- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Technology
- By Omega Team

In today’s dynamic and competitive business environment, measuring success is paramount for organizations to track progress, make informed decisions, and drive performance improvement. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and metrics serve as essential tools for quantifying and evaluating performance against strategic objectives. This article explores the intricacies of measuring success with KPIs and metrics, delving into fundamental principles, frameworks, benefits, challenges, and the pivotal role of management in optimizing performance measurement processes.
Understanding of Measuring Success with KPIs and Metrics
KPIs and metrics are quantifiable measures used to assess performance and progress toward organizational goals and objectives. While KPIs are specific indicators directly linked to strategic objectives, metrics encompass a broader range of performance measures that provide insights into various aspects of organizational performance. Effective performance measurement requires a clear understanding of organizational objectives, alignment with strategic priorities, and the identification of relevant KPIs and metrics tailored to specific business processes and functions.
Key Principles
Several key principles underpin the effective use of KPIs and metrics:
Alignment with Strategic Objectives:
KPIs and metrics must align closely with the organization’s strategic objectives and overarching goals. They serve as compass points guiding organizational efforts toward desired outcomes. Alignment ensures that performance measurement efforts are purposeful and directly contribute to the achievement of strategic priorities.
If an organization’s strategic objective is to increase customer satisfaction, relevant KPIs might include metrics such as Net Promoter Score (NPS), customer retention rate, and customer feedback ratings. These KPIs directly reflect the organization’s strategic focus on enhancing customer experience and loyalty.
Relevance and Specificity:
KPIs and metrics should be relevant to the organization’s goals and objectives, measurable, and actionable. They should provide specific insights into performance and enable informed decision-making at all levels of the organization.
A relevant KPI should reflect a critical aspect of organizational performance and be directly tied to strategic objectives. For example, in a manufacturing company aiming to reduce production costs, a relevant KPI could be the ratio of production costs to revenue. This metric provides a specific measure of cost efficiency and enables the organization to track progress toward its cost reduction goals.
Clarity and Consistency:
Clear and consistent definition of KPIs and metrics is essential to ensure common understanding and alignment across the organization. Clear definitions prevent ambiguity and confusion, enabling stakeholders to interpret and use performance data effectively.
Organizations should establish clear definitions and methodologies for calculating KPIs and metrics to ensure consistency and reliability of performance data. For example, if a company measures employee productivity using a metric such as output per hour worked, it should clearly define how output and working hours are quantified to avoid discrepancies in measurement.
Continuous Improvement:
Performance measurement is an iterative process that requires ongoing review, refinement, and improvement. Organizations should regularly evaluate the relevance, effectiveness, and impact of KPIs and metrics and adjust them as needed to reflect changing priorities and circumstances.
Continuous improvement involves soliciting feedback from stakeholders, monitoring changes in the business environment, and adapting performance measurement practices accordingly. For instance, if market conditions shift, an organization may need to revise its sales targets or update its customer satisfaction metrics to reflect evolving customer preferences and expectations.
By adhering to these key principles, organizations can develop a robust framework for performance measurement that drives strategic alignment, fosters accountability, and facilitates continuous improvement.
Frameworks & Practices
Numerous frameworks and best practices guide organizations in the development and implementation of KPIs and metrics:
SMART Criteria:
The SMART criteria provide a structured framework for setting meaningful and effective KPIs. SMART stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. KPIs should meet each of these criteria to ensure they are well-defined and actionable.
- Specific: KPIs should clearly define what is being measured and the desired outcome.
- Measurable: KPIs should be quantifiable and measurable to track progress accurately.
- Achievable: KPIs should be attainable within the organization’s resources and capabilities.
- Relevant: KPIs should directly contribute to organizational goals and strategic objectives.
- Time-bound: KPIs should have a defined timeframe or deadline for achievement.
- For example, if an organization aims to improve employee productivity, a SMART KPI could be “Increase average sales per employee by 10% within the next quarter.” This KPI is specific (average sales per employee), measurable (10% increase), achievable (within the next quarter), relevant (contributes to productivity improvement), and time-bound (quarterly target).
Balanced Scorecard (BSC):
The Balanced Scorecard is a strategic management framework that translates an organization’s vision and strategy into a comprehensive set of KPIs across four perspectives: Financial, Customer, Internal Processes, and Learning and Growth. The BSC provides a balanced view of organizational performance and helps align KPIs with strategic objectives.
- Financial Perspective: KPIs related to financial performance, such as revenue growth, profitability, and return on investment (ROI).
- Customer Perspective: KPIs related to customer satisfaction, loyalty, retention, and market share.
- Internal Processes Perspective: KPIs related to operational efficiency, quality, innovation, and process improvement.
- Learning and Growth Perspective: KPIs related to employee training, development, engagement, and organizational culture.
- By using the Balanced Scorecard framework, organizations can ensure that KPIs are balanced across different aspects of performance and aligned with strategic priorities, enabling a holistic view of organizational success.
Benchmarking:
Benchmarking involves comparing an organization’s performance against industry peers, competitors, or best practices to identify areas for improvement and set performance targets. Benchmarking KPIs against external benchmarks helps organizations gauge their relative performance and identify opportunities for enhancement.
- Internal Benchmarking: Comparing performance across different departments or divisions within the organization
- Competitive Benchmarking: Comparing performance against direct competitors or industry peers.
- Best Practice Benchmarking: Identifying and adopting best practices from industry leaders or top-performing organizations.
- For example, if a retail company wants to improve its customer service performance, it may benchmark its KPIs such as average response time, customer satisfaction scores, and resolution rates against industry benchmarks or top-performing competitors to identify areas for improvement and set performance targets accordingly.
Data-driven Decision Making:
Data-driven decision-making involves using data and analytics to inform strategic decisions and optimize performance. Organizations can leverage advanced analytics techniques, such as predictive modeling, machine learning, and data visualization, to analyze performance data, identify trends and patterns, and make data-driven decisions based on insights derived from KPIs and metrics.
- Predictive Analytics: Using historical data to forecast future trends and outcomes, enabling proactive decision-making and strategic planning.
- Machine Learning: Leveraging algorithms to analyze large volumes of data, identify patterns, and make predictions or recommendations based on KPIs and performance metrics.
- Data Visualization: Using graphical representations such as charts, graphs, and dashboards to visualize performance data and communicate insights effectively to stakeholders.
- By adopting a data-driven approach to decision-making, organizations can optimize performance, identify opportunities for improvement, and drive strategic initiatives based on objective insights derived from KPIs and metrics.
- By incorporating these frameworks and practices into their performance measurement processes, organizations can develop robust, well-defined KPIs and metrics that drive strategic alignment, foster accountability, and facilitate continuous improvement across all levels of the organization.
Benefits of KPIs and metrics
The benefits of measuring success with Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and metrics underscores the importance of these tools in driving organizational performance and achieving strategic objectives:
Performance Transparency:
- KPIs and metrics provide transparency into organizational performance, enabling stakeholders at all levels to assess progress towards strategic objectives and make informed decisions. Transparency fosters trust and accountability within the organization, as stakeholders have access to objective performance data that allows for meaningful discussions and actions.
- For example, transparently sharing KPIs related to sales revenue, customer satisfaction, and employee productivity allows stakeholders to understand the organization’s performance in key areas and identify opportunities for improvement or celebration of success.
Performance Accountability:
- KPIs and metrics create accountability by establishing clear performance expectations, tracking progress, and holding individuals and teams accountable for results. When employees are aware of their performance targets and how they contribute to organizational goals, they are more motivated to achieve and exceed expectations.
- By linking individual and team objectives to specific KPIs, organizations can create a culture of accountability where employees take ownership of their performance and work collaboratively towards shared goals.
Performance Improvement:
- KPIs and metrics facilitate performance improvement by identifying areas of strength and weakness, guiding resource allocation, and informing strategic initiatives and process improvements. By regularly monitoring performance data and analyzing trends, organizations can identify opportunities for optimization and implement targeted interventions to drive performance improvement.
- For instance, if a KPI reveals a decline in customer satisfaction scores, the organization can conduct root cause analysis to identify the underlying issues and implement corrective actions, such as training programs for customer service staff or process improvements in complaint resolution.
Strategic Alignment:
- KPIs and metrics help align individual and team goals with organizational objectives, ensuring that efforts are focused on activities that drive value and contribute to overall business success. By cascading KPIs throughout the organization, from top-level strategic goals to departmental and individual objectives, organizations ensure alignment and coherence in performance measurement efforts.
- When employees understand how their individual performance contributes to broader organizational goals, they are more engaged and motivated to achieve success. Strategic alignment ensures that everyone is working towards a common purpose, maximizing the organization’s collective impact.
Informed Decision-Making:
- KPIs and metrics provide leaders and decision-makers with data-driven insights that support informed decision-making. By analyzing performance data and trends, decision-makers can identify emerging opportunities, anticipate challenges, and make evidence-based decisions that drive organizational success.
- For example, if a KPI indicates a decline in product quality, decision-makers can allocate resources to quality improvement initiatives, adjust production processes, or invest in employee training to address the issue proactively, thereby minimizing the impact on customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
- By leveraging the benefits of KPIs and metrics, organizations can enhance performance, foster a culture of accountability and continuous improvement, and achieve greater alignment with strategic objectives. Ultimately, KPIs and metrics serve as invaluable tools for driving organizational success in an increasingly competitive and dynamic business environment.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their benefits, measuring success with KPIs and metrics presents several challenges and considerations:
Data Quality and Availability:
- One of the primary challenges organizations encounter is ensuring the quality and availability of data used to measure KPIs and metrics. Inaccurate, incomplete, or unreliable data can lead to misleading performance insights and flawed decision-making. Additionally, data may be scattered across disparate systems or departments, making it challenging to aggregate and analyze effectively.
- Organizations must invest in data governance processes, data validation procedures, and data integration technologies to ensure data accuracy, consistency, and accessibility. By establishing data quality standards and protocols, organizations can mitigate the risk of relying on unreliable data for performance measurement.
Complexity and Overload:
- Organizations may struggle with selecting the right KPIs and metrics and avoiding measurement overload. Too many KPIs can overwhelm stakeholders, dilute focus, and obscure critical performance insights, while insufficient KPIs may fail to provide a comprehensive view of organizational performance.
- To address this challenge, organizations should prioritize KPIs that align closely with strategic objectives and provide actionable insights. They should also strike a balance between leading and lagging indicators, focusing on both short-term operational performance and long-term strategic goals. Regular reviews and refinements of KPI portfolios can help streamline measurement efforts and ensure relevance and effectiveness.
Subjectivity and Bias:
- KPIs and metrics may be subject to interpretation and bias, particularly when they involve subjective measures or qualitative data. Biases in data collection, analysis, or interpretation can distort performance insights and undermine the validity of decision-making processes.
- Organizations must be vigilant in identifying and mitigating biases in performance measurement. This may involve establishing objective criteria and benchmarks for measuring performance, conducting sensitivity analyses to assess the impact of different assumptions or methodologies, and fostering a culture of transparency and accountability in performance reporting.
Resistance to Change:
- Implementing KPIs and metrics may face resistance from employees who perceive them as intrusive, punitive, or threatening to autonomy. Resistance to change can impede adoption and acceptance of performance measurement initiatives, undermining their effectiveness and value.
- Organizations should communicate the purpose and benefits of performance measurement transparently and involve employees in the development and implementation process. By soliciting feedback, addressing concerns, and emphasizing the positive impact of performance measurement on individual and organizational success, organizations can overcome resistance and foster buy-in and ownership among employees.
Cost and Resource Constraints:
- Developing and maintaining robust performance measurement systems requires significant investments in technology, talent, and resources. Organizations with limited budgets or competing priorities may struggle to allocate sufficient resources to performance measurement initiatives, compromising their effectiveness and sustainability.
- Organizations must carefully assess their resource requirements and prioritize investments in performance measurement based on anticipated benefits and strategic importance. Leveraging scalable technologies, outsourcing non-core functions, and fostering cross-functional collaboration can help organizations optimize resource allocation and maximize the value of performance measurement efforts.
- By addressing these challenges proactively and implementing best practices in performance measurement, organizations can overcome obstacles and unlock the full potential of KPIs and metrics to drive strategic alignment, foster accountability, and achieve organizational success.
Perspective & Role of Omega Consulting
Omega Consulting plays a crucial role in helping organizations overcome challenges and maximize the benefits of measuring success with Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and metrics. Here’s how Omega Consulting contributes to optimizing performance measurement processes:
Strategy Alignment:
Omega Consulting assists organizations in aligning KPIs and metrics with strategic objectives, ensuring that performance measurement efforts are closely tied to overall business goals and priorities. By conducting strategic assessments and stakeholder consultations, Omega Consulting helps organizations identify key performance drivers and develop KPI frameworks that support strategic alignment.
KPI Development
Omega Consulting provides expertise in developing meaningful and effective KPIs that provide actionable insights into organizational performance. Drawing on industry knowledge and best practices, Omega Consulting helps organizations select KPIs that are relevant, specific, and measurable, tailored to their unique business needs and objectives.
Data Analytics:
Omega Consulting leverages advanced data analytics techniques to derive insights from KPIs and metrics, enabling organizations to make data-driven decisions and optimize performance. By employing predictive modeling, machine learning, and data visualization tools, Omega Consulting helps organizations analyze performance data, identify trends and patterns, and uncover actionable insights to drive continuous improvement.
Process Improvement:
Omega Consulting supports organizations in optimizing performance measurement processes and systems to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and effectiveness. Through process audits, gap analyses, and performance reviews, Omega Consulting helps organizations identify opportunities for process improvement, streamline data collection and reporting processes, and implement best practices to enhance performance measurement capabilities.
Change Management:
Omega Consulting assists organizations in managing change and overcoming resistance to performance measurement initiatives. By conducting change readiness assessments, stakeholder engagement sessions, and communication campaigns, Omega Consulting helps organizations build awareness, understanding, and support for performance measurement initiatives, fostering a culture of accountability and continuous improvement
Training and Capacity Building:
Omega Consulting provides training and capacity-building programs to equip organizations with the skills and knowledge needed to implement and manage performance measurement systems effectively. Through workshops, seminars, and coaching sessions, Omega Consulting empowers employees at all levels to understand the importance of performance measurement, use KPIs and metrics effectively, and drive performance improvement initiatives.
Technology Integration:
Omega Consulting assists organizations in integrating technology solutions to support performance measurement efforts. By evaluating software platforms, selecting appropriate tools, and overseeing implementation and integration processes, Omega Consulting helps organizations leverage technology to automate data collection, analysis, and reporting, improving efficiency and accuracy in performance measurement.
Overall, Omega Consulting plays a vital role in guiding organizations through the complex process of measuring success with KPIs and metrics. By providing strategic guidance, technical expertise, and implementation support, Omega Consulting helps organizations optimize performance measurement processes, drive strategic alignment, and achieve their business goals effectively and efficiently.
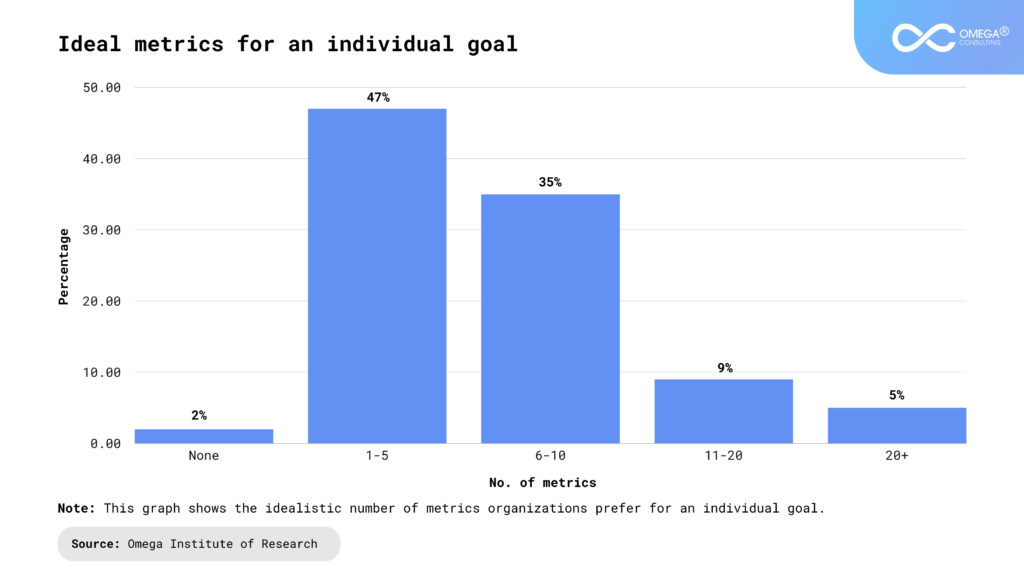
Conclusion
In conclusion, the effective measurement of success through Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and metrics is essential for organizations striving to achieve their strategic objectives and drive continuous improvement. As highlighted throughout this article, KPIs and metrics provide valuable insights into organizational performance, enabling stakeholders to track progress, make informed decisions, and optimize resources effectively.
By adhering to key principles such as alignment with strategic objectives, relevance, clarity, and continuous improvement, organizations can develop robust performance measurement frameworks that align with their strategic priorities and drive accountability and transparency across all levels of the organization. Leveraging frameworks and best practices such as the SMART criteria, Balanced Scorecard, benchmarking, and data-driven decision-making, organizations can ensure that their KPIs and metrics are meaningful, actionable, and aligned with organizational goals.
Despite the benefits of measuring success with KPIs and metrics, organizations must navigate various challenges, including data quality and availability, complexity, bias, resistance to change, and resource constraints. However, with the support of management consulting firms like Omega Consulting, organizations can overcome these challenges and maximize the value of their performance measurement initiatives. Omega Consulting provides strategic guidance, technical expertise, and implementation support to help organizations develop and implement effective performance measurement systems, optimize processes, and drive continuous improvement.
Measuring success with KPIs and metrics is not just a matter of tracking numbers; it is about driving strategic alignment, fostering accountability, and empowering organizations to achieve their full potential. By embracing a data-driven approach to performance management, organizations can navigate complexity, overcome challenges, and unlock opportunities for growth and innovation in an increasingly competitive and dynamic business environment. With the right strategy, tools, and support, organizations can harness the power of KPIs and metrics to drive sustainable success and create value for all stakeholders.
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/t/technicalindicator.asp
- https://www.klipfolio.com/blog/kpi
- https://balancedscorecard.org/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Balanced_scorecard
- https://www.whatmatters.com/resources/okrs-smart-goals-difference-between
- https://sloanreview.mit.edu/video/making-strategic-decisions-with-data/
- https://www.ibm.com/blog/building-a-culture-of-data-driven-decisions-and-insights-with-ibm-business-analytics/
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions