- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Technology
- By Omega Team
Operational efficiency is not merely a goal—it’s a fundamental requirement for survival and growth. As competition tightens across industries, companies are under constant pressure to do more with less. Whether it’s reducing costs, increasing output, or improving customer satisfaction, the need to streamline operations is paramount.
Operational efficiency is the cornerstone that supports these objectives. It involves optimizing processes to minimize waste, reduce costs, and improve productivity without sacrificing quality. This comprehensive guide explores the importance of operational efficiency, delves into actionable strategies for streamlining processes, and examines the impact on both cost reduction and productivity enhancement.
Understanding Operational Efficiency: The Core of a Competitive Business
Operational efficiency is all about doing more with less. At its core, it measures how effectively a business converts its inputs—such as labor, materials, and technology—into outputs, which can be goods or services. The goal is to achieve maximum output while using the least resources possible. This concept is not limited to cutting costs; it’s also about improving quality, enhancing customer satisfaction, and making the organization more agile and adaptable to change.
To understand operational efficiency better, consider it through a set of key performance indicators (KPIs) that act as the backbone of this concept:
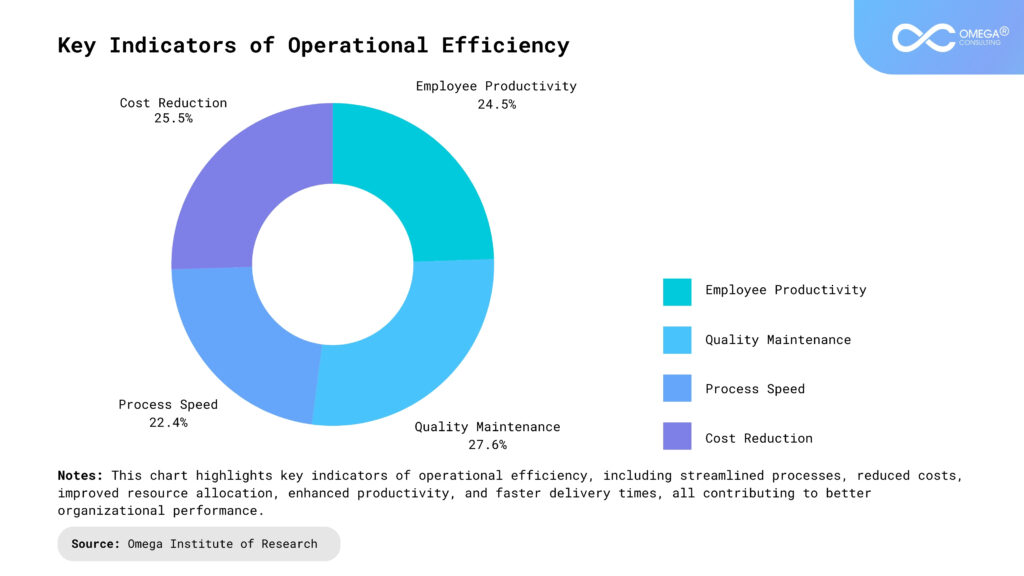
Key Indicators of Operational Efficiency
Cost Reduction: How effectively does the organization lower operational expenses without compromising on the quality of its product or service? This can range from minimizing material waste to optimizing labor costs through automation or outsourcing.
Process Speed: Efficiency is also measured by the speed at which processes can be completed. Faster processes often lead to quicker turnaround times, allowing businesses to deliver to customers faster and stay competitive.
Quality Maintenance: Can the organization maintain or even improve the quality of its offerings while cutting costs and speeding up processes? Operational efficiency should never come at the expense of quality, as customer satisfaction is tied to consistent value.
Employee Productivity: How well does the company utilize its workforce? Are employees empowered with the right tools and processes to work efficiently? High employee productivity is often a sign of well-optimized operations.
Achieving operational efficiency can dramatically impact an organization’s bottom line. It reduces unnecessary expenditures, increases output, and improves customer experience, all of which contribute to the long-term sustainability and success of the business.
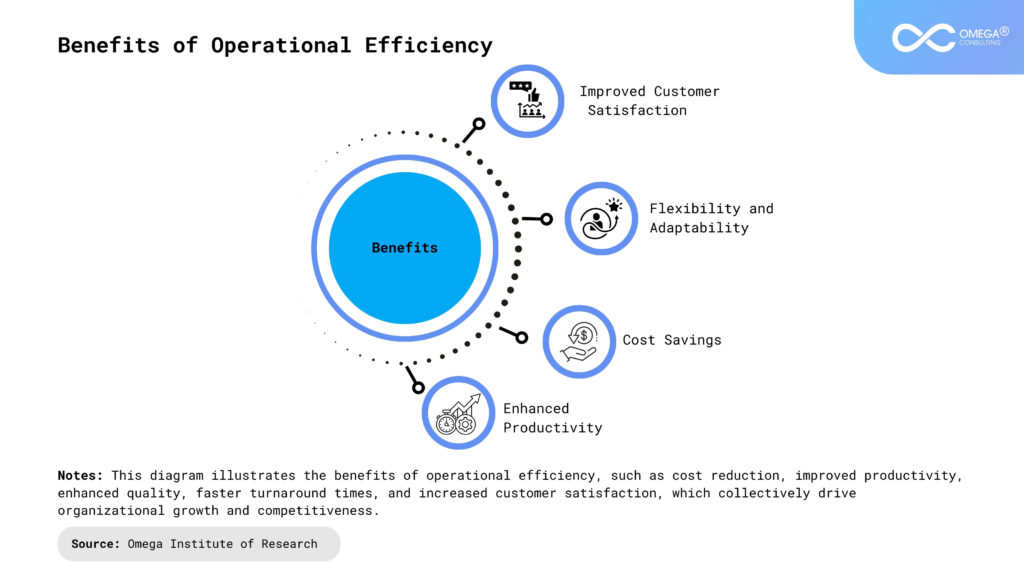
The Far-Reaching Benefits of Operational Efficiency
Operational efficiency goes beyond just cutting costs or boosting productivity. It has far-reaching benefits that can shape the future of a business. Here are the most significant advantages:
Cost Savings
The most immediate and visible benefit of streamlining processes is cost savings. When operations run efficiently, businesses can reduce overhead expenses, such as labor costs, inventory holding costs, and energy consumption. By eliminating redundant processes, companies can reinvest the saved capital into more value-adding activities, such as innovation or customer service.
For example, automating tasks like data entry, payroll management, or inventory tracking can significantly lower human error rates and reduce the need for extensive labor, freeing up resources to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Enhanced Productivity
Efficiency doesn’t just lower costs—it allows businesses to get more done in less time. Streamlined processes ensure that employees aren’t bogged down with unnecessary steps, approvals, or manual tasks. This directly boosts productivity, as employees can focus on the tasks that truly matter and add value to the business.
For instance, a company that implements automated tools for customer service might find that its employees can handle more complex queries while routine tasks (like answering frequently asked questions) are managed by bots. This dual focus improves overall output and ensures that customer issues are resolved more quickly.
Improved Customer Satisfaction
Operational efficiency has a direct impact on customer satisfaction. When processes are streamlined, orders are fulfilled faster, services are delivered more reliably, and the quality remains high. Customers expect speed, quality, and consistency—and efficient operations make all of these possible.
A retail business, for example, that optimizes its supply chain to reduce shipping times and inventory errors will naturally see improved customer feedback. Faster delivery, accurate orders, and quick resolutions to complaints make customers more loyal to the brand, driving long-term profitability.
Flexibility and Adaptability
In a rapidly evolving market, flexibility is key. Efficient businesses can pivot quickly to respond to new customer demands, market trends, or technological advancements. Companies that have eliminated operational inefficiencies are more agile and can adapt to changes without significant disruptions.
For example, a manufacturer with a lean production system can easily adjust production volumes based on demand fluctuations, ensuring they never overproduce or underdeliver.
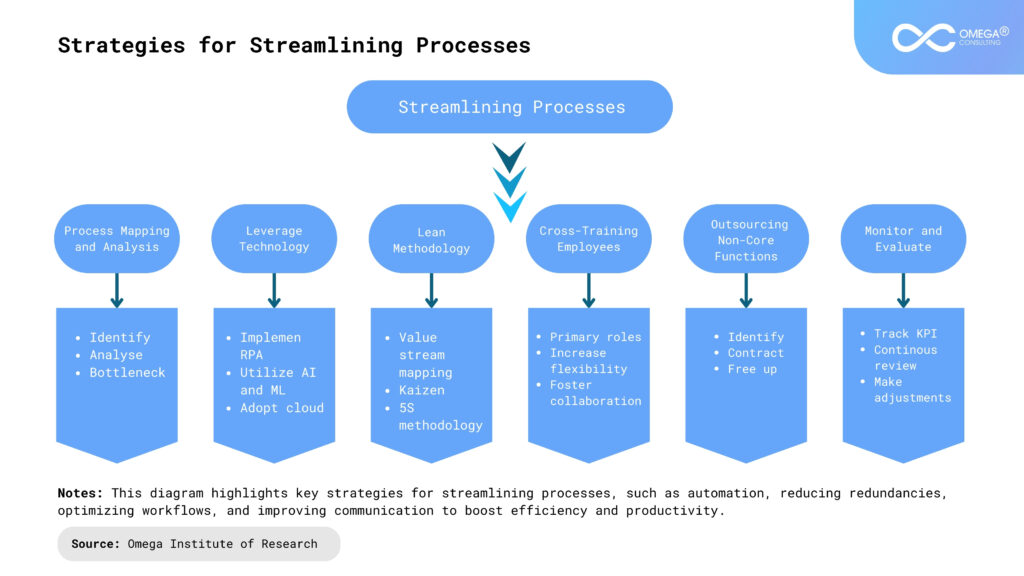
Key Strategies for Streamlining Processes
To achieve operational efficiency, businesses must take deliberate steps to optimize their processes. Below are several detailed strategies that companies can implement to streamline operations, reduce costs, and boost productivity:
Process Mapping and Analysis
Before you can improve efficiency, you must first understand your existing processes in detail. Process mapping is a technique where businesses document every step involved in a workflow. This helps create a clear, visual representation of how work flows through different departments or functions within the company.
By laying out all tasks in a process, organizations can identify which activities add value and which are redundant or wasteful.
How to Implement Process Mapping
- Break down each process step-by-step: This includes every task, from initiation to completion. For example, if you’re mapping the order fulfillment process, break it down into tasks like order receipt, picking, packing, shipping, and post-delivery follow-up.
- Analyze time, cost, and resource allocation for each step: Measure how much time each task takes, how much it costs, and what resources (e.g., labor or technology) are required.
- Identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies: Where do delays occur? What tasks are repeated unnecessarily? For example, you may discover that manual data entry in multiple systems is slowing down the entire order process.
Leverage Technology
Technology is a powerful enabler of operational efficiency. By automating routine, repetitive tasks, businesses can drastically reduce human error, save time, and lower costs. Today, advancements in automation, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and cloud computing have made it easier than ever for businesses to optimize their processes.
Key Technological Tools to Consider
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Software robots can handle tasks like invoice processing, customer data entry, or managing transactions across multiple systems. This frees up human workers to focus on more strategic, higher-value tasks.
- AI and Machine Learning: AI can enhance decision-making by analyzing large datasets and identifying patterns that humans might miss. For example, predictive analytics can help companies optimize their inventory levels by forecasting demand more accurately.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud platforms allow for greater collaboration across teams, especially for businesses with remote or distributed workforces. Cloud solutions also reduce the need for costly on-site infrastructure, which helps lower IT expenses.
Lean Methodology
Lean methodology, which originated from manufacturing practices like Toyota’s Production System, is centered around minimizing waste and creating more value for customers with fewer resources. This strategy applies not only to production but to nearly any business process.
Lean Principles
- Value Stream Mapping: Similar to process mapping, this technique focuses specifically on the value-adding steps in a process. Non-value-adding activities (e.g., waiting, transporting materials without processing) are identified and removed.
- Kaizen (Continuous Improvement): A core tenet of lean, Kaizen emphasizes making small, incremental improvements over time. Employees at all levels are encouraged to contribute ideas for improving processes, fostering a culture of continuous learning and innovation.
- 5S Methodology: The 5S approach to workplace organization (Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain) ensures that work environments are clean, organized, and standardized, which improves efficiency and reduces time wasted searching for tools or materials.
Cross-Training Employees
Cross-training employees involves teaching them how to perform tasks or roles outside their immediate job functions. This strategy not only makes your workforce more versatile but also mitigates risks associated with employee absenteeism or turnover.
Benefits of Cross-Training
- Increased Flexibility: Cross-trained employees can cover for one another during peak times or unexpected absences. This flexibility ensures that key processes continue running smoothly, regardless of staffing issues.
- Improved Collaboration: When employees understand how other departments function, they’re more likely to collaborate effectively and appreciate how their work impacts the larger organization.
- Higher Job Satisfaction: Cross-training gives employees a broader skill set, making them more valuable to the company and often leading to greater job satisfaction and career growth opportunities.
Outsourcing Non-Core Functions
Outsourcing allows companies to offload non-core functions to external service providers, freeing up resources to focus on their primary business activities. By outsourcing tasks like IT support, payroll processing, or customer service, businesses can often achieve higher efficiency at a lower cost than if they managed these functions internally.
Commonly Outsourced Functions
- IT and Technical Support: Outsourcing IT services to a third party ensures that systems remain operational without the need for an in-house team.
- Human Resources and Payroll: Payroll management can be complex and time-consuming. Outsourcing allows companies to focus on employee development and engagement rather than administrative tasks.
Overcoming Challenges to Operational Efficiency
While operational efficiency offers many advantages, businesses often face challenges when implementing these strategies. Some of the most common obstacles include:
Resistance to Change: Employees may resist changes, especially when new technologies or processes are introduced. It’s essential to have a robust change management strategy that includes clear communication, training, and support to help employees adapt.
Upfront Technology Costs: Although technology can significantly improve efficiency, the initial investment in new systems or software can be high. However, businesses should view this as a long-term investment that will lead to cost savings and productivity gains down the road.
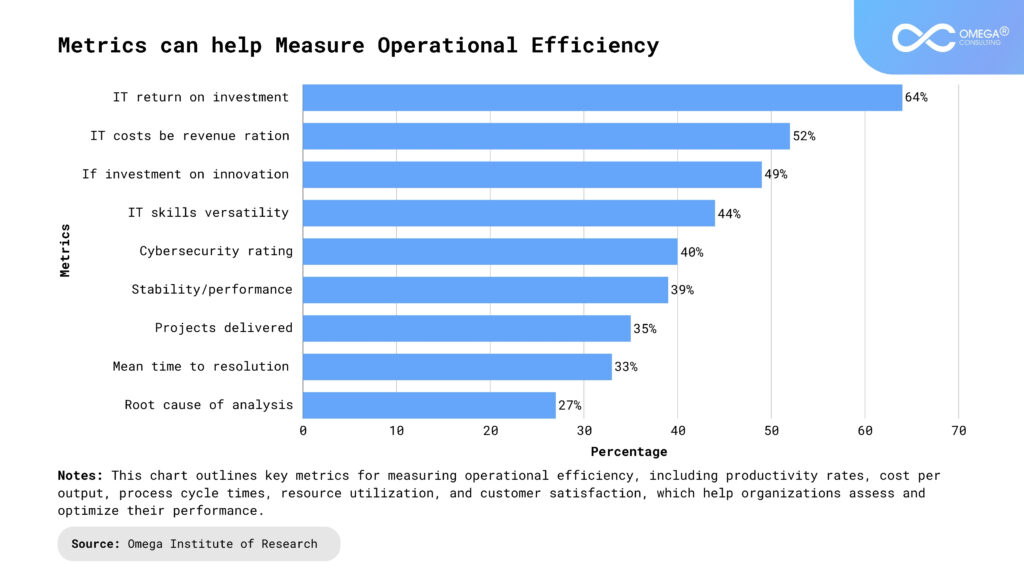
Difficulty in Measuring Efficiency: Without clear metrics, it can be challenging to measure the impact of efficiency initiatives. Establishing KPIs from the outset ensures that progress can be tracked and adjustments made where necessary.
Departmental Silos: Operational inefficiencies often arise when departments operate in isolation. Breaking down these silos through improved communication and collaboration is crucial to achieving company-wide efficiency.
Case Studies in Operational Efficiency
Toyota: Lean Manufacturing and Just-In-Time (JIT)
Toyota pioneered the Lean Manufacturing philosophy and Just-In-Time (JIT) system to minimize waste and optimize production processes. By producing goods only when needed and focusing on continuous improvement (Kaizen), Toyota significantly reduced inventory costs and streamlined operations. This approach has made Toyota one of the most efficient automakers globally, and its methods have been adopted across various industries.
Amazon: Inventory and Supply Chain Optimization
Amazon’s operational efficiency stems from its advanced use of automation and data analytics. By employing robots in its warehouses and using AI for dynamic pricing and demand forecasting, Amazon has minimized labor costs, improved order fulfillment speeds, and optimized inventory management. These efficiencies allow Amazon to deliver products quickly and at a lower cost, solidifying its dominance in e-commerce.
Southwest Airlines: Simplified Operations
Southwest Airlines has streamlined its operations by using a single aircraft model (Boeing 737) to reduce maintenance complexity and training costs. Additionally, the airline’s quick turnaround times and simplified boarding processes minimize delays and improve fleet utilization. This focus on operational efficiency has allowed Southwest to maintain profitability and offer competitive fares in a challenging industry.
Future Trends in Operational Efficiency
AI and Machine Learning
AI and Machine Learning (ML) will drive operational efficiency by enhancing predictive capabilities. AI can analyze large datasets to forecast equipment failures, optimize maintenance schedules, and anticipate demand fluctuations. This enables businesses to reduce downtime, streamline operations, and improve productivity by making real-time adjustments based on accurate predictions and insights.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) will boost operational efficiency through real-time monitoring and data collection. IoT sensors in equipment and supply chains provide valuable insights into performance and conditions, allowing for proactive maintenance, efficient inventory management, and reduced waste. This connected approach enhances decision-making and operational agility.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) will advance from automating routine tasks to handling more complex processes. By integrating with AI, RPA can perform decision-making and problem-solving tasks, automating knowledge work and freeing up employees to focus on strategic activities. This will further streamline operations and improve overall efficiency.
Sustainability-Driven Efficiency
As sustainability becomes a priority, operational efficiency will align with eco-friendly practices. Companies will adopt energy-efficient technologies and circular economy principles, reducing waste and lowering costs. This focus on sustainability will drive innovation and operational improvements while meeting environmental goals.
Remote Work and Digital Collaboration
The shift to remote work will necessitate digital-first operations and advanced collaboration tools. Efficient virtual workspaces, automated processes, and robust communication platforms will be essential for managing distributed teams and maintaining productivity. This transition will help businesses reduce overhead costs and enhance operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Achieving operational efficiency is not a destination but a dynamic journey of perpetual enhancement. It involves relentlessly refining processes and adapting to evolving business landscapes. Organizations set the stage for enduring success and competitive advantage by streamlining operations to cut costs and boost productivity.
The essence of operational efficiency lies in fostering a culture of continuous improvement. This mindset empowers every team member to contribute ideas and innovations, driving the organization toward greater agility, cost-effectiveness, and quality. Embracing this ethos ensures that efficiency becomes an integral part of the organizational fabric, leading to sustained growth, heightened customer satisfaction, and a robust position in the market. Through persistent effort and adaptation, businesses can transform operational efficiency from a mere goal into a strategic asset that propels them toward long-term success.
- https://fastercapital.com/content/Operational-Efficiency--Streamlining-Processes-to-Maximize-Profitability.html
- https://www.runn.io/blog/operational-efficiency
- https://www.workast.com/blog/7-tips-to-streamline-business-processes-and-boost-efficiency/
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/streamlining-operations-guide-cost-cutting-business-luis-mercado-phr-vzvdc/
- https://www.wrike.com/blog/roadmap-to-organizational-efficiency/
- https://fastercapital.com/content/Operational-efficiency--Streamlining-Operations--A-Turnaround-Blueprint.html
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions