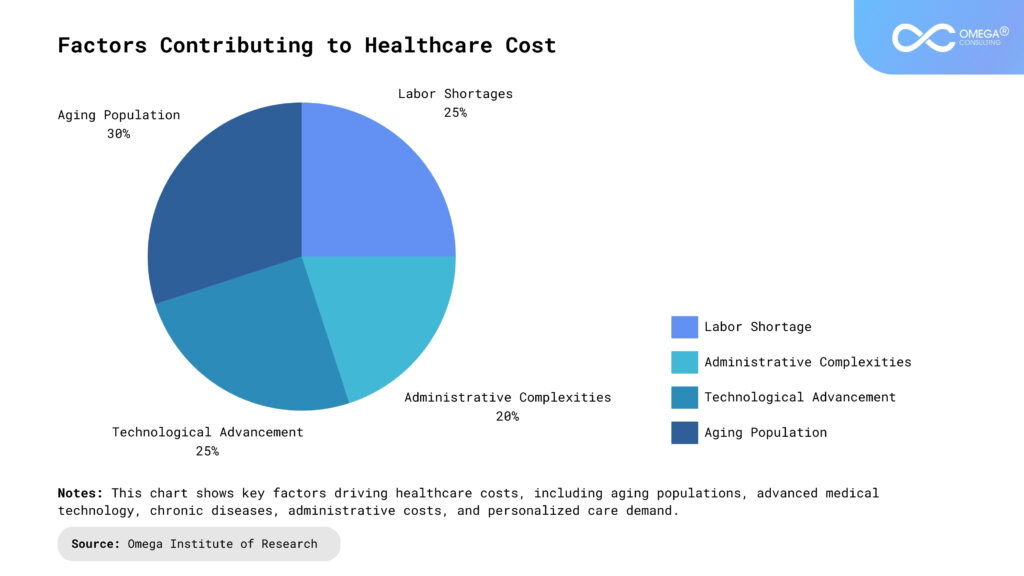
Healthcare costs have been on an upward trajectory for decades, and several underlying factors continue to intensify economic challenges in 2024.
Aging Population: With the number of elderly Americans increasing rapidly, there is a growing demand for medical services, particularly for chronic conditions and long-term care. This aging demographic consumes a disproportionate amount of healthcare resources, contributing significantly to rising healthcare costs.
Technological Advancements: While innovations in medical technology, such as robotic surgeries, advanced diagnostics, and AI-driven healthcare tools, enhance patient care, they come with substantial initial investments. Healthcare institutions face high costs related to acquiring new technologies, training staff, and maintaining infrastructure.
Administrative Complexities: The U.S. healthcare system’s administrative overhead, characterized by complex billing procedures and regulatory requirements, contributes heavily to rising costs. Hospitals and clinics often struggle with labor-intensive billing systems and compliance with stringent regulations, which drives inefficiencies and increases costs.
Labor Shortages: The shortage of healthcare professionals, including nurses, physicians, and technicians, adds significant financial strain to healthcare institutions. The demand for skilled healthcare workers continues to outpace supply, leading to higher wages, employee burnout, and higher turnover rates. This labor crisis makes it difficult for providers to manage staffing costs effectively while maintaining the quality of care.
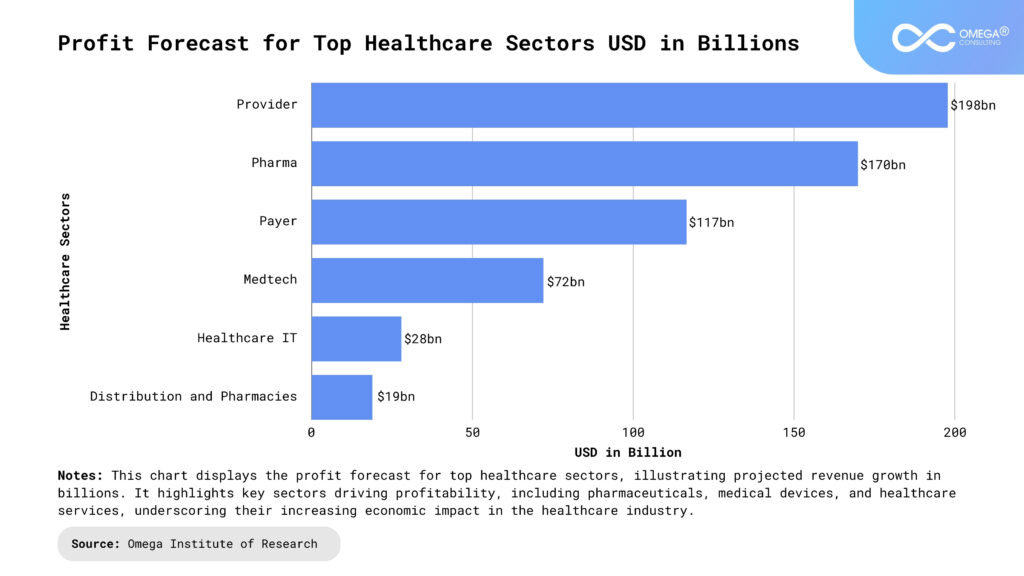
Outsourcing in Healthcare: A Strategic Cost-Saving Response
As economic pressures mount, healthcare organizations are increasingly turning to outsourcing as a strategy to manage costs and streamline operations. Outsourcing allows healthcare providers to delegate non-core functions to third-party vendors, reducing overhead and allowing them to focus on patient care. Several key areas have seen substantial outsourcing activity:
Administrative Services: Healthcare organizations often outsource administrative tasks such as billing and revenue cycle management, helping them navigate the complex U.S. medical billing system. Third-party providers specialize in reducing billing errors, improving cash flow, and accelerating the claims process, which is essential in the current landscape of high operational costs.
Human Resources and Payroll: Outsourcing human resources functions, including payroll management and staff recruitment, enables healthcare institutions to focus more on patient care while ensuring compliance with labor laws and regulations. External vendors can manage workforce needs efficiently, especially in times of high turnover and labor shortages.
IT and Cybersecurity: The growing reliance on digital infrastructure has led many organizations to outsource IT services and cybersecurity management. This approach reduces internal IT overhead while providing access to 24/7 technical support and strengthening cybersecurity defenses. With cybersecurity attacks becoming more frequent in healthcare, ensuring data security is paramount.
Clinical Outsourcing: Outsourcing is also transforming clinical services. Telemedicine, for example, allows healthcare institutions to partner with third-party providers, giving patients access to care without the need for significant investments in personnel or technology. Similarly, diagnostic services like radiology and pathology are being outsourced to specialized providers, enabling quicker and more cost-effective results.
Pharmacy Benefit Management (PBM) and Supply Chain Management:
Pharmaceuticals are one of the largest expenses in healthcare. Outsourcing PBM allows organizations to optimize drug costs and ensure patients have access to necessary medications. Likewise, supply chain management outsourcing ensures efficient delivery of medical supplies, reducing costs associated with procurement, inventory, and distribution.
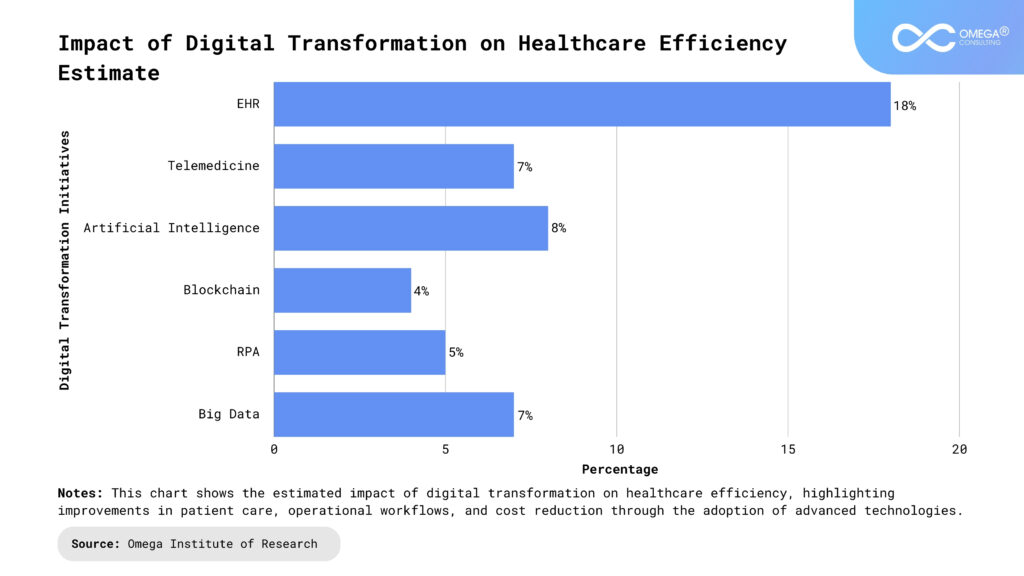
Digital Transformation in Healthcare: A Catalyst for Efficiency and Improved Care
Digital transformation is reshaping the healthcare industry, providing tools and technologies that improve care delivery and operational efficiency. As healthcare institutions strive to manage costs, digital technologies are pivotal in creating a more sustainable healthcare ecosystem.
Electronic Health Records (EHRs):
The widespread adoption of EHRs has revolutionized patient data management, improving communication across healthcare providers and reducing administrative burdens. EHRs ensure seamless access to patient histories, aiding in more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment plans. This technology reduces errors, streamlines workflows, and boosts overall efficiency.
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telemedicine, and it remains an essential tool in 2024. Telehealth platforms allow providers to deliver care remotely, reducing strain on healthcare facilities and improving access to care for patients in underserved areas. Remote monitoring technologies, especially for chronic disease management, allow real-time tracking of patient health metrics, reducing hospital admissions and emergency visits.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are making healthcare smarter. AI-powered diagnostic tools improve the accuracy of diagnoses by analyzing vast amounts of patient data. For example, AI-driven predictive analytics help healthcare providers anticipate patient outcomes, such as the likelihood of readmission, enabling proactive interventions. In addition to clinical applications, AI automates routine administrative tasks such as scheduling, billing, and claims processing, reducing human error and driving significant cost savings.
Blockchain Technology: Data privacy remains a critical concern in healthcare, and blockchain technology offers a solution by providing a secure, decentralized system for managing medical records. Blockchain ensures data integrity, enhances cybersecurity, and simplifies regulatory compliance, particularly in areas like HIPAA.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA): RPA allows healthcare institutions to automate repetitive tasks like claim processing and scheduling, improving processing times and reducing errors. This automation frees up staff time to focus on patient care, ultimately enhancing service delivery.
Predictive Analytics and Big Data: Predictive analytics driven by big data helps healthcare providers optimize resource allocation, predict future healthcare needs, and identify high-risk patient populations. This data-driven approach enables more targeted interventions and preventive care, improving patient outcomes while reducing unnecessary spending.
Synergy of Outsourcing and Digital Transformation
Outsourcing and digital transformation are not mutually exclusive strategies; in fact, they complement each other. Outsourcing IT services, for example, enables healthcare institutions to focus on implementing cutting-edge technologies like AI and telemedicine without being weighed down by operational inefficiencies. This integrated approach maximizes both cost savings and care quality improvements, helping healthcare organizations remain competitive in a rapidly changing environment.
By outsourcing non-core functions, healthcare providers can realize immediate cost savings, while digital transformation initiatives offer long-term operational improvements. Together, these strategies create a more flexible, efficient, and resilient healthcare system capable of meeting the evolving demands of patients and providers.
Challenges and Considerations: A Closer Look
While outsourcing and digital transformation offer substantial benefits to healthcare organizations, they also present several challenges that need to be managed carefully to avoid risks to patient care, operational efficiency, and compliance.
Regulatory Compliance
Healthcare organizations face stringent regulatory requirements, particularly when outsourcing functions such as billing, revenue cycle management, or data handling. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is one of the most critical regulations that govern patient data privacy and security. Non-compliance with HIPAA can lead to significant penalties and legal repercussions, making it essential for healthcare providers to ensure that third-party vendors adhere to these rules.
Before partnering with an external provider, healthcare organizations must conduct thorough vetting to ensure that the vendor has the necessary security protocols, data encryption practices, and compliance certifications. Additionally, contractual agreements should clearly outline the provider’s responsibilities in safeguarding patient data, ensuring regular audits, and maintaining updated security measures.
Investment Costs
Digital transformation often involves significant upfront costs, which can be a barrier for many healthcare organizations, especially smaller practices or community hospitals. Technologies such as AI for diagnostic assistance, Electronic Health Records (EHRs), and telemedicine platforms require substantial investment not only in software and hardware but also in integration into existing systems. Moreover, maintaining and updating these technologies can incur ongoing costs.
Beyond the financial investment in technology, healthcare organizations must also invest in training their workforce. Implementing new systems often requires employees, from administrators to clinicians, to undergo extensive training, which consumes time and resources. In the interim, productivity may decline as staff members adjust to new workflows. For example, moving from paper-based records to EHRs can initially slow down operations due to the learning curve involved.
To mitigate these costs, healthcare providers must conduct a cost-benefit analysis to evaluate the long-term financial and operational advantages of digital tools. Often, the savings generated from improved efficiency, reduced errors, and better resource allocation offset the initial investment over time.
Operational Disruption
Transitioning to outsourced services or implementing new digital technologies can disrupt daily operations if not executed properly. Outsourcing functions such as IT, diagnostics, or administrative services can lead to delays or communication breakdowns if the external provider is not fully aligned with the healthcare organization’s workflows. Similarly, implementing new technologies such as AI or telemedicine may temporarily impact service delivery due to system integration challenges or staff unfamiliarity with the new tools.
Healthcare organizations need to plan these transitions carefully, ensuring that they develop comprehensive implementation strategies. This includes conducting pilot programs, training staff in advance, and maintaining open communication with third-party vendors. A phased approach to implementation can help mitigate disruptions by allowing healthcare providers to address issues incrementally before rolling out the new system organization-wide.
Another potential source of disruption arises when an outsourcing provider or digital technology underperforms, leading to inefficiencies or errors. Healthcare organizations should have contingency plans in place, such as backup providers or systems, to ensure continuity of care in case outsourced services fall short.
Quality Control
One of the most significant risks of outsourcing clinical services, such as telemedicine or diagnostic testing, is maintaining quality control. Since these services directly impact patient care, healthcare organizations must ensure that third-party providers meet the same standards of care they would uphold in-house. For instance, outsourced telemedicine services should align with the organization’s clinical protocols, provide timely consultations, and maintain patient engagement.
Without proper oversight, there is a risk that the quality of outsourced services may deteriorate over time, which could negatively impact patient outcomes. Healthcare institutions need to establish performance metrics and conduct regular audits of their outsourcing partners to ensure quality standards are maintained. In some cases, healthcare providers might also require the third-party vendor to undergo certifications or accreditations that validate their service quality.
Regular feedback loops between healthcare organizations and outsourcing partners are crucial. They allow healthcare providers to address concerns quickly and make adjustments to the service agreement or workflow as necessary. Outsourcing agreements should include provisions for performance monitoring, including response times, error rates, and patient satisfaction.
Data Security and Interoperability
In an era where healthcare data breaches are increasingly common, another key consideration is data security. As healthcare organizations share patient data with external vendors or integrate new digital systems, they must ensure that these solutions are fully secure against potential cyber threats. This requires rigorous testing of the vendor’s security systems and protocols for how patient information is transmitted, stored, and hi accessed. Blockchain technology or end-to-end encryption solutions are often explored as ways to enhance security.
Interoperability is another challenge in digital transformation. Many healthcare organizations use different systems that may not communicate seamlessly with new technology platforms. For example, implementing a new AI diagnostic tool may be challenging if it does not integrate well with existing EHRs. This could lead to data silos, where patient information is fragmented across different systems, making it harder for healthcare professionals to access comprehensive patient records. To address this, healthcare providers must ensure that new digital systems are compatible with existing infrastructure or invest in interoperability solutions that facilitate smooth data exchange across platforms.
Change Management
The success of both outsourcing and digital transformation initiatives depends heavily on the organization’s ability to manage change. These processes often require significant shifts in how healthcare professionals work, which can encounter resistance from staff. Physicians, nurses, and administrative personnel may be skeptical of new technologies, worry about job displacement, or feel uncomfortable with relying on third-party vendors for critical services.
Effective change management strategies should involve clear communication about the benefits of these initiatives, including how they will improve patient care and reduce workloads. Training programs should be comprehensive, ongoing, and responsive to staff concerns. Healthcare leaders also need to foster a culture of innovation, where new technologies and workflows are seen as opportunities for growth rather than threats.
Cost Considerations
The rising costs in healthcare, particularly those related to an aging population, technological investments, and labor shortages, are a central challenge in 2024. These costs strain budgets across the healthcare system, creating a need for solutions like outsourcing and digital transformation that offer immediate relief and long-term efficiency.
- Outsourcing: By outsourcing non-core functions such as administrative services (billing, HR, payroll), clinical services (telemedicine, diagnostics), and IT (cybersecurity, data management), healthcare providers can save substantial costs. Outsourcing allows hospitals to eliminate the expenses tied to hiring, training, and maintaining in-house staff for these functions.
- Digital Transformation: The adoption of electronic health records (EHRs), AI tools, and remote monitoring technologies not only improves care quality but also reduces operational costs in the long run by streamlining workflows, reducing errors, and enabling real-time monitoring of patient conditions, which prevents costly emergency visits and readmissions.
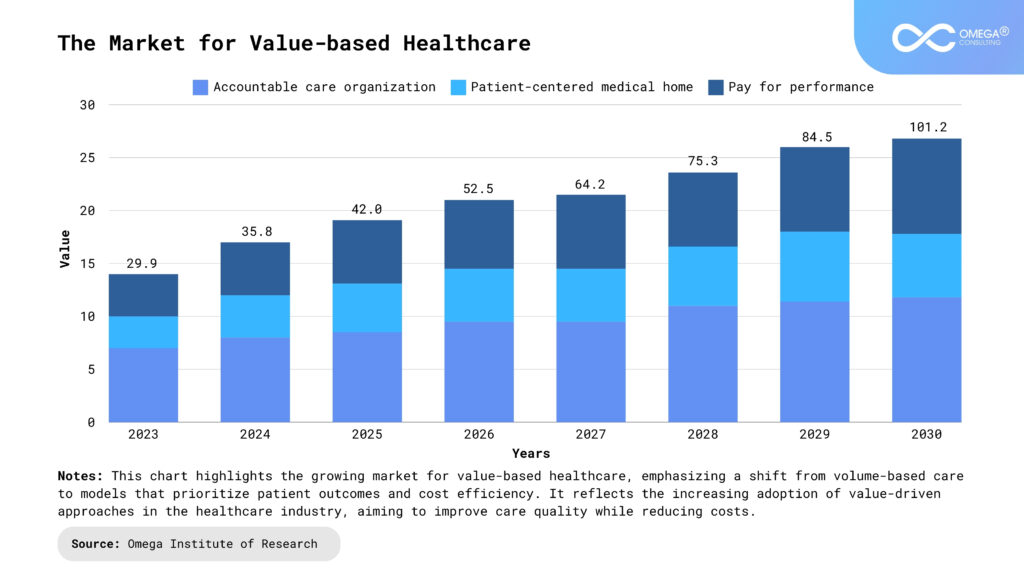
Data as a Driver for Efficiency
Healthcare organizations generate massive amounts of data, which can be harnessed through digital transformation to enhance decision-making, predict trends, and personalize care.
- EHRs and Predictive Analytics: Electronic Health Records consolidate patient data into one accessible format, which improves coordination across providers. Predictive analytics driven by AI can use this data to identify high-risk patients, optimize resource allocation, and reduce preventable hospitalizations. This leads to cost reductions and improved patient outcomes.
- Big Data in Supply Chain Management: Leveraging data analytics allows healthcare organizations to better manage inventory, predict medication shortages, and streamline procurement, reducing unnecessary spending on supplies and pharmaceuticals.
Benefits of Outsourcing and Digital Transformation
- Operational Efficiency: Outsourcing reduces the burden on internal staff, allowing them to focus on patient care rather than administrative tasks. For example, by outsourcing revenue cycle management, healthcare providers can reduce billing errors, accelerate cash flow, and navigate the complex U.S. medical billing system more effectively.
- Improved Care Quality: Digital transformation tools such as AI-driven diagnostic systems, telemedicine, and blockchain for secure data management enhance the quality of care by making healthcare more accessible, improving diagnostic accuracy, and ensuring patient data is safe.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Outsourcing and digital solutions provide healthcare institutions with the flexibility to scale operations according to demand. For instance, telemedicine platforms can expand patient access to specialized care without the need for physical infrastructure, while outsourced IT services can adjust to growing cybersecurity needs as patient data volumes increase.
Case Studies
The Cleveland Clinic: Outsourcing IT and Data Management
Challenge:
The Cleveland Clinic, one of the largest healthcare systems in the U.S., faced rising IT costs and cybersecurity risks, especially as they expanded into telemedicine and electronic health records. Managing these IT infrastructures in-house became resource-intensive and costly.Solution:
The Cleveland Clinic outsourced its IT services and data management to a third-party provider that specialized in healthcare technology. This partnership allowed them to enhance their cybersecurity, ensure 24/7 technical support, and integrate advanced AI analytics into patient care without the need for large-scale internal investments.Outcome:
The outsourcing arrangement reduced IT-related expenses by 15%, improved the speed and efficiency of internal workflows, and significantly enhanced data security. The partnership also enabled the clinic to scale its IT operations efficiently as patient demand for telemedicine surged.Johns Hopkins Medicine: AI-Powered Predictive Analytics
Challenge:
Johns Hopkins Medicine was facing high rates of patient readmissions, leading to increased healthcare costs and lower patient satisfaction. Their challenge was to find a way to predict and prevent these readmissions effectively.Solution:
Johns Hopkins invested in AI-driven predictive analytics to anticipate patients at high risk of readmission based on historical data, including demographic factors, medical history, and care management strategies. They also outsourced the management of this AI system to a specialized third-party provider to ensure the system was optimized for their needs.Outcome:
Within the first year of implementation, Johns Hopkins saw a 20% reduction in patient readmissions. By targeting high-risk patients with personalized follow-up care and interventions, the hospital improved both patient outcomes and operational efficiency. The partnership also reduced administrative burdens on staff by automating patient risk analysis.Mayo Clinic: Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring
Challenge:
The Mayo Clinic sought to expand its reach to rural areas where access to healthcare was limited. However, building new physical facilities was not financially feasible, and there was a need for innovative ways to deliver care remotely.Solution:
Mayo Clinic partnered with third-party telemedicine providers and invested in remote monitoring technologies. These partnerships allowed the clinic to deliver specialized care, such as cardiology and oncology consultations, to patients across the country without the need for them to visit a physical facility. Remote monitoring enabled physicians to track chronic conditions in real-time and intervene when necessary.Outcome:
The Mayo Clinic expanded its patient base by 30% in rural areas, reducing travel time for patients and providing faster access to specialists. The program also led to a significant decrease in hospital admissions and emergency room visits for patients with chronic conditions, such as heart disease and diabetes, which improved both patient outcomes and cost efficiency.Future Trends in Outsourcing and Digital Transformation
As healthcare continues to evolve, several key trends are emerging that will shape the future of outsourcing and digital transformation.
AI-Driven Personalized Medicine
Trend:
Artificial intelligence (AI) will continue to play a pivotal role in personalizing medical treatments. AI will be increasingly used to analyze genetic information, lifestyle data, and clinical histories to tailor medical treatments to the individual patient. This move towards personalized medicine can result in more effective treatments and lower healthcare costs by reducing trial-and-error approaches.Impact on Outsourcing:
AI development requires highly specialized skills, and healthcare organizations will likely outsource AI-powered solutions, including data analysis and AI-driven diagnostic tools, to experts in the field. This approach allows for quicker adoption of cutting-edge AI technologies without significant internal investment.Blockchain for Secure Data Management
Trend:
As concerns about data privacy and security grow, blockchain will become more widely adopted to safeguard patient information. Blockchain offers a decentralized and tamper-proof way to store medical records, ensuring data integrity and protecting against cyberattacks.Impact on Outsourcing:
Managing blockchain systems will likely be outsourced to specialized providers that can ensure HIPAA compliance, security, and scalability. Healthcare organizations can rely on third-party blockchain services to manage patient data securely while reducing the costs associated with in-house IT teams.Expansion of telemedicine and hybrid care models
Trend:
Telemedicine is expected to expand beyond its current scope, evolving into a hybrid care model that integrates virtual and in-person visits seamlessly. This shift will be driven by patient demand for convenience and access to care, especially for chronic disease management and mental health services.Impact on Outsourcing:
Healthcare organizations will increasingly outsource telemedicine platforms to specialized providers to manage the complex infrastructure required for virtual care. This will include outsourcing video conferencing, secure data transmission, and remote monitoring services, allowing healthcare institutions to focus on core care delivery without building these systems in-house.Conclusion
The U.S. healthcare system continues to face rising economic pressures driven by an aging population, rising costs, and workforce shortages. To address these challenges, healthcare providers are turning to outsourcing and digital transformation as key strategies to reduce operational costs while maintaining care quality. Outsourcing administrative, clinical, and IT functions offers immediate cost-saving benefits, while digital transformation enables long-term operational efficiencies through innovations like AI, telemedicine, and predictive analytics.
Together, these strategies represent a comprehensive approach to building a more resilient, flexible, and high-performing healthcare system, equipped to meet the growing demands of patients in the future. By effectively leveraging outsourcing and digital technologies, healthcare institutions can mitigate economic pressures, improve patient outcomes, and ensure the sustainability of care delivery in 2024 and beyond.
- https://www.aha.org/news/headline/2024-05-02-new-aha-report-highlights-mounting-financial-challenges-hospitals
- https://www.ispor.org/heor-resources/more-heor-resources/us-healthcare-system-overview/us-healthcare-system-overview-background-page-1
- https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/healthcare/our-insights/healthcares-next-chapter-whats-ahead-for-the-us-healthcare-industry
- https://usafacts.org/topics/health/
- https://www.skyramtechnologies.com/blog/success-stories-digital-transformation-healthcare-industry-use-cases/
- https://www.bea.gov/data/special-topics/health-care
- https://www.statista.com/outlook/hmo/digital-health/united-states
- https://www.peerbits.com/blog/digital-transformation-in-healthcare.html
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions