- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Technology
- By Omega Team

In the tech-driven business landscape, CIOs and CTOs wield significant influence as they navigate through diverse data management options. Cloud computing, a transformative force, places these leaders at the forefront of choosing the ideal cloud model. Amid the considerations of public, private, and hybrid clouds, the latter holds special relevance. Hybrid cloud solutions, blending public and private attributes, align seamlessly with the strategic goals of tech leaders. CIOs and CTOs, charged with optimizing IT infrastructure, find in hybrid clouds a compelling solution for scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. This article explores how hybrid clouds, with their agility, security assurances, cost optimization, and robust disaster recovery capabilities, become indispensable tools in the arsenal of technology executives.
Decoding Cloud Computing Models
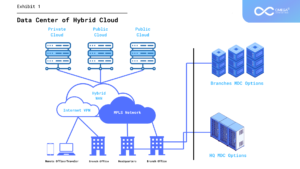
Public Cloud: Public clouds, home to industry giants like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, open their doors to the vast internet landscape. Understanding the allure of scalability, cost-effectiveness, and the convenience of outsourcing infrastructure management is the foundational step.
The Rise of Hybrid Cloud
As businesses ascend the cloud hierarchy, the unique ascent of hybrid clouds becomes apparent, addressing concerns that surface in the ever-shifting business landscape.
Flexibility and Scalability: Flexibility is the heartbeat of hybrid clouds. Organizations can scale seamlessly, harnessing the power of public clouds during peaks while safeguarding sensitive data and crucial workloads in a private realm. This symphony of adaptability ensures peak performance without compromising security.
Data Security and Compliance: In hybrid clouds, data security and compliance emerge as stalwart guardians. Sensitive information finds refuge on-premises or within private clouds, ensuring adherence to industry regulations. Public clouds then become allies, reserved for less sensitive operations, striking a balance between security and efficiency.
Cost Optimization: Economic considerations are the architects of business decisions. Hybrid clouds, with their strategic balance, allow organizations to dance between capital and operational expenses. The cost advantages of public clouds are harnessed for non-sensitive workloads, while the ongoing expenses of maintaining a private infrastructure are avoided.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: In the unpredictable theater of business, disaster recovery, and business continuity take center stage. Hybrid clouds, with their robust framework, offer a script for backup and recovery. Critical data finds a sanctuary in the public cloud, ensuring continuity in the face of on-premises disasters.
The concept of businesses ascending the cloud hierarchy and leveraging hybrid clouds to address specific concerns is well-captured. Below are specific points in each section:
Enterprises with Varied Workloads:
-
Data-Intensive Industries: Sectors dealing with large volumes of data, such as finance, healthcare, and research, leverage hybrid clouds to manage sensitive information on-premises or within private clouds while utilizing the scalability of public clouds for data processing and analytics.
-
E-Commerce Giants: Companies in the e-commerce sector often rely on hybrid clouds to balance the scalability required during peak periods, like sales events, while securing customer data and transactions in a private cloud or on-premises.
Regulated Industries:
-
Finance and Banking: Highly regulated industries, like finance and banking, prioritize data security and compliance. Hybrid cloud solutions enable these businesses to maintain control over critical financial data while optimizing operational costs through the use of public clouds for less sensitive operations.
-
Healthcare Providers: Healthcare organizations, dealing with sensitive patient data and stringent compliance requirements, find hybrid clouds beneficial. They can store patient records securely in a private cloud or on-premises, ensuring compliance, while utilizing public clouds for non-sensitive tasks.
Scalability-Driven Businesses:
-
Tech Startups: Scalability is often a key consideration for tech startups that experience rapid growth. Hybrid clouds allow these businesses to scale seamlessly during high-demand periods without compromising on data security.
-
Media and Entertainment: Industries dealing with variable workloads, like media and entertainment, benefit from the adaptability of hybrid clouds. They can handle content distribution using public clouds while securing intellectual property and sensitive data in a private environment.
Hybrid Cloud Adoption
Hybrid Cloud Adoption Trends:
-
Industry-Specific Adoption Patterns: Analyze how different industries are adopting hybrid clouds. Identify patterns, challenges, and successes in sectors such as healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and more.
-
Geographical Variations: Explore how hybrid cloud adoption varies across different regions and countries. Consider regulatory differences, infrastructure maturity, and cultural factors influencing adoption.
-
Size of Organizations: Investigate whether the adoption of hybrid clouds differs based on the size of organizations. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) might have different adoption challenges compared to large enterprises.
Hybrid Cloud Performance Metrics:
-
Benchmarking Performance: Establish performance benchmarks for organizations adopting hybrid clouds. Compare factors like application response times, data transfer speeds, and overall IT efficiency between hybrid and other cloud models.
-
Scalability Analysis: Assess how effectively organizations can scale their operations using hybrid clouds. Analyze case studies to understand the scalability limitations and successes in different scenarios.
Challenges and Considerations
While the allure of the hybrid cloud model is undeniable, challenges lurk in uncharted territories, demanding organizations to fortify their strategies with refined precision.
1. Integration Complexity
The integration of public and private cloud environments introduces complexities that require astute navigation. A carefully devised integration strategy becomes the compass, ensuring the seamless flow of data and optimal application performance across diverse cloud landscapes.
2. Data Transfer Costs
The movement of data between public and private clouds may incur costs, becoming a crucial aspect of the economic calculus. Organizations must master the art of optimizing data transfer strategies, unraveling the intricacies of provider pricing models to manage these costs and maximize operational efficiency effectively.
3. Skilled Personnel
The operational demands of a hybrid cloud environment necessitate a skilled workforce proficient in navigating both public and private cloud infrastructures. Investments in training and recruitment become imperatives, ensuring organizations can extract maximum value from their hybrid cloud investments.
Conclusion
In the intricate and dynamic world of cloud computing, the choice between public, private, and hybrid clouds emerges as a linchpin decision for businesses navigating the digital landscape. While each cloud model boasts its merits, the hybrid cloud stands as a testament to versatility and strategic brilliance. Its unique ability to seamlessly integrate the best attributes of both public and private clouds positions it as the cornerstone for modern enterprises, providing a resilient foundation for scalability, security, and cost optimization.
As technology advances, businesses stand at the precipice of unprecedented possibilities, and the hybrid cloud model beckons as a gateway to innovation and progress. It is not merely a choice in technology but a strategic symphony that unlocks new dimensions of potential and propels industries toward a future defined by continuous innovation and unparalleled efficiency.
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions

