- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Technology
- By Omega Team

Change is inevitable in any organization, driven by factors such as technological advancements, market trends, or internal restructuring. However, managing change effectively is often a complex process that requires careful planning, execution, and adaptation. Change management is the structured approach organizations use to transition individuals, teams, and the entire organization from the current state to a desired future state. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of navigating change management, exploring its principles, frameworks, benefits, challenges, and the crucial role of consulting firms like Omega Consulting in facilitating successful transitions.
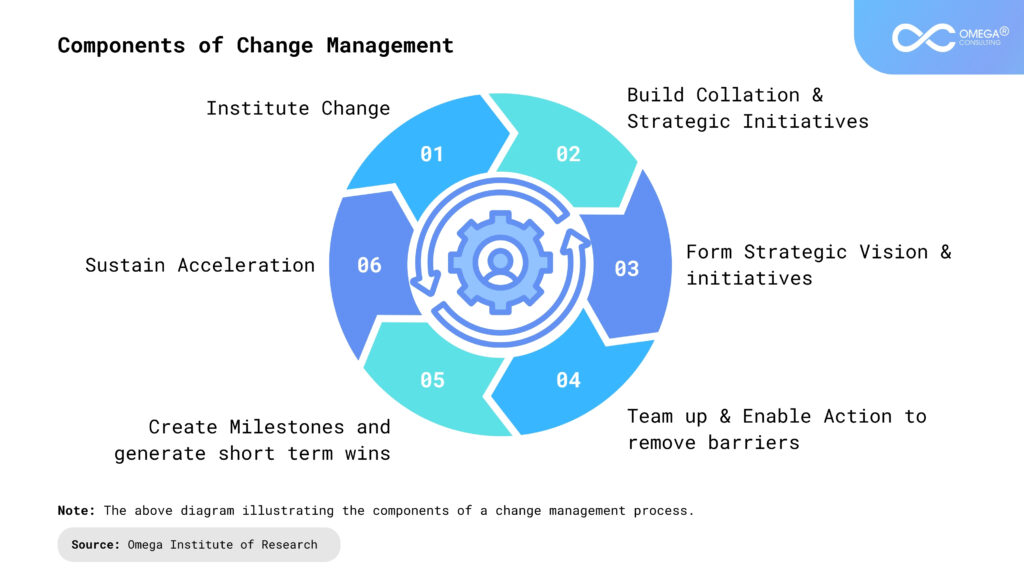
Understanding of Navigating Change Management
Understanding the topic of change management requires delving into its multifaceted nature, which extends beyond mere organizational restructuring or process improvement. At its core, change management acknowledges the human dimension of change – the emotional, psychological, and behavioral aspects that individuals and groups experience when confronted with new ways of working or thinking.
Firstly, change is a fundamental aspect of organizational life. Whether prompted by external pressures such as technological advancements, market fluctuations, or internal drivers like strategic shifts or leadership transitions, change is inevitable. However, recognizing the need for change is only the first step. Understanding how to navigate it effectively is where change management comes into play.
Secondly, change management recognizes that organizations are composed of people – individuals with unique perspectives, motivations, and reactions to change. While change initiatives often focus on implementing new systems, processes, or structures, the success of these initiatives ultimately depends on the people who must adopt and embrace them. This understanding underscores the importance of addressing the human side of change, including managing resistance, fostering buy-in, and supporting individuals through the transition process.
Moreover, change management involves anticipating and addressing the various challenges and complexities that accompany organizational change. These challenges may include resistance from stakeholders, cultural barriers within the organization, or uncertainties about the future. By understanding these challenges and their potential impact, change management enables organizations to develop proactive strategies for mitigating risks and maximizing the likelihood of successful change adoption.
Furthermore, change management is not a one-size-fits-all approach. It recognizes that different individuals and groups may respond to change differently based on factors such as their roles within the organization, their level of involvement in the change process, and their past experiences with change. Therefore, effective change management requires a tailored approach that takes into account the unique needs, concerns, and perspectives of various stakeholders.
In essence, understanding change management goes beyond recognizing the need for change; it involves recognizing the human dimension of change, anticipating and addressing challenges, and adopting a tailored approach that fosters engagement, resilience, and ultimately, success. By embracing this understanding, organizations can navigate change more effectively, achieving their desired outcomes while minimizing disruption and maximizing value for all involved.
Key Principles
The key principles of change management serve as guiding tenets that organizations adhere to when navigating through periods of transition. These principles form the foundation upon which successful change initiatives are built, ensuring that they are effectively planned, communicated, and executed. Let’s delve into each of these principles to understand their significance in driving successful change:
- Leadership Commitment: Leadership commitment is paramount to the success of any change initiative. When organizational leaders actively champion the change, it sends a clear message to employees that the change is a priority and that their support is unwavering. Leadership commitment involves not only endorsing the change but also actively participating in its planning, implementation, and reinforcement. Leaders serve as role models, inspiring confidence, and demonstrating the behaviors and attitudes expected of others during the change process.
- Clear Communication: Effective communication is essential for ensuring that everyone understands the purpose, rationale, and expected outcomes of the change. Clear communication involves providing timely and relevant information to employees at all levels of the organization, addressing questions, concerns, and misconceptions, and soliciting feedback to ensure that messages are understood and resonate with the audience. Communication should be transparent, honest, and consistent, fostering trust and minimizing uncertainty among stakeholders.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Engaging stakeholders throughout the change process is critical for building ownership, alignment, and commitment. Stakeholders include not only employees but also customers, suppliers, shareholders, and other parties affected by the change. Engaging stakeholders involves soliciting their input, involving them in decision-making processes, and addressing their concerns and interests. By involving stakeholders early and often, organizations can gain valuable insights, build consensus, and create a sense of shared responsibility for the success of the change initiative.
- Flexible Planning: Change is inherently unpredictable, and no amount of planning can anticipate every possible challenge or obstacle. Therefore, change management requires a flexible and adaptive approach to planning that allows for adjustments based on feedback, new information, and changing circumstances. Flexible planning involves setting clear objectives and milestones, identifying potential risks and mitigation strategies, and maintaining agility and responsiveness throughout the change process. By being prepared to pivot and adapt as needed, organizations can better navigate uncertainty and overcome obstacles as they arise.
- Empathy and Support: Change can be disruptive and unsettling for employees, triggering feelings of uncertainty, anxiety, and resistance. Therefore, change management requires empathy and support to help individuals navigate through the transition process. Empathy involves understanding and acknowledging the emotions and concerns of employees, while support involves providing resources, training, and assistance to help them cope with change effectively. By demonstrating empathy and providing support, organizations can foster a culture of trust, resilience, and collaboration, enabling employees to embrace change and contribute to its success.
In summary, the key principles of change management – leadership commitment, clear communication, stakeholder engagement, flexible planning, and empathy and support – provide a framework for guiding organizations through periods of transition. By adhering to these principles, organizations can increase the likelihood of successful change adoption, minimize resistance and disruption, and ultimately achieve their desired outcomes.
Frameworks & Practices
Frameworks and practices in change management provide structured approaches and methodologies for organizations to effectively plan, implement, and sustain change initiatives. These frameworks offer guidance on various aspects of change management, from diagnosing the need for change to managing resistance and measuring success. Let’s explore some prominent frameworks and practices in more detail:
- Kotter’s 8-Step Process: Developed by Harvard Business School professor John Kotter, this framework outlines a sequential approach to leading change. The eight steps include:
- Creating a sense of urgency
- Forming a powerful coalition
- Creating a vision for change
- Communicating the vision
- Empowering employees to act on the vision
- Generating short-term wins
- Consolidating gains and producing more change
- Anchoring new approaches in the organization’s culture
Kotter’s 8-Step Process provides a comprehensive roadmap for change leaders, emphasizing the importance of building momentum, aligning stakeholders, and embedding change into the organizational culture.
- ADKAR Model: The ADKAR Model focuses on individual change by addressing five key elements necessary for successful adoption:
- Awareness of the need for change
- Desire to participate and support the change
- Knowledge of how to change
- Ability to implement required skills and behaviors
- Reinforcement to sustain the change
The ADKAR Model provides a systematic approach to understanding and addressing the psychological transitions individuals undergo during change, helping organizations tailor their change management strategies to meet the needs of employees at each stage of the change process.
- Prosci’s Change Management Process: Prosci’s methodology is based on research and best practices from thousands of change management practitioners worldwide. It consists of three phases:
- Prepare: Assessing change readiness, developing change management plans, and building a coalition of sponsors and change agents.
- Manage: Implementing change management plans, communicating effectively, and engaging stakeholders throughout the change process.
- Reinforce: Monitoring and measuring change progress, celebrating successes, and reinforcing new behaviors and practices to sustain change.
Prosci’s Change Management Process emphasizes the importance of integrating change management activities into project plans and building change management competency within the organization.
- Lewin’s Change Management Model: Developed by psychologist Kurt Lewin, this model is based on the idea that change involves three stages:
- Unfreeze: Creating a sense of dissatisfaction with the status quo and preparing individuals for change.
- Change: Implementing new practices, processes, or structures.
- Refreeze: Embedding the change into the organization’s culture and ensuring that it becomes the new norm.
Lewin’s Change Management Model provides a simple yet powerful framework for understanding the change process and guiding interventions at each stage.
- Agile Change Management: Inspired by agile principles from software development, Agile Change Management focuses on flexibility, collaboration, and iterative improvement. It emphasizes:
- Iterative planning and execution
- Continuous stakeholder engagement and feedback
- Rapid adaptation to changing circumstances
- Empowering teams to make decisions and take ownership of change initiatives
Agile Change Management is particularly well-suited for complex, fast-paced environments where traditional change management approaches may be too rigid or slow to keep pace with evolving needs.
These frameworks and practices provide organizations with valuable tools and methodologies for navigating the complexities of change. By selecting and adapting the most appropriate frameworks to their specific context, organizations can increase the likelihood of successful change adoption and achieve their desired outcomes effectively and efficiently.
Benefits
Effective change management offers a myriad of benefits for organizations, stakeholders, and individuals involved in the change process. These benefits extend beyond mere implementation of new processes or systems; they encompass broader organizational objectives and contribute to long-term success. Let’s explore some of the key benefits of change management in more detail:
- Increased Adaptability: In today’s rapidly evolving business environment, adaptability is crucial for survival. Change management equips organizations with the tools and processes necessary to respond effectively to external pressures, market shifts, technological advancements, and competitive threats. By fostering a culture of agility and resilience, change management enables organizations to navigate uncertainty and capitalize on emerging opportunities more effectively.
- Enhanced Employee Engagement: Clear communication, stakeholder involvement, and support mechanisms inherent in change management foster a sense of ownership, empowerment, and commitment among employees. When employees feel engaged and valued, they are more likely to embrace change, contribute their ideas and efforts, and align their behaviors with organizational goals. This increased engagement leads to higher morale, productivity, and retention rates, creating a positive ripple effect throughout the organization.
- Improved Risk Management: Change inherently involves risk, including potential disruptions to operations, resistance from stakeholders, and unforeseen challenges. Change management provides a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating these risks, thereby minimizing the likelihood of project delays, budget overruns, and operational disruptions. By proactively managing risk throughout the change process, organizations can increase the likelihood of successful outcomes and protect their investments in change initiatives.
- Faster Time to Value: Change management accelerates the pace at which organizations realize the benefits of change. By providing clear objectives, timelines, and milestones, change management ensures that change initiatives are executed efficiently and effectively. Moreover, by minimizing resistance and disruption, change management reduces downtime and accelerates the adoption of new processes, technologies, or ways of working. This faster time to value allows organizations to capitalize on opportunities sooner, gaining a competitive edge in the marketplace.
- Enhanced Organizational Resilience: Change management builds organizational resilience by equipping employees with the skills, mindset, and support necessary to navigate uncertainty and adversity. By fostering a culture of continuous learning, adaptation, and innovation, change management enables organizations to thrive in volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous (VUCA) environments. This resilience enables organizations to weather challenges, seize opportunities, and emerge stronger and more agile in the face of change.
In summary, effective change management offers a range of benefits that contribute to organizational success, including increased adaptability, enhanced employee engagement, improved risk management, faster time to value, and enhanced organizational resilience. By investing in change management, organizations can position themselves for long-term growth, innovation, and competitive advantage in an ever-changing business landscape.
Conclusion
Navigating change management is a multifaceted endeavor that requires a strategic approach, empathetic leadership, and proactive engagement with stakeholders. Change is inevitable in today’s dynamic business environment, driven by technological advancements, market shifts, and internal restructuring. However, the success of change initiatives hinges on how effectively organizations plan, communicate, and execute these changes.
Throughout this article, we’ve explored various aspects of change management, including its principles, frameworks, benefits, and challenges. We’ve highlighted the importance of leadership commitment, clear communication, stakeholder engagement, flexible planning, and empathy and support as key principles that underpin successful change management efforts.
Furthermore, we’ve discussed several frameworks and practices that organizations can leverage to navigate change effectively, including Kotter’s 8-Step Process, the ADKAR Model, Prosci’s Change Management Process, Lewin’s Change Management Model, and Agile Change Management. These frameworks provide organizations with structured approaches and methodologies for planning, implementing, and sustaining change initiatives, tailored to their specific needs and circumstances.
The benefits of effective change management are numerous, including increased adaptability, enhanced employee engagement, improved risk management, faster time to value, and enhanced organizational resilience. By investing in change management, organizations can position themselves for long-term success, enabling them to thrive in an increasingly competitive and uncertain business environment.
In conclusion, change management is not just about implementing new processes or systems; it’s about empowering people, fostering a culture of innovation, and driving organizational transformation. By embracing change management principles, leveraging proven frameworks and practices, and partnering with experienced consultants like Omega Consulting, organizations can navigate change with confidence, achieving their desired outcomes and realizing their full potential in an ever-changing world.
- https://www.prosci.com/blog/change-management-process
- https://www.prosci.com/methodology/adkar
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/315745050_Change_Management
- https://www.prosci.com/blog/6-references-to-make-the-case-for-change-management
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11528-022-00775-0
- https://hbr.org/2021/01/an-agile-approach-to-change-management
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions