- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Retail
- By Omega Team
The retail industry is experiencing dramatic upheaval, driven by technologies like automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and e-commerce platforms. These innovations, while improving efficiency and customer experience, are fundamentally reshaping the workforce. This article explores the causes and consequences of job disruption in retail and offers strategies for adapting to this rapidly changing environment. From cashier-less checkout systems to algorithm-driven inventory management, the traditional roles of retail workers are being redefined. Companies are increasingly relying on data analytics to make real-time decisions, reducing the need for manual intervention. As a result, employees must now acquire new digital skills to stay relevant in a tech-first retail landscape.
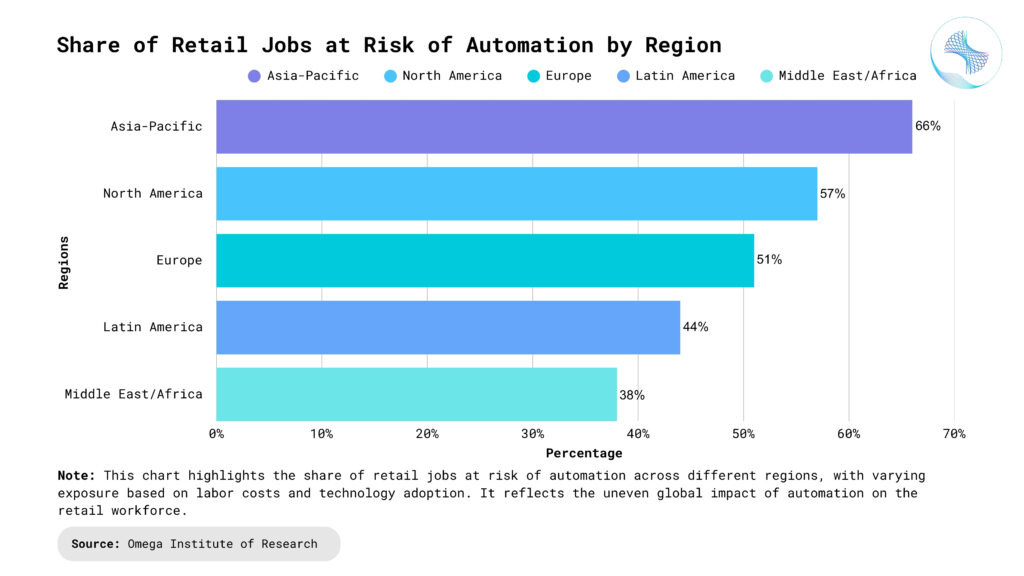
What’s Fueling Job Disruption in Retail
Rise of E-Commerce: Online shopping platforms have revolutionized consumer purchasing habits by offering convenience, speed, and personalized experiences. As a result, traditional stores are losing foot traffic and struggling to justify their operational costs. Retailers that fail to invest in digital channels are increasingly shutting down locations or reducing staff. Additionally, mobile shopping apps and AI-powered recommendation engines are drawing customers away from in-person retail. The shift to e-commerce means fewer opportunities for in-store roles and a growing need for digital infrastructure support.
Automation and Self-Service Technologies: Retailers are replacing traditional checkout counters with self-service kiosks and mobile payment systems to streamline transactions. Robots and inventory-scanning machines now assist with shelf stocking, pricing, and auditing. This trend minimizes the need for human intervention in many front-line and back-end retail processes. Automation reduces errors, increases efficiency, and lowers labor costs—but also displaces entry-level workers. The transition requires fewer staff on the floor and more technical support personnel behind the scenes.
AI and Data-Driven Personalization: AI is enabling retailers to offer hyper-personalized experiences, from product recommendations to dynamic pricing strategies. These capabilities allow businesses to respond instantly to customer behavior and preferences. However, they reduce the need for human decision-making in marketing, merchandising, and customer support. Sophisticated algorithms can now handle complex decisions that once required human input, accelerating a shift toward data-driven automation. The growing reliance on machine learning systems limits creative autonomy in traditional roles.
Supply Chain Digitization: Retailers are digitizing supply chains using IoT sensors, AI, and robotics to improve logistics efficiency and reduce waste. Smart warehouses can now operate with minimal human oversight, handling inventory, packing, and distribution tasks. This evolution threatens the job security of many warehouse and transportation workers. Automated systems also enable real-time tracking and predictive maintenance, which further reduces the demand for manual monitoring. The optimization of supply chains prioritizes machine precision over human labor.
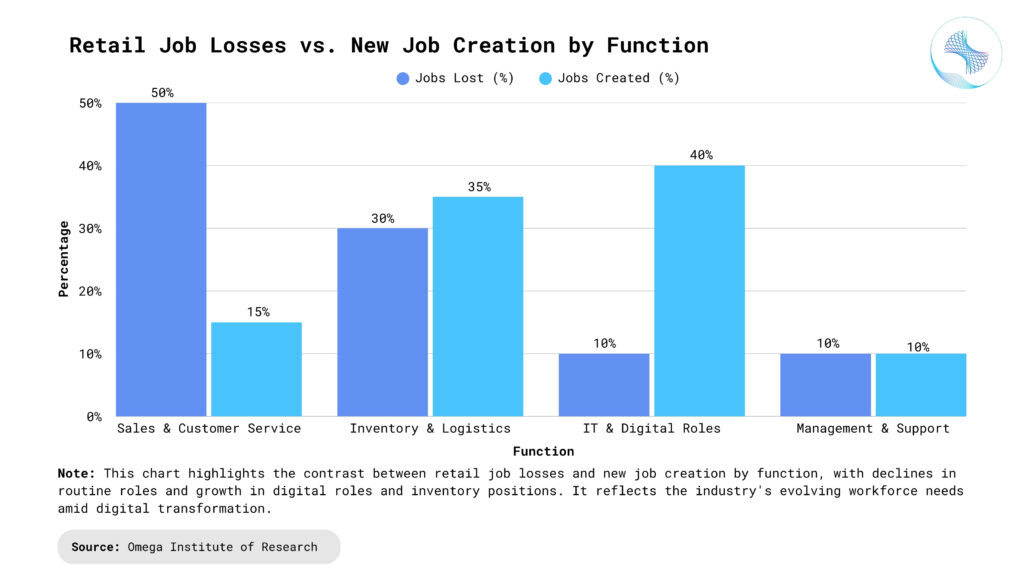
How Technology is Reshaping Roles in Retail
Cashiers and Sales Clerks: Self-checkout machines and mobile point-of-sale systems have significantly reduced the demand for cashiers. In addition, many consumers now shop online, eliminating the need for in-store assistance. As these technologies advance, customer-facing roles are diminishing in number and importance. Retailers increasingly deploy contactless payment and QR code scanners, allowing one employee to oversee multiple self-checkout points. The reduced need for interpersonal service impacts both full-time positions and casual employment.
Stockroom and Inventory Workers: Automated inventory systems and RFID technology streamline stock management and reduce manual labor. Robots now scan shelves, move goods, and even restock items in some advanced facilities. These developments directly impact the need for human workers in logistics and stockroom environments. Fewer workers are required to perform repetitive stocking and sorting tasks, particularly in large-scale retail chains and warehouses. Predictive stock forecasting further reduces reliance on human judgment in supply planning.
Customer Service Representatives: Chatbots and virtual assistants handle basic customer queries 24/7 across websites, social media, and messaging apps. With advancements in natural language processing, these AI tools are increasingly able to resolve issues that once required human support. As a result, traditional customer service roles are being downsized or offshored. AI systems can now detect sentiment, adjust tone, and escalate only the most complex issues to human agents. The shift toward digital interaction reduces the number of available call center and help desk positions.
Store Managers: Automation tools and centralized management systems allow regional teams to oversee multiple locations with fewer personnel. Store managers are now expected to monitor performance dashboards and implement system-generated recommendations. Their roles are shifting away from people management toward operational oversight and data interpretation. Managers must be data-literate and tech-savvy to lead teams in environments where technology dictates performance metrics. This evolution redefines leadership, emphasizing systems thinking over traditional managerial experience.
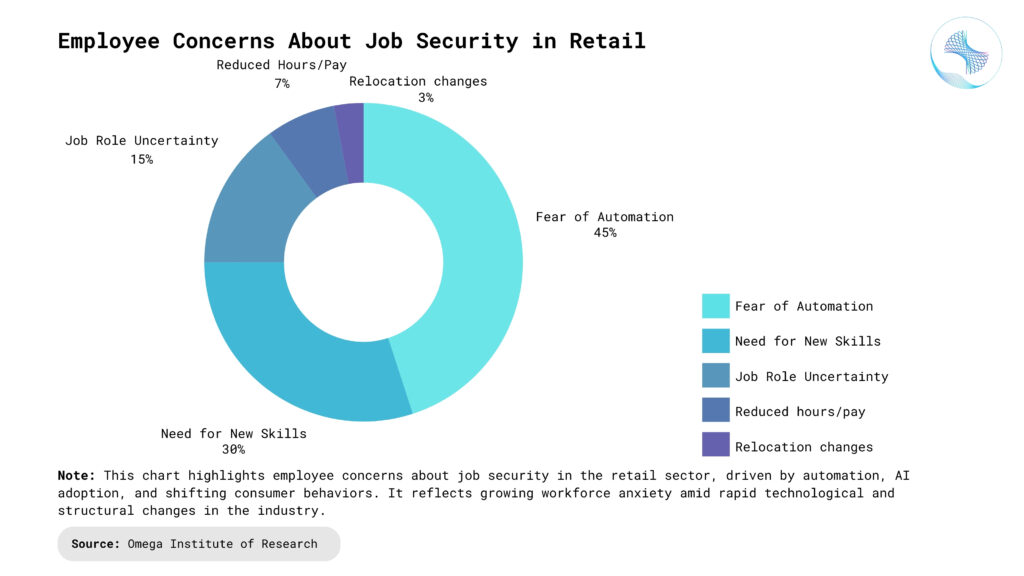
The Human Toll of Job Disruption in Retail
Low-Income Workers: Retail jobs have historically served as a lifeline for individuals without higher education or formal training. As automation replaces these entry-level roles, vulnerable populations face increased unemployment and economic hardship. Without intervention, this trend may exacerbate social inequality and widen the wealth gap. Communities that rely on retail for accessible employment may struggle with rising poverty and limited upward mobility. This disruption highlights the urgent need for inclusive economic policies and accessible education.
Urban and Rural Divide: Urban centers benefit from infrastructure, reskilling opportunities, and proximity to tech-driven jobs, while rural areas often lack these advantages. Retail closures in smaller towns can lead to a domino effect on local economies. This creates geographic disparities in employment and access to essential services. Rural communities may experience population decline as young workers migrate to cities in search of jobs. Revitalization efforts must prioritize rural digital inclusion and local business support to address this imbalance.
Skill Polarization: Technology is driving a wedge between high-skill and low-skill roles, erasing many middle-skill jobs that once offered career mobility. The workforce is becoming increasingly bifurcated, with demand rising for both highly specialized technical experts and low-wage service workers. This polarization makes it harder for displaced retail employees to transition into sustainable careers. Without targeted retraining programs, many workers risk falling into long-term unemployment or underemployment. Bridging the skill gap will be essential for maintaining social cohesion and economic stability.
The Skills Gap Crisis in Retail
Digital Retail and Tech-Driven Roles: As traditional roles decline, new job categories are emerging in areas like e-commerce, UX design, and digital marketing. These roles require creativity, data literacy, and digital proficiency—skills that can be learned with targeted training. Retailers must invest in workforce development to fill these growing skill gaps. Career pathways are also expanding in fields such as online customer experience, logistics tech, and platform engineering. Organizations that foster digital talent internally can better adapt to shifting industry demands.
Hybrid Retail Models: Models like BOPIS (Buy Online, Pick Up In Store), “click-and-collect,” and virtual showrooms blend digital and physical experiences. These innovations create demand for employees who can manage both online platforms and in-store customer interactions. Hybrid roles reward flexibility and tech-savvy customer service. Employees in these models must juggle digital tools, real-time inventory systems, and face-to-face engagement. This hybridization supports a more personalized customer journey while offering new professional avenues for retail staff.
Customer Experience Specialists: With routine tasks automated, the human touch becomes a key differentiator in retail environments. Specialists in customer engagement, in-store experiences, and brand storytelling are in higher demand. These roles rely on emotional intelligence, creativity, and soft skills—traits machines struggle to replicate. Personal shoppers, brand ambassadors, and community managers will play pivotal roles in creating memorable retail experiences. Companies that prioritize these roles foster brand loyalty and human connection in increasingly digital spaces.
The Upskilling Cure for Job Disruption
Reskilling and Upskilling: Continuous learning is essential for helping workers transition into emerging roles across digital and hybrid retail environments. Training programs should focus on digital tools, customer analytics, cybersecurity, and supply chain tech. Employers, governments, and educational institutions must collaborate to make these programs accessible. Programs should be tailored to meet the specific needs of frontline workers, with micro-credentials and flexible learning paths. Building digital confidence and soft skills is equally important to ensure workers can thrive in tech-augmented retail roles.
Flexible Workforce Planning: Retailers can adapt by adopting agile workforce models that rely on part-time, freelance, and cross-functional staff. Scheduling and shift management platforms make it easier to build adaptable teams. Flexibility benefits both employees and employers by increasing resilience in a volatile market. These models also allow companies to scale operations quickly during seasonal peaks or demand fluctuations. For workers, flexible scheduling provides better work-life balance, which can improve retention and job satisfaction.
Human-Centered Automation: Instead of replacing workers entirely, companies can design technology that enhances human performance. For example, AI tools can assist store associates in recommending products or analyzing customer data. This approach improves efficiency while preserving meaningful employment. By integrating automation with human intuition and emotional intelligence, retailers can create superior customer experiences. Empowered employees become more productive and engaged when technology supports rather than threatens their roles.
Policy and Social Support: Governments must develop inclusive policies that support displaced workers through unemployment benefits, training subsidies, and wage protection. Social safety nets must evolve to reflect the realities of a gig and automated economy. Without intervention, retail job losses could trigger long-term socioeconomic consequences. Public-private partnerships can help create regional training hubs, promote digital inclusion, and fund innovation in workforce transition programs. Stronger protections for gig and contract workers are also essential as non-traditional employment becomes more common in retail.
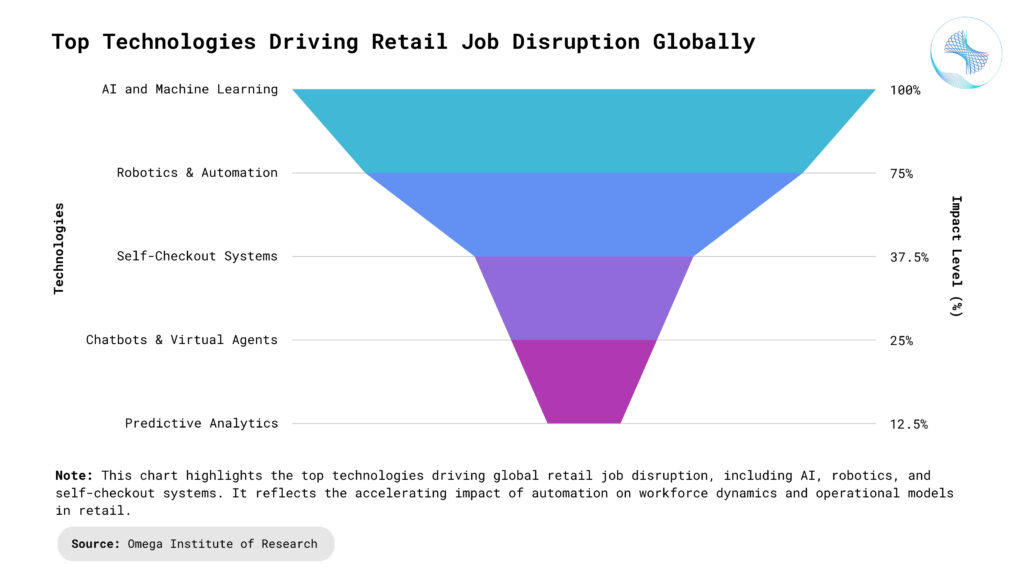
Retail’s New Job Landscape
Tech-Savvy Professionals: Tomorrow’s retail professionals will need to understand data, automation, and digital commerce strategies. Roles in digital merchandising, AI ethics, and omnichannel retail will expand. Companies will seek out employees who can navigate both technological systems and business environments. They must be comfortable working with dashboards, analytics tools, and customer behavior data to drive strategic decisions. As retail increasingly converges with tech, these professionals will bridge the gap between IT and in-store operations, ensuring seamless customer experiences.
Creative Content Creators and Influencers: Retail is increasingly intertwined with entertainment, branding, and social media. Influencers, livestream hosts, and content marketers will shape product discovery and customer engagement. These roles combine storytelling, community building, and real-time interaction. They play a crucial role in driving impulse purchases and fostering brand loyalty through visual, interactive, and immersive content.
Supply Chain and Logistics Coordinators: As back-end systems become more complex and tech-driven, skilled coordinators are needed to manage AI, drones, and automated distribution centers. These jobs involve real-time decision-making, process optimization, and tech integration. Workers will need both logistical expertise and digital fluency. The growing focus on same-day delivery and sustainable logistics adds new layers of complexity to supply chain roles.
Customer Experience and Personalization Specialists: As retail becomes more customer-centric, the demand for professionals who can deliver personalized, memorable shopping experiences will soar. These specialists will leverage advanced CRM systems, AI-driven recommendation engines, and real-time customer feedback to tailor interactions across both digital and physical touchpoints.
Conclusion
The retail industry is not dying, it’s transforming. Automation and e-commerce are redefining what work looks like in this space, challenging outdated roles and creating new possibilities. By embracing reskilling, investing in people, and humanizing automation, we can ensure that the future of retail remains inclusive, sustainable, and filled with opportunity. This transformation requires coordinated efforts from retailers, workers, governments, and educators. Together, we can shape a retail workforce ready for the digital era resilient, empowered, and future-proof. Lifelong learning, flexible career pathways, and supportive workplace policies will play a critical role. Only by aligning innovation with human values can we truly unlock the potential of retail’s next chapter.
- https://www.netsuite.com/portal/resource/articles/erp/retail-industry-challenges.shtml
- https://www.businessinsider.com/retail-technology-players-changing-shopping-trends-2022-6
- https://draup.com/talent/whitepapers/how-reskilling-the-retail-industry-talent-can-address-workforce-disruption/
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/how-generative-ai-transforming-future-retail-jill-puleri-standish-v9l4e/
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions