- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Technology
- By Omega Team

Human augmentation (HA) focuses on cognitive and physical improvement by adding or expanding (bodily) functions with the help of technological means.
Examples of augmentations include genetic modifications, pacemakers, prosthetics, wearable devices, and chip implants. But there is a difference between a technology tool and a technological augmentation. A laptop would not be considered an augmentation, but a smartphone, and especially a smartwatch, could be considered an augmentation. It lets you have the ability to access any information whenever you want. For a technology to be an augmentation instead of just a tool, it needs to be a persistent and intuitive part of the human experience on a moment-by-moment basis. A tool never becomes a part of your identity, but an augmentation almost surely has to.
Misinterpretation of “Human Augmentation”
There exists a significant overlap between the terms human enhancement, biohacking and transhumanism because it is often used in the same context. But they differ for the following:
Human enhancement. Improving the human body and/or performances. It is used interchangeably with human augmentation but does not require the use of technology. The term human enhancement spans over a greater area. For example, it includes physical enhancements which could be cosmetics (plastic surgery & orthodontics).
Biohacking. The self-improvement of the human body using experimental technologies. Also known as DIY biology — is an extremely broad field that covers a huge range of activities, from performing science experiments on yeast or other organisms to tracking your own sleep and diet to young blood transfusion by pumping a younger person’s blood into your veins with the purpose of fighting aging.
Transhumanism. A speculative philosophical movement which objective is to break through the biological boundaries of the human body. Transhumanists support the emergence and convergence of technologies including nanotechnology, biotechnology, and information technology, as well as hypothetical future technologies like simulated reality, artificial intelligence, superintelligence, chemical brain preservation, and cryonics. They believe that humans should use these technologies to become more than humans.
Categories
Human augmentation can be divided into three divisions depending on how they alter the human ability:
Replication of human ability. Prosthetic limbs for the disabled, hearing aids for the deaf, and voice synthesizers for the mute are examples of human augmentations that restore or replicate typical human abilities. These fall into the category of replication.
Supplementation of human ability. Human augmentations that improve our ability to do something fall under the category of supplementation. This includes devices that artificially increase our strength, enhance our sight beyond normal limits, or increase our intelligence.
Exceeding human ability. Human augmentations that allow us to do things that we cannot do on our own belong to the category of exceeding augmentation. This includes things like the ability to fly, breathe underwater, see ultraviolet or infrared light, and smell chemicals not currently detectable by the human olfactory sense.
Applications of Human Augmentation
Sensory Augmentation: using machine learning to enhance radiologists’ abilities to do more accurate x-ray diagnoses or enhancing my ability to back out of driveways by sensing the garbage cans that are blocking the path.
Real-Time Conversation Translation: the world is more interconnected than ever. People constantly travel for leisure and business. So, being able to plug something in your ear and understand the local people will make a huge difference in how we communicate as humans.
Modern Hearing Aids With iPhone Compatibility: modern units can integrate seamlessly with the iPhone for calls, listening to music and using Siri. With better sound quality, great battery life and smaller form factors, modern hearing aids augment poor hearing and deliver the capability of modern earbuds in popular use.
Exoskeletons For Workplace Safety: exoskeletons assist freight loaders and maintenance workers to lift heavier loads of up to 200 lbs., without fatigue or strain. Emerging technologies like these ensure higher levels of workplace health and safety, as well as the empowerment of workers to be twice as productive.
Brain-Computer Interfaces: This means using technology to directly communicate with other human body parts. For now, it is being used to treat paralysis and to help patients gain mobility. In the future, however, BCI users can connect their bodies directly to the internet or other services.
Commercial opportunities
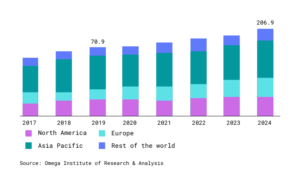
More and more companies and organizations notice the market opportunities of human augmentation. Figure 1 shows the market of human augmentation worldwide.
Figure 1: Human Augmentation Market By Region (USD Billion)
Three examples of commercial applications include:
Gartner
The company publishes a report each year with the 10 most important technology trends. In the 2019 autumn edition, human augmentation had its first occurrence. The researchers even expect a BYOE-policy (‘bring your own device’ policy) to be introduced in IT organizations. Employees are allowed to use their own enhancement at work under BYOE. Expected by Gartner, this will be allowed at 30% of IT organizations by 2023.Kaspersky
Another company to notice the potential of human augmentation is Kaspersky, which is a Russian service provider of anti-virus software and information security. The company Opinium Research performed research in July of 2020 under more than fourteen thousand European inhabitants, including France, Germany, the United Kingdom and the Netherlands.Kaspersky sees the commercial potential of human augmentation. The conclusion from their report accordingly is: ‘We just have started if it comes to human augmentation. The debate about the opportunities and risks arises and will develop in the coming decades.’
Accenture
James Wilson and Paul Daugherty from Accenture in Harvard Business conclude that replacing staff yields profit mostly in the short term. Car manufacturer BMW reported an improvement of 85% productivity after replacing a fully automated process with a team consisting of humans and robots.That is the essence of human augmentation: not to replace humans with robots, but to have machines that expand and improve human possibilities.
Future Outlook
The use of human augmentation can be positive, but some debate the ethical implications of testing on animals and the possibility that neurotech could be used for control, manipulation, or lead to privacy breaches of the society. For HA to be beneficial for us, it first needs to be analyzed and explored very carefully. If that is the case, human augmentations will transform the world and it would be life-changing for those who need it the most. By embracing the power of neurotech and genetic engineering fairly and equitably, people with disabilities and illnesses can dramatically improve their lifestyles. It would allow us to do what we never thought possible, making us much more efficient in the way that we work with machines, and even eliminating weaknesses.
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions