- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Technology
- By Omega Team

In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, organizations are increasingly turning to data cloud migration to drive agility, scalability, and innovation. This transformative process involves moving digital assets—ranging from databases and applications to entire IT infrastructures—from traditional on-premises environments to cloud-based platforms. By embracing cloud migration, businesses can unlock new efficiencies, streamline operations, and respond more swiftly to changing market demands. The shift not only reduces dependency on costly hardware and complex legacy systems but also empowers teams to leverage advanced analytics, automation, and global accessibility. As industries seek to remain competitive and resilient, data cloud migration is emerging as a strategic imperative, reshaping how organizations manage, secure, and utilize their most valuable digital resources for long-term growth and success.
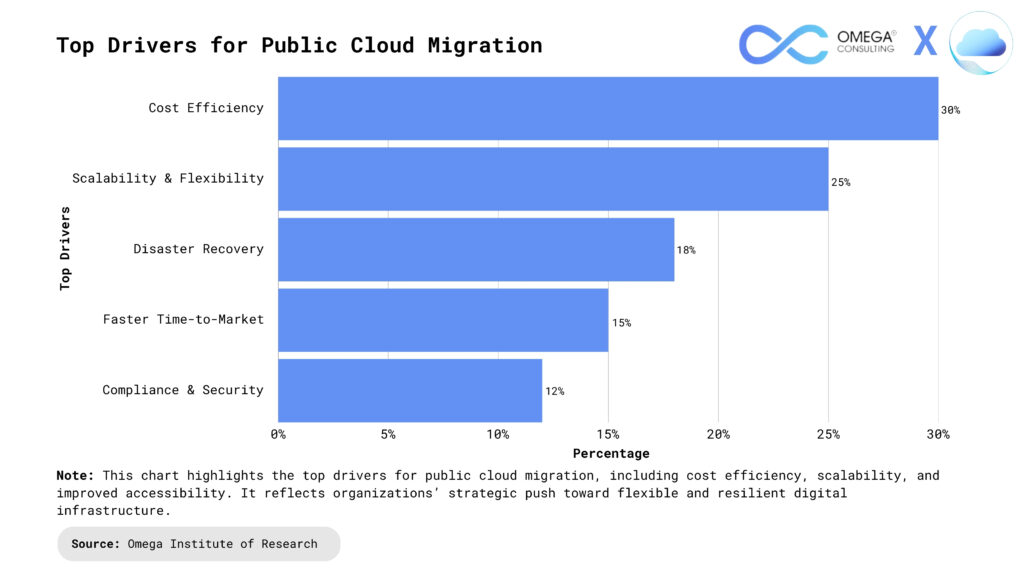
Assessing Readiness for Cloud Migration
A thorough assessment of readiness is the foundation of any successful cloud migration. Organizations must begin by clearly defining their migration objectives and business goals, such as cost optimization, scalability, or enhanced agility. Next, a comprehensive evaluation of the existing IT infrastructure is essential—this includes analyzing hardware, networks, storage, and virtualization capabilities to identify gaps or limitations that may hinder migration. Applications and workloads should be reviewed for cloud compatibility, taking into account architecture, dependencies, and performance requirements. Security and compliance are critical; organizations must assess data sensitivity, privacy concerns, and regulatory obligations to ensure a secure and compliant transition. Additionally, analyzing performance and scalability needs, as well as reviewing IT operations and organizational readiness, helps uncover potential challenges and informs a strategic migration plan.
Building a Cloud Migration Strategy
Establishing clear goals: A successful cloud migration strategy starts with defining precise business objectives, such as cost savings, improved agility, or enhanced performance. These goals guide every decision throughout the process, from selecting the right cloud provider to determine which workloads to migrate and in what order.
Assessing the current IT landscape: Organizations must conduct a thorough assessment of their existing infrastructure, applications, and data. This includes mapping dependencies, identifying critical systems, and evaluating which assets are best suited for migration. Understanding these interdependencies helps prioritize workloads and minimizes disruption during the transition.
Choosing the migration approach: Selecting the appropriate migration strategy—such as rehosting, replatforming, refactoring, repurchasing, retiring, or retaining—depends on technical requirements and business priorities. Each approach has its own trade-offs in complexity, cost, and long-term benefit, so organizations should build a business case for each workload, considering total cost of ownership and future scalability.
Selecting the right cloud provider: Evaluating potential cloud providers is crucial. Key considerations include performance, scalability, security features, compliance support, integration capabilities, and cost structures. The right provider should align with organizational needs and offer the flexibility to avoid vendor lock-in.
Developing a comprehensive migration plan: A detailed migration plan outlines resources, timelines, responsibilities, and risk mitigation measures. It should address compliance, security, and contingency plans, ensuring a coordinated and efficient transition. Automation and infrastructure as code (IaC) can streamline deployment, reduce errors, and enhance consistency.
Continuous monitoring and optimization: After migration, ongoing monitoring and optimization are essential to ensure workloads perform as expected, costs remain controlled, and security and compliance are maintained. Regular reviews and updates help organizations adapt to evolving business needs and fully realize the benefits of cloud transformation.
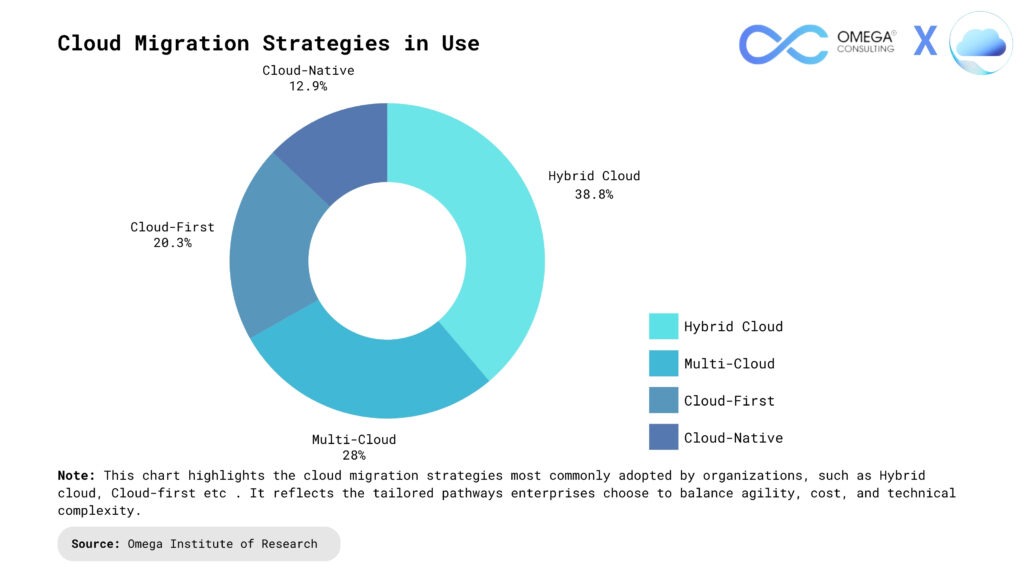
Detailed Migration Planning
Preparation: Detailed migration planning starts with a thorough inventory of all applications, data, and dependencies. Teams map out which workloads are most critical and determine the optimal sequence for migration. This step includes identifying potential risks, setting clear objectives, and defining success metrics. Early preparation helps organizations anticipate challenges and reduces the likelihood of unexpected downtime or data loss during migration.
Resource Allocation: Careful planning ensures that the right resources—personnel, tools, and budget—are in place for each phase. By assigning clear roles and responsibilities, organizations can streamline communication and decision-making. Utilizing automation tools and cloud-native services can further optimize resource use, minimize manual intervention, and keep the migration on schedule and within budget.
Testing: Thorough testing is essential before, during, and after migration. Pilot migrations or dry runs allow teams to validate processes, uncover issues, and refine procedures without impacting production systems. Testing data integrity, application functionality, and performance ensures that workloads will operate smoothly in the new cloud environment. This step also provides valuable feedback for continuous improvement.
Communication: Effective communication keeps all stakeholders informed and engaged throughout the migration. Regular updates, clear documentation, and accessible support channels help address concerns and foster collaboration. Transparent communication also ensures that end-users are prepared for changes, reducing resistance and smoothing the adoption of new cloud-based systems.
Monitoring & Optimization: Continuous monitoring post-migration ensures workloads perform efficiently in the cloud environment. Teams track performance metrics, security compliance, and cost patterns to identify optimization opportunities. Implementing automated scaling, adjusting resource allocation, and refining configurations based on real-time data helps maintain service levels and reduce operational expenses. Proactive optimization ensures the cloud infrastructure evolves with business needs while maximizing ROI.
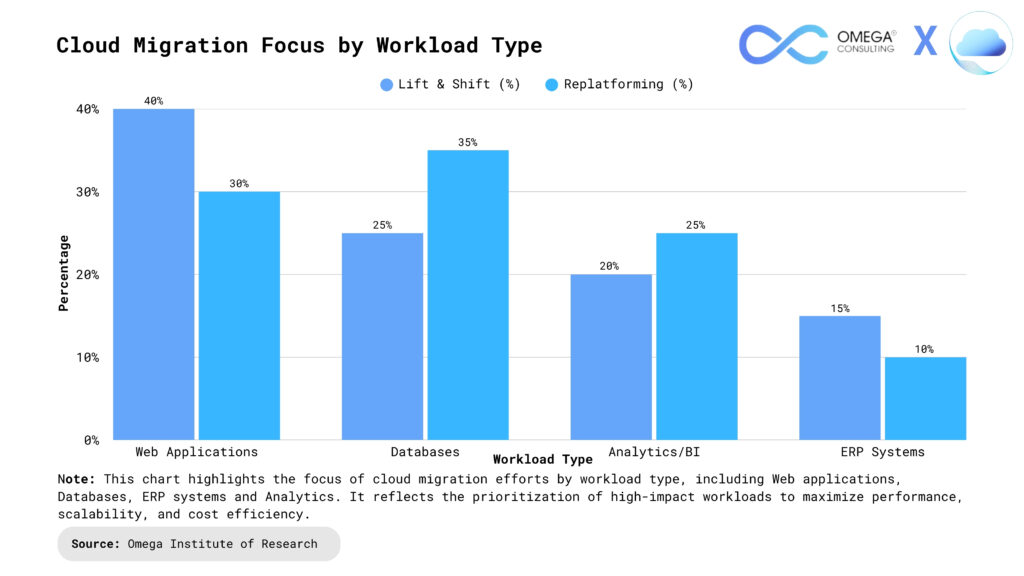
Data Migration Execution
Data Preparation: Before migration begins, organizations inventory and classify all data, ensuring it is clean, deduplicated, and formatted for the target cloud environment. Dependencies between data sets are mapped to determine the optimal migration sequence and minimize disruption. This step also includes creating robust backup strategies and setting up security controls to protect sensitive data during transfer.
Pilot Migration: A small, representative subset of data is migrated first as a pilot. This step helps identify potential issues, test migration tools, and refine processes without risking critical workloads. Lessons learned here inform the full migration plan and allow teams to adjust strategies for efficiency and reliability. Pilot migrations also provide an opportunity to validate migration scripts and automation in a controlled setting.
Full Data Transfer: With pilot feedback incorporated, the full-scale migration proceeds. Data is transferred using cloud-native tools or third-party services, either in phases or all at once, depending on business needs. Continuous monitoring is essential to detect errors, data loss, or integrity issues during transfer. Automated alerts and real-time dashboards help teams respond quickly to any problems and maintain visibility throughout the process.
Validation and Cutover: After migration, teams validate the data in the new environment, checking for completeness, accuracy, and performance. Only once stakeholders confirm successful transfer is the old system decommissioned. Ongoing synchronization and monitoring may continue temporarily to ensure business continuity and address any post-migration issues promptly. Detailed documentation of results and a formal sign-off process help confirm migration success.
Post-Migration Testing: Following cutover, comprehensive post-migration testing is conducted to ensure data integrity, system performance, and application functionality in the new environment. This includes data validation, performance benchmarking, and user acceptance testing to confirm that business operations remain uninterrupted. Rollback plans and ongoing monitoring are maintained to address any residual issues and to ensure long-term stability.
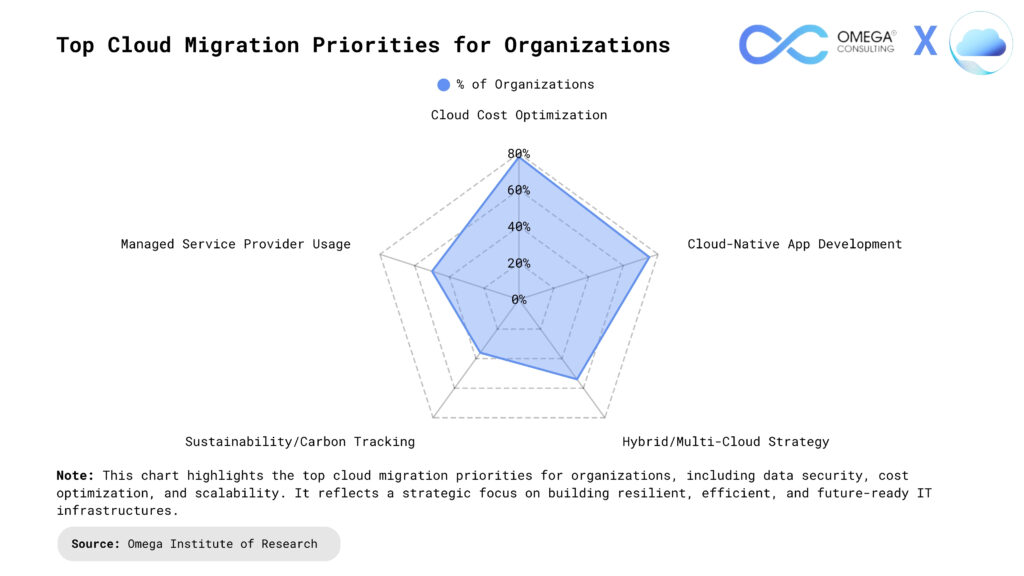
Application Migration and Testing
Functional Validation: Migrated applications must be thoroughly tested to ensure all features and workflows operate correctly in the cloud environment. This includes verifying that core functionality remains intact and that the user experience is consistent with the original system. Early detection of issues helps prevent disruptions and supports a smooth transition. Automated testing tools can accelerate this process and catch subtle errors that manual tests might miss.
Performance Testing: Applications undergo rigorous performance testing to assess responsiveness, scalability, and stability under various load conditions. This step ensures that cloud infrastructure can handle peak demands without degradation, maintaining service quality and reliability for end users. Performance metrics such as latency, throughput, and resource utilization are monitored and analyzed to identify bottlenecks and optimize configurations.
Integration Testing: Testing focuses on verifying seamless interaction between migrated applications and cloud services, APIs, and third-party tools. Identifying and resolving integration issues early prevents data flow disruptions and ensures interoperability across the new environment. Special attention is given to cross-system dependencies and data synchronization to maintain business continuity.
Security and Compliance: Security testing uncovers vulnerabilities specific to the cloud environment, validating access controls, encryption, and compliance with regulatory standards. Ensuring robust security protects sensitive data and maintains organizational trust. Regular audits and automated compliance checks help organizations stay aligned with evolving industry regulations.
User Acceptance Testing (UAT): End users participate in validating the application’s functionality and usability in the new environment. Their feedback confirms that the migrated application meets business needs and supports operational workflows effectively. UAT also provides an opportunity to gather insights for further optimization and training needs before full deployment.
Post-Migration Operations and Optimization
Continuous Monitoring: After migration, organizations implement continuous monitoring to track system health, application performance, and user experience in the cloud environment. Automated alerts and dashboards help teams quickly identify and resolve issues, ensuring high availability and reliability. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and supports ongoing operational excellence.
FinOps Practices: Cloud financial management, or FinOps, is adopted to optimize cloud spending and align costs with business value. Teams collaborate across finance, operations, and engineering to analyze usage patterns, allocate costs, and set budgets. Regular cost reviews and forecasting help prevent overspending, while showback and chargeback models promote accountability across departments.
Auto-Scaling and Resource Optimization: Auto-scaling tools are configured to dynamically adjust compute, storage, and network resources based on real-time demand. This ensures optimal performance during peak usage while minimizing costs during low-traffic periods. Resource tagging and rightsizing further enhance efficiency by identifying underutilized assets and reallocating or decommissioning them as needed.
Cost-Monitoring Tools: Organizations leverage cloud-native and third-party cost-monitoring tools to gain visibility into usage and spending. These tools provide detailed reports, anomaly detection, and recommendations for savings opportunities. Alerts for budget thresholds and cost spikes enable timely interventions, supporting a culture of cost-conscious cloud operations.
Ongoing Optimization: Post-migration, regular reviews of workloads, configurations, and security policies are conducted to ensure continuous improvement. Teams experiment with new cloud services, adopt automation, and refine architectures to enhance performance, security, and cost efficiency. Feedback loops and performance benchmarking help drive innovation and maximize the long-term value of cloud investments.
Conclusion
Cloud migration drives business transformation by providing agility, scalability, and cost efficiency, fostering innovation and market responsiveness. It reduces the need for on-premises infrastructure management, allowing IT teams to concentrate on strategic initiatives. Benefits include lower costs, improved disaster recovery, and greater operational resilience, often resulting in less downtime and lower infrastructure expenses. Cloud migration provides access to advanced technologies like AI, enabling broader global competition. Flexible scaling, enhanced mobility, and improved collaboration support modern workforces and accelerate product launches. Multi-cloud strategies and AI tools further optimize performance, costs, and compliance. Ultimately, cloud migration enables business growth by overcoming limitations of legacy systems. Careful planning and execution allow organizations to fully utilize the cloud for innovation, resilience, and sustained competitive advantage in the digital landscape.
- https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/pages/consulting/articles/cloud-computing-case-studies.html
- https://www.infosys.com/services/application-modernization/case-studies/cloud-migration-modernization.html
- https://www.accenture.com/cr-en/case-studies/cloud/sap-next-gen-cloud-delivery
- https://datapao.com/cloud-migration-case-studies/
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions