- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Technology
- By Omega Team
Introduction
A QR code is quite similar to a bar code. Still, it conveys data in two dimensions (horizontally and vertically), so it can store significantly more data than a one-dimensional bar code. Unlike bar codes, which are limited to 20 alphanumeric characters, QR codes can store thousands of characters. Thus, a QR code can distribute multimedia content, landing pages, or eBooks. However, QR codes can do much more, instructing a phone to conduct specific actions. For instance, a theater company could provide a QR code that will take the users to their website for show times and ticket information and embeds information about the dates, times, and locations of upcoming engagements into the phone’s calendar.History Of QR Codes
In 1994, Denso Wave (a subdivision of Denso Corporation) announced the release of the QR code. The acronym QR in the name stands for “quick response,” which was the concept for the code. Masahiro Hara and his development team are credited as the creators of the QR code. Still, even Hara was unsure if it could overtake barcodes as the standard for a two-dimensional code. The QR code became very popular in the auto industry thanks to Hara and his team and contributed significantly to efficiency across many tasks, including production and shipping. Customers across all sectors demanded transparency for the products they were buying, and the QR code was a great tool to store all of this information. All of this was crucial to the rise of the QR code, but the key aspect for the substantial increase in the usage of the QR code was Denso Wave’s decision to allow the QR code for public service so that anyone could use it freely. Even though Denso Wave kept the rights to the QR code, they never exercised them due to Hara’s goal of the QR code being used by as many people as possible. In 2002 the QR code proliferated in popularity amongst the Japanese due to the increased usage of mobile phones with QR codes.QR Code Structure
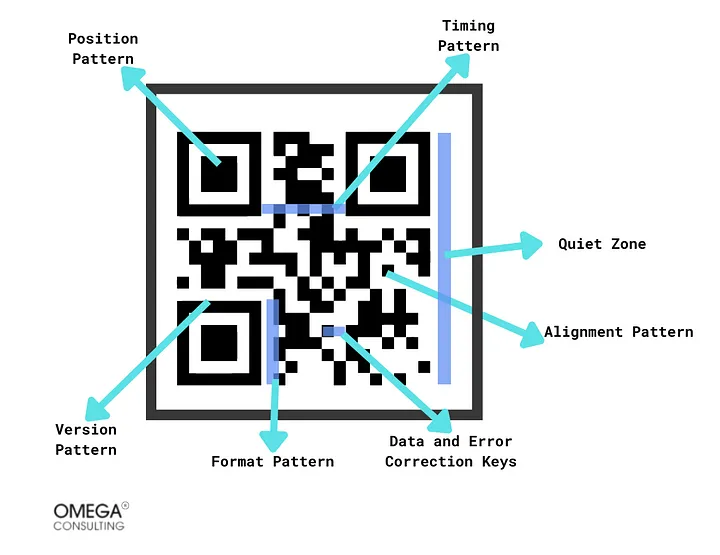
Seven essential elements are there in a QR code:1. Version pattern
These patterns designate the QR code version. The version of the code is determined by the number of modules (the tiny black squares). There are forty QR code variants, from version 1 to version 40. Version 1 contains twenty-one modules. Each succeeding version adds four modules until version 40, which has 177 modules. The more modules contained within a QR code, the greater its storage capacity.
2. Format pattern
These patterns contain information regarding error correction and the data disguise of the code. Error correction guarantees that the QR code can be decoded despite being partially obscured or damaged.
3. Data and error correction keys
The actual informationcontained within the QR code is stored in these patterns.
4. Position pattern
These patterns signify the proper QR code orientation.
5. Alignment pattern
This pattern enables decoding of the QR code from any angle. Therefore, even if the code is examined inverted or at an unusual angle, it can be scanned without issue.
6. Timing pattern
These patterns enable the decoder to ascertain the data matrix’s breadth.
7. Quiet zone
This is the empty space surrounding the code. Important because it enables the decoder to distinguish the QR code from its environment.
Exhibit 1
QR Code StructureA QR code structure consists of seven essential elements which are depicted in the figure below.
Static vs. Dynamic QR Code
QR codes vary in appearance based on the encoded data and function and can be broadly classified as static or dynamic.
Static QR codes
Once a static QR code has been generated, it cannot be altered. This is optimal for mass-producing QR codes for an event. Its lack of creativity and inability to track scanning frequency are its disadvantages. The QR code for your Wi-Fi password is an excellent example of a static QR code.
Dynamic QR codes
Dynamic QR codes enable you to modify the code as often as necessary. When the code is scanned, you are redirected to the URL it contains. Thesecodes provide the flexibility to package your design, such as by incorporating contrasting colors. Additionally, they can monitor and measure advertising statistics.
The Rising trend of QR Codes
As you can imagine, the ascent of the smartphone is directly correlated with the rise of QR codes worldwide. In 2011 significant sellers in the United States began implementing QR codes in their stores, but there were substantial complications with the user experience. In 2011, only 31% of the American population was estimated to own a smartphone. At the time, people had to download unique apps onto their phones just to recognize a QR code; companies did not implement an accessible mobile phone interface, leading to users being turned off from attempting to use QR codes. QR codes were way ahead of their time, and companies did not know how to use this technology. As of 2021, 88% of Americans are estimated to own a smartphone. Over those ten years, consumers have become more tech-savvy, as have the companies implementing QR code technology. For example, Apple was one of the first phone companies to design a QR code reader directly into the camera. This feature was unveiled with Apple’s unveiling of its IOS11 in 2017, and other companies such as Samsung and Google were quick to follow. In 2020 it was estimated that 11 million households scanned a QR code. After the COVID-19 pandemic, companies have embraced QR codes due to their versatility and usefulness. It is an excellent option to help companies keep track of marketing campaigns without spending much money.Exhibit 2
Percentage of Americans with SmartphonesThe most recent US cell phone ownership statistics by year indicate that the proportion of Americans with smartphones has increased over the past decade.
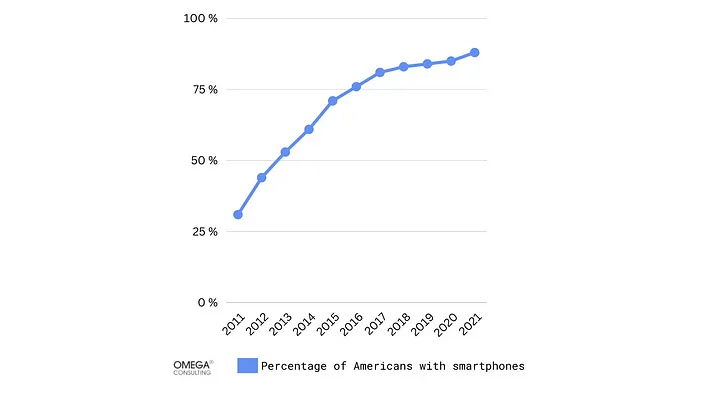
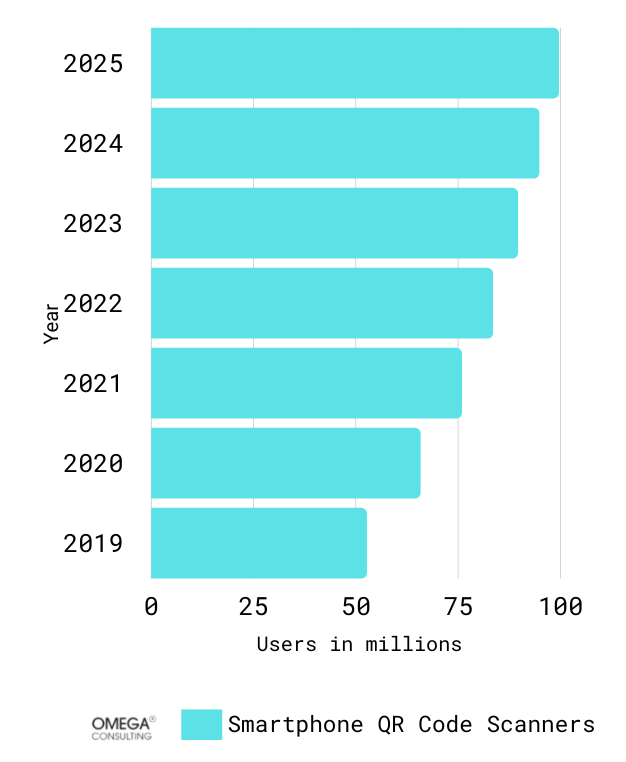
Exhibit 3
U.S. smartphone QR code scannersIn the U.S., the number of smartphone users who can utilize a QR code will increase substantially from 83.4 million in 2022 to 99.5 million in 2025. Currently, the majority of smartphone cameras can read QR codes, which facilitates their use and subsequent adoption.
Business Applications of QR Codes
Website Traffic and landing pagesA business’s digital presence is no longer optional. Even if you only sell offline, your business must have a website in this Internet-enabled, highly-connected world. A website provides information about your business, fosters meaningful relationships, and collects first-party data, among other functions. Over 70% of small enterprises actually have a website. QR codes enable offline users to access your website. You can generate a URL QR code for your website and place it on printed advertisements, billboards, product packaging, etc. Customers can use it to access your website.
Sharing contact details
Representatives of sales and marketing, as well as service providers such as insurance agents, real estate agents, etc., must continually expand their network and interact with prospective customers. Most professionals use business cards to exchange contact information and develop relationships. Although business cards are a tried-and-true networking instrument, they have disadvantages. People must manually input your information into their phones in order to save you as a contact. It istime-consuming and error-prone; consequently, 88% are discarded. Also, business cards have limited capacity, so you must reprint them if you need to alter any information.
Mobile Application downloads
The mobile application industry is thriving. Over 4.8 million mobile applications are available for distribution on various app stores, and mobile apps are anticipated to generate over $935 billion by 2023. Due to the exponential growth of mobile adoption and utilization, mobile applications are one of the most effective channels for engaging an audience, fostering brand loyalty, and driving revenue. With so many apps on the market, however, app proprietors need an effective strategy to promote app downloads. QR codes can increase the number of app installations. You can generate an App Download QR code that directs users to a display page with iOS and Android version download links. There is only one QR code required for all your app download URLs.
Sharing Business Information
You can share extensive information about your business using QR codes. You cangenerate a business QR code that directs people to a page with all the information about your business. This includes the business’s location, contact information, business hours, and website, among other information.
Smart product packaging
Before purchasing, Consumers want to know everything about the product. However, product packaging has limited capacity, so it is only possible to include some pertinent information. Here is where QR codes save the day. You can print a QR code on product packaging to share product-specific details. For instance, you can generate a PDF comprising all the product’s specifications or a video demonstrating the manufacturing process through a QR code.
Feedback and reviews
Every organization requires a strategy for collecting consumer feedback. Only one of every twenty-six customers complains; the rest go to your competitors. Collecting and acting on customer feedback can aid customer retention and brand loyalty. One can use a feedback QR code to collect feedback efficiently. Users can scan the QR code to give feedback and provide comments. When visitors check out of a restaurant, hotel, or retail store, QR codes can be placed on the invoicing counter to collect feedback. If there is a physical product, you can place QR codes for feedback on the packaging.
Enable digital payments
In 2021, global QR code payments were valued at $2.2 trillion and are projected to reach $2.7 trillion by 2025. QR codes enable in-store digital payments, and modest businesses worldwide accept QR code payments. Setting up QR code payments is straightforward and fast. The establishment costs are negligible, and there is no need for a high-tech infrastructure or costly apparatus. Simply generate a payment QR code and display it in your store, restaurant, hotel, etc. QR code payments are also convenient for consumers. In physical stores, they can pay digitally by scanning a QR code and confirming the transaction. There is no requirement to carry currency or debit cards.
Business Outlook
Teeth, an upscale bar in San Francisco, has been very fond of implementing QR codes. Every single table at Teeth comes equipped with a QR code, which customers can scan from their phone, and the entire menu will become available for the customer to browse the customer can insert their credit card information and complete their order directly, all without touching a physical piece of paper or interacting with a server. Businesses have been effectively utilizing QR codes because it gives them another tool for tracking and targeting analytics. QR codes have allowed businesses to create databases of their customers’ order histories and personnel information. Furthermore,companies have gathered data on consumer spending habits. Half of all full-service restaurants have added QR code menus since the beginning of the Coronavirus pandemic. As we return to life post-COVID, companies do not want to give up QR code benefits. It has been estimated that restaurants with QR code menus can save 30 to 50 percent. Digital menus have also been found to persuade people to spendmore because companies can add pictures of food, they otherwise would not have the space for on a traditional menu. The heavy involvement of QR codes seems obvious, but there are criticisms. Some customers tend to have said that although the virtual menus are convenient when they go to a fine dining establishment, they prefer a physical menu.
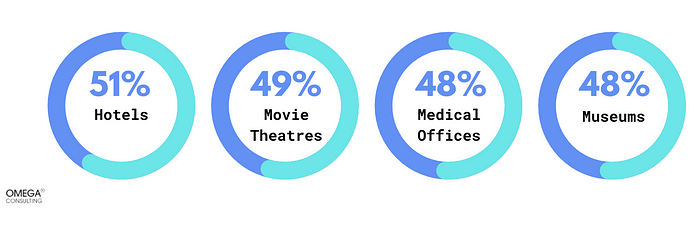
Exhibit 4
Sectors using QR Code in day- day operationsAccording to a recent survey conducted by Adweek and Morning Consult. In Hotels (51%), movie theaters (49%), medical offices (48%) and museums (48%) people would like to use QR technology. As preferences of the consumer continue to evolve, it is anticipated that QR codes will continue to play a significant role in numerous industries post-pandemic.
Marketing Opportunities
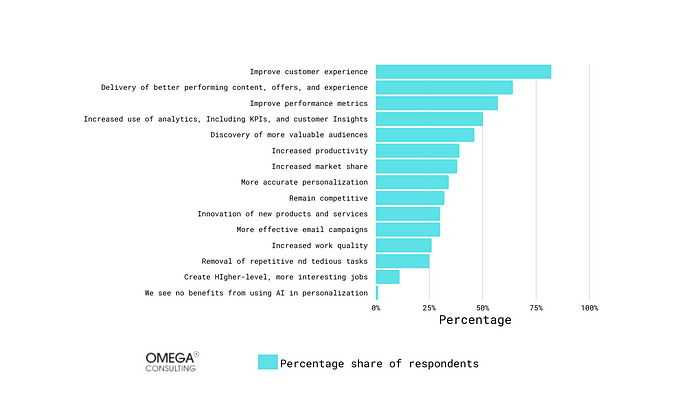
Marketing is a very costly part of running a business. Companies admire the cost-effectiveness of QR codes and all the analytics you can keep on your marketing campaign. Companies like Coca-Cola have had campaigns where they have placed a QR code on every one of their cans that customers could scan and sign up to win prizes and cash rewards. Businesses want to market themselves by focusing on making things as feasible as possible for customers. Over the past decade, companies have become very innovative in using QR codes. Businesses have implemented QR codes so well into everyday life that you most likely don’t notice how often you use them. One of the very first companies that specialized in mobile payment was PayPal which implements a brilliant way to use QR codes on their app; that is, instead of typing a person’s username in when you want to send or request money from them, you can simply scan a QR code on their phone. You will promptly be sent to a screen to do as you like. More modern companies such as Venmo and CashApp have had this feature since their inception. Companies use QR codes for more than just marketing; they also want to make things as convenient for customers/users as possible. Airlines have added QR codes to their boarding passes, so customers can simply scan them and add their pass straight to their phone, so customers don’t have to hold onto a piece of paper while navigating the airport. This makes everyone’s life much easier and tremendously makes things easier for the passenger.Exhibit 5
Leading reasons to use AI for marketing personalizationThe below statistics depicts the percentage of B2B and B2C professionals’ reason to use AI for marketing personalization in the field of financial services, retail, technology, travel and hospitality Industries.
Conclusion
The invention of the QR code took place in the year 1994, and for many years it was one of the world’s best-kept secrets. Companies eventually figured out it was a genius technology but could not properly implement it the way they wanted because the technology was not advanced enough to keep up with the QR code. A device that was created to help track shipping and production has begun to revolutionize aspects of society and business that we could have never even imagined. Companies will continue to find ways to involve QR codes in every single element they can because there are simply far too many advantages to using them. It took a global pandemic to advance the use of QR codes. Consumers are adjusting to a reality where traditional experiences will soon become digitalized, and that is a reality that we must all adapt to. Companies will inevitably incorporate this technology better than others, and there will surely be companies that will elevate themselves dramatically because of their QR code incorporation. The idea of everything becoming might not be well accepted by everyone and they will be reluctant to make that change. Still, like everything else in our society, people will adapt, becoming the new normal.Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions