- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Technology
- By Omega Team

Humanoid robots have long captured the imagination of science fiction writers, filmmakers, and technologists alike. From the charming R2-D2 and C-3PO in “Star Wars” to the eerily lifelike replicants in “Blade Runner,” humanoid beings have been a staple of speculative fiction. However, in recent years, advancements in robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) have brought us closer to realizing these once-fantastical creations. Today, humanoid robots are no longer confined to the realm of fiction but are making strides in various fields, from assisting in household chores to aiding in complex surgeries. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of humanoids and explore their evolution, capabilities, and implications for the future.

The Evolution of Humanoids
The concept of humanoid robots dates back centuries, with ancient myths and folklore often featuring mechanical beings crafted by skilled artisans or brought to life by mystical forces. However, it wasn’t until the 20th century that the idea of humanoid robots gained serious attention from scientists and engineers.
One of the earliest attempts at creating a humanoid robot was by the Czech playwright Karel Čapek, who coined the term “robot” in his 1920 play “R.U.R.” (Rossum’s Universal Robots). These robots, though not strictly humanoid in appearance, laid the groundwork for future explorations into creating machines that resembled humans.
In the following decades, researchers made significant strides in robotics technology, culminating in the development of the first true humanoid robot, WABOT-1, in Japan in the early 1970s. Standing at 1.6 meters tall and weighing 220 pounds, WABOT-1 could walk, grip objects with its hands, and even communicate in Japanese using a synthesizer.
Since then, humanoid robotics has continued to progress rapidly, with researchers around the world pushing the boundaries of what these machines can achieve. Today, humanoid robots come in various shapes and sizes, ranging from small, human-like assistants to larger, more advanced models capable of performing complex tasks.
Capabilities of Humanoid Robots
Modern humanoid robots are equipped with a wide range of sensors, actuators, and AI algorithms that enable them to interact with their environment and perform tasks with remarkable dexterity and intelligence. Some of the key capabilities of humanoid robots include:
- Locomotion: Many humanoid robots are capable of walking, running, and even climbing stairs, thanks to advanced motion control algorithms and sophisticated leg mechanisms.
- Manipulation: With articulated limbs and precision grippers, humanoid robots can manipulate objects with a level of dexterity approaching that of a human hand. This makes them ideal for tasks such as assembling products on an assembly line or performing delicate surgical procedures.
- Communication: Humanoid robots are equipped with speech recognition and synthesis capabilities, allowing them to understand and respond to verbal commands. Some models are also equipped with expressive facial features that enable them to convey emotions through facial expressions.
- Learning and Adaptation: Through machine learning algorithms, humanoid robots can learn from experience and adapt their behavior to new situations. This enables them to perform a wide range of tasks autonomously, from navigating unfamiliar environments to interacting with humans in naturalistic ways.
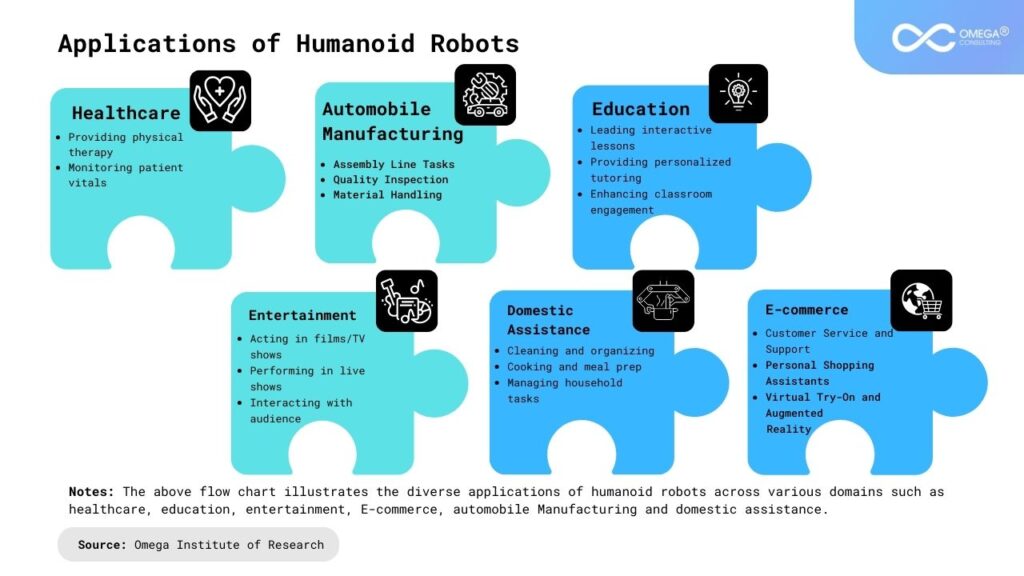
Applications of Humanoid Robots
The versatility and adaptability of humanoid robots make them well-suited for a wide range of applications across various industries. Some of the most promising areas where humanoid robots are making an impact include:
- Healthcare: Humanoid robots are being used to assist healthcare professionals in tasks such as patient care, rehabilitation therapy, and medical imaging. Their ability to perform repetitive tasks with precision and consistency makes them valuable assets in healthcare settings.
- Education: In classrooms and educational settings, humanoid robots are being used to engage students in interactive learning experiences. These robots can serve as tutors, mentors, or companions, providing personalized instruction and support to learners of all ages.
- Entertainment: From theme parks to movie sets, humanoid robots are becoming increasingly common in the entertainment industry. These robots can entertain audiences with their lifelike movements and interactions, adding an extra element of excitement to live performances and attractions.
- Domestic Assistance: In the home, humanoid robots are being developed to assist with household chores such as cooking, cleaning, and caregiving. These robots can help elderly or disabled individuals maintain their independence and quality of life by assisting with everyday tasks.
- Automobile manufacturing: Humanoid robots streamline automobile manufacturing by performing assembly tasks, conducting quality control inspections, and optimizing material handling and logistics. They enhance efficiency, accuracy, and productivity throughout the production process.
- E-commerce: Automate warehouse tasks like order fulfilment, optimize customer service with personalized assistance, and explore last-mile delivery options, offering efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Advancements in Humanoid Robotics: Overcoming Challenges through AI Integration
Despite decades of research and development, the field of humanoid robotics still grapples with numerous challenges. Chief among these hurdles is the quest to develop a seamless fusion of physical structure and software programming that enables efficient bipedal locomotion. Presently, humanoid robots often struggle with slow walking speeds and difficulty adapting to new environments. To address this, advanced simulation software is employed, creating virtual models that integrate with AI algorithms like Reinforcement Learning. This approach, akin to how children learn to walk through trial and error, allows humanoid robots to refine their gait patterns over time, optimizing efficiency. Additionally, Deep Neural Networks play a pivotal role in humanoid robotics, equipping robots with the ability to perceive and understand their surroundings. Through AI algorithms in Neural Networks and Natural Language Processing, robots can interpret visual and audio data, further enhancing their interaction capabilities. Ongoing research focuses on optimizing these algorithms to improve speed and accuracy, signaling promising advancements in the field.
The Future of Humanoid Robotics
As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of humanoid robots will only continue to grow. Future generations of humanoid robots may possess even greater autonomy, intelligence, and adaptability, enabling them to perform a wider range of tasks in a variety of environments.
However, along with the potential benefits of humanoid robotics come ethical and societal considerations that must be addressed. Questions surrounding job displacement, privacy, and the ethical treatment of robots are becoming increasingly important as humanoid robots become more integrated into our daily lives.
Ultimately, the future of humanoid robotics holds immense promise for improving our quality of life and advancing human-robot interaction in ways we can only imagine. By continuing to push the boundaries of technology and exploring the ethical implications of our creations, we can ensure that humanoid robots remain a force for good in the world.

Conclusion
Humanoid robots have transitioned from the realm of science fiction to become a tangible reality with the potential to revolutionize numerous industries and aspects of everyday life. With their advanced capabilities and versatility, humanoid robots are poised to play a significant role in shaping the future of technology and human-robot interaction. As we continue to explore the possibilities of this exciting field, it’s essential to approach the development and deployment of humanoid robots with careful consideration for the ethical, societal, and philosophical implications they entail.
Download the extended Humanoid Report
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/computer-science/humanoid-robots
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/cognitiveworld/2019/02/25/artificial-intelligence-in-humanoid-robots/?sh=5212d35224c7
- https://spectrum.ieee.org/humanoid-robots
- https://www.packworld.com/machinery/robotics/article/22880432/humanoid-robots-and-the-ai-that-drives-them
- https://www.voanews.com/a/do-we-really-need-humanoid-robots-/7342666.html
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions