- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Information Technology
- By Omega Team
Businesses must make a crucial choice about their IT infrastructure in today’s rapidly evolving technology environment: whether to move to the cloud or maintain an on-premises configuration. This decision has a big impact on scalability, costs, and operational efficiency. Every choice has specific benefits and disadvantages. It is essential to comprehend these distinctions to make a decision that fits your business strategy. This in-depth article explores the subtle differences between cloud and on-premises solutions and offers a thorough analysis to assist you in choosing the one that best suits your needs.
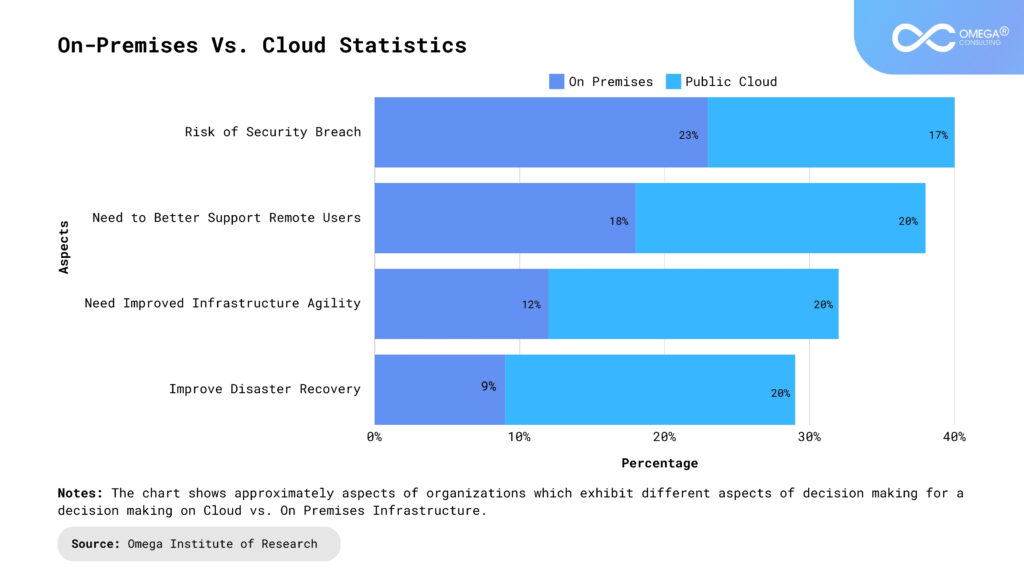
On-premises Solutions
On-premises solutions refer to hosting all IT infrastructure, including servers, storage, and networking equipment, within the physical premises of a business. This traditional model requires significant investment in hardware and ongoing maintenance.
Advantages
Control and Customization
On-premises solutions offer unparalleled control over the IT environment. Businesses can customize hardware and software to meet specific needs, which is particularly beneficial for organizations with unique or complex operational requirements. This level of control allows for fine-tuning of systems to optimize performance and functionality.
Data Security and Compliance
For businesses dealing with highly sensitive information, on-premises solutions provide a higher degree of data security. Data is stored locally, simplifying the enforcement of stringent security protocols and compliance with industry regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA. This is especially crucial for sectors like healthcare, finance, and government.
Performance and Reliability
On-premises infrastructure can deliver superior performance, especially for applications requiring low latency or high bandwidth. With direct access to hardware, businesses can optimize performance without depending on external networks. This setup often results in more reliable and consistent performance, which is critical for mission-critical applications.
Disadvantages
High Initial and Ongoing Costs
The initial capital expenditure for on-premises infrastructure can be substantial. Businesses must invest in purchasing hardware, and software licenses, and employing IT staff for maintenance and support. Additionally, ongoing costs for power, cooling, hardware upgrades, and repairs can accumulate over time, impacting the overall budget.
Scalability Challenges
Scaling an on-premises environment can be cumbersome and expensive. As the business grows, additional hardware and space are required, leading to potential delays and increased costs. This inflexibility can hinder a business’s ability to quickly respond to changing demands or opportunities.
Maintenance and Management
Managing an on-premises IT infrastructure demands continuous maintenance and monitoring. This includes regular software updates, hardware repairs, and security patching. The need for dedicated IT staff to handle these tasks can strain resources, particularly for smaller businesses.
Cloud Solutions
Cloud solutions involve hosting IT infrastructure, applications, and data on servers managed by third-party cloud service providers. These resources are accessed over the Internet, allowing businesses to leverage the provider’s infrastructure and services without the need for significant on-site hardware.
Advantages
Cost Efficiency
Cloud solutions offer significant cost savings with a pay-as-you-go model, ideal for startups and small businesses. Key savings include:
- AWS: Up to 72% savings with Reserved Instances and up to 90% with Spot Instances.
- GCP: Up to 30% savings with Sustained Use Discounts and up to 57% with Committed Use Contracts.
- Azure: Up to 72% savings with Reserved VM Instances and up to 90% with Spot VMs.
Examples include Netflix saving millions annually on AWS and Evernote cutting operational costs by 40% on Google Cloud. Cloud solutions provide flexible, scalable, and cost-effective IT infrastructure, improving cash flow and operational efficiency.
Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud services offer unmatched scalability and flexibility. Businesses can easily scale their resources up or down based on demand without the need for additional hardware or lengthy provisioning processes. This elasticity is ideal for businesses experiencing rapid growth, seasonal fluctuations, or sudden changes in workload.
Accessibility and Collaboration
With cloud solutions, employees can access applications and data from anywhere with an internet connection. This enhances collaboration, particularly for remote or distributed teams, and supports business continuity during emergencies or unforeseen events. The cloud’s inherent flexibility enables seamless integration with various tools and platforms, facilitating efficient workflows.
Disadvantages
Data Security and Privacy
While cloud providers implement robust security measures, businesses must contend with data privacy concerns. Sensitive data stored off-premises may be subject to external threats, and businesses must ensure compliance with data protection regulations. Choosing a reputable cloud provider with strong security protocols is essential to mitigate these risks.
Downtime and Reliability
Relying on cloud providers means that businesses are dependent on their uptime and reliability. While most providers offer high availability, outages can occur, potentially impacting business operations. It’s crucial to evaluate a provider’s track record and service level agreements (SLAs) to ensure they meet your business’s reliability requirements.
Limited Control and Customization
Cloud solutions offer less control over the underlying infrastructure. Customizing hardware and software to meet specific needs can be challenging, and businesses must rely on the provider’s capabilities and service offerings. This lack of control may be a drawback for businesses with highly specialized IT requirements.
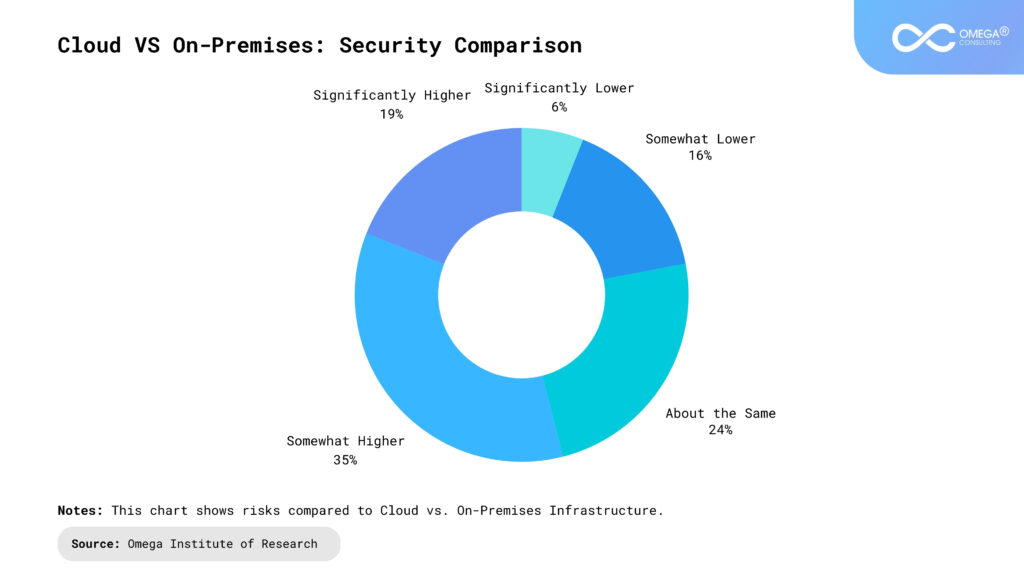
Fresh Things to Think About
Hybrid Solutions
Definition
A hybrid solution combines both on-premises and cloud infrastructures, allowing businesses to leverage the advantages of both models. Critical data and applications can be kept on-premises, while less sensitive operations can be moved to the cloud. Examples of hybrid solutions include:
- Microsoft Azure Stack: Extends Azure services to on-premises data centers, enabling consistent application development and deployment.
- AWS Outposts: Bring AWS infrastructure, services, and operating models to virtually any data center or on-premises facility for a seamless hybrid experience.
- Google Anthos: Allows applications to run unmodified on existing on-premises hardware or in the public cloud, providing a consistent development and operations experience.
Advantages
Hybrid solutions offer a balanced approach, providing the control and security of on-premises systems along with the scalability and flexibility of the cloud. This model is ideal for businesses looking to gradually transition to the cloud or those needing to maintain certain operations in-house due to regulatory or performance reasons.
Disadvantages
Managing a hybrid environment can be complex and requires robust integration and management tools. Ensuring seamless interoperability between on-premises and cloud systems can be challenging and may require specialized skills and resources.
Implementation Strategy for Hybrid Solutions
- Assess Business Needs: Identify which applications and data are critical and need to remain on-premises, and which can be moved to the cloud for flexibility and scalability.
- Select the Right Tools: Choose integration and management tools that support hybrid environments, such as Azure Arc, AWS Systems Manager, or Google Anthos.
- Develop a Clear Architecture Plan: Design a hybrid architecture that ensures seamless connectivity and data flow between on-premises and cloud components. This should include network configuration, security protocols, and data management strategies.
- Invest in Training: Equip IT staff with the necessary skills and knowledge to manage and operate hybrid systems effectively. This might involve training on new tools, cloud platforms, and best practices for hybrid integration.
- Implement Robust Security Measures: Ensure data security and compliance by implementing strong security measures across both on-premises and cloud environments. This includes encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
Industry-Specific Considerations
Manufacturing
Manufacturing businesses often require robust, reliable, and low-latency IT systems to support production lines and inventory management. On-premises solutions can offer the performance and reliability needed for these critical operations, though cloud solutions are increasingly being adopted for non-critical applications and data analytics.
Retail
Retail businesses benefit from the cloud’s scalability, particularly during peak shopping seasons. Cloud solutions enable easy scaling of e-commerce platforms and customer relationship management (CRM) systems. However, point-of-sale (POS) systems and in-store operations might still rely on on-premises solutions for reliability.
Education
Educational institutions increasingly adopt cloud solutions for online learning platforms, student information systems, and collaborative tools. The cloud’s flexibility supports diverse learning environments and remote access, which has become essential in recent years. However, on-premises solutions may still be used for administrative systems requiring high security.
Future-Proofing Your IT Strategy
Technological Advancements
Technological advancement is rapid, and businesses must ensure their IT infrastructure can adapt to new technologies. Cloud solutions typically offer better future-proofing as providers continually update their services with the latest innovations. On-premises solutions require significant investment to upgrade, which can be a slower process.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Cloud providers often operate energy-efficient data centers, which can help businesses reduce their carbon footprint. On-premises solutions require businesses to manage their energy consumption, which might not be as efficient. Considering the environmental impact of your IT infrastructure is increasingly important for corporate social responsibility.
Energy Efficiency
- Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE):
-
- Cloud Providers: Leading cloud providers often report low PUEs (e.g., 1.1 to 1.3), meaning they use 10-30% additional energy beyond the IT equipment load for cooling and other overhead.
- On-Premises: Typically, smaller or less optimized data centers may have PUEs ranging from 1.5 to 2.5 or higher.
Renewable Energy Usage
- Renewable Energy Percentage:
-
- Cloud Providers: Many major cloud providers (e.g., AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure) are committed to using a significant percentage of renewable energy. For instance, Google claims to match 100% of its global electricity use with renewable energy.
- On-Premises: The percentage of renewable energy used depends on the local utility grid and the business’s initiatives to source green power.
Carbon Emissions
- Carbon Intensity (gCO2/kWh):
-
- Cloud Providers: Providers often operate in regions with lower carbon intensity or purchase carbon offsets. For example, some data centers might operate at less than 100 gCO2/kWh.
- On-Premises: This will vary significantly depending on the location and energy sources used. Average grid electricity can range from 400 gCO2/kWh to 900 gCO2/kWh or higher in coal-dependent regions.
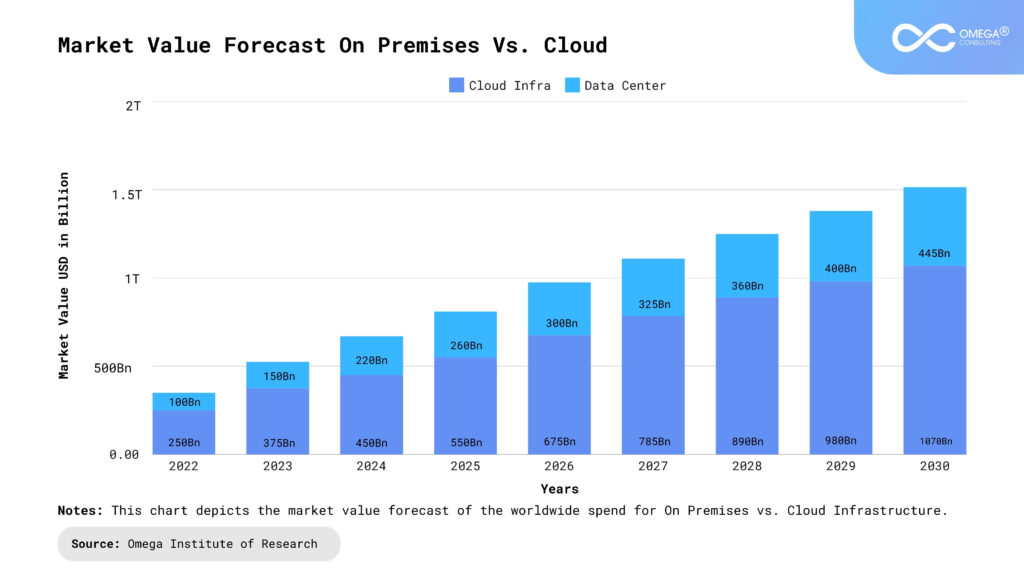
Case Studies
Company A – Financial Services
Background
Company A is a financial services firm handling sensitive client data and requiring high levels of security and compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA.
On-premises Implementation
Initially, Company A used an on-premises IT infrastructure to maintain control over their data and ensure compliance. They invested heavily in robust security measures and employed a large IT team for continuous monitoring and maintenance. This setup provided the control and customization they needed but incurred high costs and demanded significant resources for upkeep.
Transition to Hybrid Model
As the company grew, it faced challenges in scaling its on-premises infrastructure and began exploring hybrid solutions. They moved less sensitive operations, such as marketing and customer relationship management, to the cloud while keeping core financial applications and sensitive data on-premises. This transition allowed them to leverage the scalability and cost-efficiency of the cloud for non-critical functions while maintaining control over sensitive information.
Outcome
The hybrid model provided a balanced approach, reducing costs and improving scalability without compromising security. Company A was able to respond more quickly to market changes and client needs, demonstrating the effectiveness of a hybrid approach in a highly regulated industry.
Company B – E-commerce
Background
Company B is an e-commerce company experiencing rapid growth and seasonal fluctuations in traffic, particularly during the holiday season.
Cloud Adoption
Company B adopted a cloud-first strategy from the start, leveraging the scalability and flexibility of cloud solutions. They utilized cloud services for their entire IT infrastructure, including their e-commerce platform, customer relationship management, and data analytics. This approach allowed them to scale resources up or down based on demand without significant upfront investment.
Benefits
The cloud solution provided Company B with the agility to handle peak traffic periods seamlessly and cost-effectively. The pay-as-you-go model enabled them to manage costs efficiently, and the accessibility of cloud services supported a distributed workforce, enhancing collaboration and productivity.
Challenges
Despite the benefits, Company B faced challenges related to data security and downtime. They implemented robust security measures and chose a reputable cloud provider to mitigate these risks. Additionally, they developed a disaster recovery plan to ensure business continuity during outages.
Outcome
The cloud-first strategy allowed Company B to maintain agility and cost-efficiency, supporting their rapid growth and fluctuating demands. Their proactive approach to security and reliability ensured a robust and resilient IT infrastructure.
Future Trends
Edge Computing
Edge computing involves processing data closer to its source rather than relying solely on centralized cloud data centers. This approach reduces latency and bandwidth usage, making it ideal for real-time applications.
Implications
Edge computing is expected to complement both cloud and on-premises solutions. Businesses can process critical data at the edge for faster response times while using cloud services for storage and less time-sensitive processing. This hybrid approach enhances performance and reduces latency, particularly for IoT applications, autonomous vehicles, and real-time analytics.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Cloud and On-premises Solutions
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are becoming integral to business operations, providing insights and automation across various functions. Cloud providers offer AI and ML services that can be easily integrated into existing workflows. On-premises solutions can also leverage AI and ML, particularly for businesses with specific data privacy requirements.
Future Developments
As AI and ML technologies advance, their integration into cloud and on-premises solutions will become more seamless. Businesses will increasingly use these technologies to drive innovation, optimize operations, and enhance customer experiences.
Multi-cloud Strategies
Multi-cloud strategies involve using services from multiple cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in and optimize performance, cost, and reliability.
Benefits
By adopting a multi-cloud approach, businesses can leverage the strengths of different providers, enhance redundancy, and improve resilience. This strategy also allows for better cost management and flexibility in choosing the best services for specific needs.
Future Trends
Multi-cloud strategies will become more prevalent as businesses seek to balance cost, performance, and reliability. Tools and platforms that facilitate seamless integration and management of multi-cloud environments will continue to evolve, making it easier for businesses to implement and manage these strategies.
Conclusion
Deciding between on-premises and cloud solutions is a multifaceted decision that depends on various factors unique to each business. While cloud solutions offer cost efficiency, scalability, and accessibility, on-premises solutions provide control, customization, and enhanced security. Additionally, hybrid solutions offer a middle ground, combining the benefits of both models.
Businesses can make an informed decision by carefully considering factors such as business size, industry requirements, growth expectations, IT expertise, and long-term goals. Evaluating the specific needs and objectives of your business ensures a robust and adaptable IT infrastructure that supports long-term success. Ultimately, the best choice is the one that aligns with your business model, providing the flexibility and reliability needed to thrive in a dynamic market. As future trends such as edge computing, AI integration, and multi-cloud strategies emerge, businesses will have even more tools at their disposal to optimize their IT infrastructure.
- https://www.stormit.cloud/blog/comparison-on-premises-vs-cloud/
- https://morefield.com/blog/on-premises-vs-cloud/
- https://stonefly.com/blog/on-prem-vs-cloud-which-is-best-for-your-business/
- https://phoenixnap.com/blog/on-premise-vs-cloud
- https://www.clarity-ventures.com/articles/cloud-vs-on-premise-which-is-better-for-your-business
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions