- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Technology
- By Omega Team
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing industries like healthcare, finance, education, and entertainment, but its rapid advancement also brings significant ethical, social, and regulatory challenges. Concerns about bias, privacy, security, and the potential misuse of AI highlight the urgent need for a structured and responsible approach. Responsible AI, an evolving discipline, ensures that AI systems are fair, transparent, and accountable while aligning with human values. It emphasizes ethical decision-making, robust governance, and continuous monitoring to prevent unintended consequences. Organizations must adopt responsible AI principles to build trust, mitigate risks, and maximize AI’s benefits. Policymakers, businesses, and researchers must collaborate to establish clear guidelines and standards that promote ethical AI innovation. This article explores the key aspects of responsible AI, its challenges, and strategies for businesses and policymakers to implement ethical AI practices effectively.
Understanding Responsible AI
Responsible AI refers to the development and deployment of AI systems in a way that aligns with ethical guidelines, legal compliance, and societal values. It ensures AI is used for the benefit of humanity while mitigating risks associated with bias, discrimination, and misuse. Understanding responsible AI requires organizations to assess AI’s impact on different stakeholders, ensure fairness in algorithms, and create governance structures for accountability. This involves continuous evaluation of AI models, transparent decision-making processes, and the incorporation of diverse perspectives to minimize unintended harm. Companies must establish clear policies and ethical frameworks to guide AI usage, ensuring alignment with human rights and regulatory standards. Additionally, fostering AI literacy among employees and stakeholders helps in building a culture of responsibility and awareness. By prioritizing responsible AI, businesses can enhance trust, drive innovation, and create sustainable AI solutions that benefit society as a whole.
Core Principles of Responsible AI
Fairness and Bias Mitigation: AI systems must be designed to minimize biases and promote fairness. Bias in AI can arise from biased training data, algorithmic design, or systemic inequalities. Organizations must take proactive steps to detect and mitigate bias through diverse data collection, bias audits, and algorithmic fairness techniques. Regular assessments and updates to training data can help reduce disparities, ensuring AI-driven decisions do not disproportionately impact certain groups. Encouraging interdisciplinary collaboration between data scientists, ethicists, and domain experts can further enhance fairness in AI systems.
Transparency and Explainability: AI models, especially complex ones like deep learning systems, often function as “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand their decision-making processes. Responsible AI requires that AI systems be interpretable and explainable so that users can trust and understand their outputs. Explainability can be achieved through model documentation, visualization tools, and interpretable algorithms. Implementing AI transparency reports can help stakeholders assess model behavior, while user-friendly explanations ensure that AI-driven decisions remain accessible to non-technical audiences. Open-source frameworks and standardized interpretability tools can further enhance transparency.
Accountability and Governance: Organizations deploying AI must establish clear accountability frameworks. This includes defining roles and responsibilities for AI development, ensuring oversight mechanisms, and implementing ethical guidelines. AI governance frameworks should align with international ethical standards and local regulations to ensure compliance. Regular audits, risk assessments, and AI ethics committees can help ensure responsible deployment and adherence to ethical standards. Clear escalation processes should be in place to address any unintended consequences arising from AI applications.
Privacy and Security: AI systems process vast amounts of personal and sensitive data, making privacy and security paramount. Organizations must adhere to data protection regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, to ensure that data is collected, stored, and used responsibly. Techniques like differential privacy, encryption, and federated learning can help safeguard user data. Robust access control mechanisms and data anonymization practices further strengthen security, reducing risks associated with data breaches. Continuous monitoring and threat detection can help mitigate cybersecurity vulnerabilities in AI-driven applications.
Human-Centric AI: AI should be designed to augment human capabilities rather than replace them. Human-in-the-loop (HITL) approaches ensure that AI systems remain aligned with human values by incorporating human judgment and oversight in critical decision-making processes. Encouraging user feedback and iterative model improvements can enhance AI usability while ensuring ethical considerations are met. AI should be designed with inclusivity in mind, ensuring it benefits a diverse range of users across different demographics and industries.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact: AI models, especially large-scale deep learning models, consume significant computational resources, leading to high energy consumption. Sustainable AI practices involve optimizing model efficiency, using energy-efficient hardware, and exploring greener AI training methods. Organizations should invest in carbon-conscious AI practices, such as renewable energy sources for data centers, to minimize their environmental footprint. Developing lightweight AI models and promoting model-sharing strategies can also contribute to a more sustainable AI ecosystem.
Applications of Responsible AI
Healthcare: AI is revolutionizing healthcare by enabling accurate diagnostics, predictive analytics, and personalized treatment plans. Responsible AI ensures these applications are fair, transparent, and protect patient privacy. It is crucial to prevent biases in medical AI systems that could lead to misdiagnoses or disparities in treatment. AI must also comply with regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR to ensure patient data security. Implementing explainable AI in healthcare allows medical professionals to understand AI-generated recommendations, improving trust and adoption. Additionally, AI should enhance healthcare accessibility, ensuring underserved communities benefit from AI-driven innovations.
Finance: AI-driven financial models help detect fraud, automate risk assessment, and enhance customer experiences. Ensuring responsible AI in finance involves minimizing biases in credit scoring and maintaining regulatory compliance. AI should not disproportionately disadvantage specific demographics when making lending or investment decisions. Transparency in AI-powered financial tools is essential to help users understand automated decisions regarding loans, insurance, and investments. Cybersecurity measures must also be robust to protect against AI-driven fraud and financial data breaches. Furthermore, AI-driven automation should enhance financial inclusivity by providing fair and equal access to banking services.
Retail and E-Commerce: AI powers recommendation engines, personalized marketing, and demand forecasting in retail. Responsible AI practices ensure ethical advertising, fair pricing, and unbiased product recommendations. AI-driven pricing strategies should avoid discriminatory practices, ensuring that pricing models remain transparent and justifiable. Personalization algorithms should respect consumer privacy by complying with data protection regulations and allowing users to opt out. AI should be designed to prevent manipulative marketing tactics, ensuring ethical engagement with consumers. Additionally, retailers can use AI to promote sustainability by optimizing supply chains and reducing waste.
Education: AI-driven learning platforms personalize education and improve accessibility. Responsible AI ensures these platforms are inclusive, free from bias, and respect student data privacy. AI-based assessments should be fair and prevent discrimination against students from diverse backgrounds. Data privacy policies must be enforced to protect students’ personal and academic records from misuse. AI-powered tools should be designed to support educators rather than replace them, fostering a collaborative learning environment. Additionally, AI can enhance accessibility for students with disabilities, ensuring equitable learning opportunities for all.
Smart Cities and Public Services: AI helps optimize traffic management, public safety, and energy consumption in smart cities. Responsible AI ensures these applications are transparent, equitable, and consider the broader societal impact. AI-driven surveillance and law enforcement tools should be designed with strict ethical guidelines to prevent biases and safeguard civil rights. Public transportation and infrastructure AI systems should prioritize accessibility and inclusivity for all citizens. Governments must implement policies that ensure AI-powered public services do not disproportionately benefit certain groups while neglecting others. Moreover, AI can play a vital role in environmental sustainability by optimizing energy consumption and reducing urban pollution.
Benefits of Responsible AI
Enhancing Trust and Public Confidence: Organizations that implement responsible AI practices build trust among users, customers, and regulators, ensuring AI adoption is widely accepted. Transparent AI operations help alleviate fears of AI misuse and unethical behavior. Providing clear explanations for AI-driven decisions enables greater user acceptance and accountability. AI developers and companies should engage with the public through open discussions about AI ethics to foster trust. Additionally, strong ethical frameworks can prevent misinformation and AI-generated content manipulation, ensuring responsible AI use.
Reducing Legal and Compliance Risks: By aligning with ethical standards and regulatory requirements, businesses can avoid legal liabilities and ensure compliance with evolving AI regulations. AI governance policies should be regularly updated to align with international data privacy and security laws. Companies that proactively implement responsible AI practices can mitigate potential legal disputes related to biased decision-making or data misuse. Establishing AI ethics committees can help organizations stay ahead of regulatory changes and industry best practices. Moreover, responsible AI practices reduce reputational risks, ensuring that businesses maintain credibility and consumer trust.
Improving Decision-Making: Fair and transparent AI systems enhance decision-making accuracy and reliability, leading to better business outcomes and societal benefits. AI should complement human decision-makers by providing data-driven insights while allowing for human judgment in critical areas. Transparent AI models help businesses refine strategies by providing clear and justifiable recommendations. Reducing bias in AI-powered decision-making ensures that choices are made based on merit rather than systemic discrimination. Additionally, AI-driven analytics can improve efficiency in industries such as healthcare, finance, and logistics by optimizing resource allocation.
Promoting Ethical Innovation: Responsible AI encourages innovation that aligns with societal values, driving the development of AI solutions that benefit humanity while mitigating risks. Companies investing in ethical AI research can gain a competitive advantage by positioning themselves as leaders in responsible AI development. Ethical AI innovation ensures that technological advancements contribute positively to society rather than creating harm. AI-driven solutions should be designed to address global challenges such as climate change, healthcare access, and financial inclusivity. Additionally, fostering collaborations between AI developers, policymakers, and ethicists can lead to groundbreaking innovations that prioritize ethics and sustainability.
Mitigating Bias and Discrimination: By proactively addressing bias, responsible AI ensures equitable outcomes, reducing discriminatory practices and promoting fairness across industries. Regular AI audits and fairness assessments should be conducted to identify and mitigate biases in algorithms. Inclusive datasets should be used to train AI models, ensuring that diverse perspectives are represented in AI decision-making. AI systems must be regularly tested and refined to prevent unintended discrimination in hiring, lending, and law enforcement applications. Additionally, interdisciplinary teams of ethicists, sociologists, and data scientists should collaborate to ensure AI systems align with fairness and social responsibility principles.
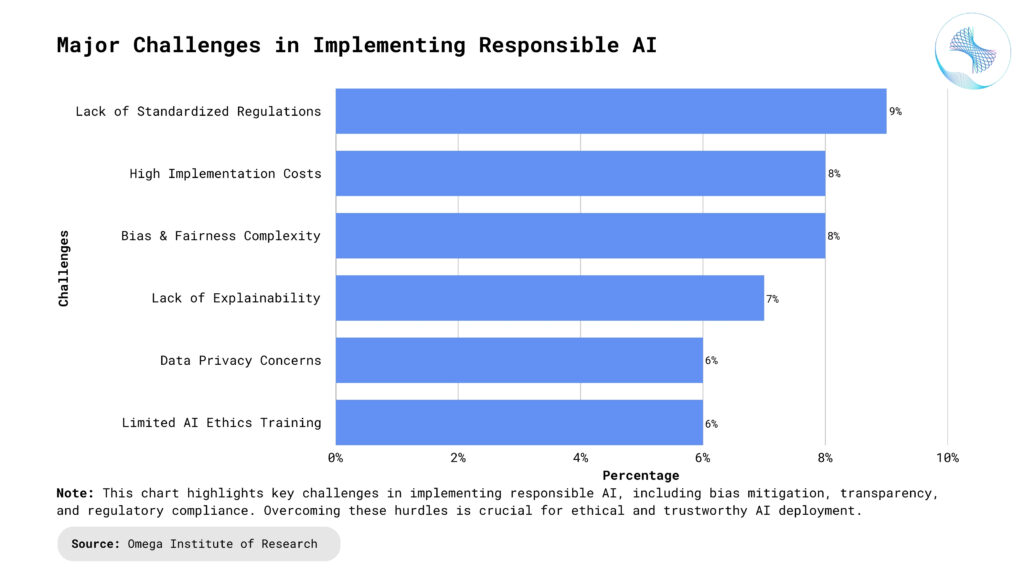
Challenges in Implementing Responsible AI
Data Quality and Bias: Ensuring high-quality, unbiased data is one of the biggest challenges in AI. Many datasets reflect historical biases, which can perpetuate discrimination if not properly addressed. Data collection processes must be carefully designed to ensure diverse representation and eliminate systemic biases. Continuous monitoring and retraining of AI models are necessary to maintain fairness as new data becomes available. Organizations must also implement bias-mitigation strategies, such as re-sampling, re-weighting, and adversarial debiasing techniques. Furthermore, transparency in dataset sources and annotation processes is crucial to ensure ethical AI applications.
Balancing Transparency and Performance: Highly interpretable models may not always achieve the best performance, while complex models with high accuracy may lack transparency. Striking a balance between performance and explainability is a continuous challenge. Developers must choose appropriate AI models based on the risk and sensitivity of their applications—high-stakes domains like healthcare and finance require greater transparency. Techniques such as model distillation can help make complex models more interpretable without sacrificing too much accuracy. Additionally, regulatory bodies are increasingly demanding AI explainability, making it a necessary trade-off in AI system design. Implementing user-friendly visualization tools can further bridge the gap between transparency and performance.
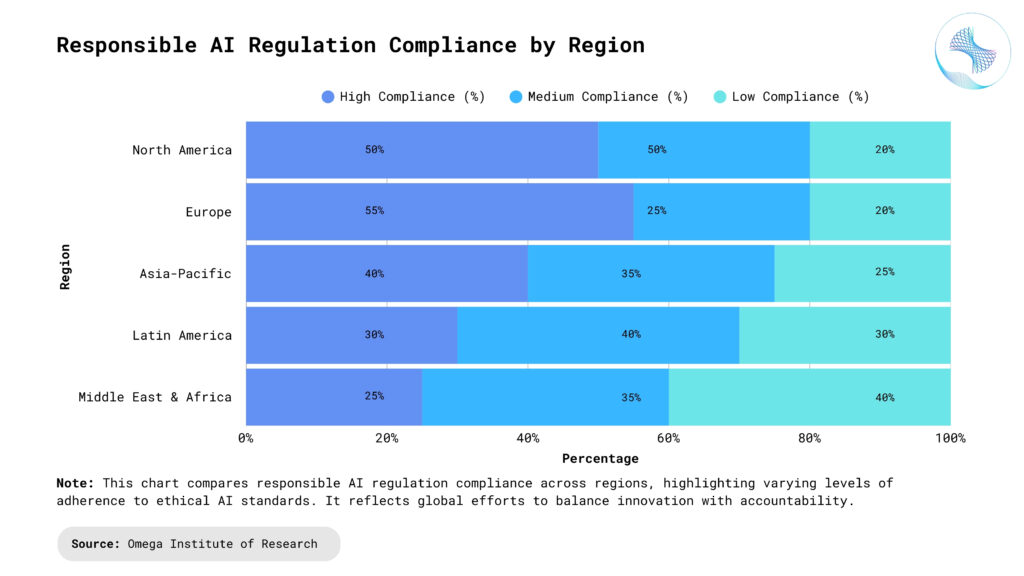
Regulatory Compliance and Global Variations: Different countries have varying AI regulations, making compliance complex for global organizations. Companies must stay updated with evolving AI laws and ensure their systems adhere to region-specific requirements. Regulations like GDPR in Europe and the AI Act introduce strict guidelines on AI deployment, requiring businesses to maintain transparency and accountability. Compliance efforts should include legal teams and AI ethicists to interpret and implement the required governance policies. Organizations operating in multiple jurisdictions must develop adaptive AI frameworks that align with diverse regulatory landscapes. Failure to comply with AI regulations can result in financial penalties, reputational damage, and loss of consumer trust.
Security Risks and Adversarial Attacks: AI systems are vulnerable to adversarial attacks, where malicious actors manipulate inputs to deceive the model. Developing robust AI security mechanisms is crucial to prevent such threats. Hackers can exploit weaknesses in AI models to generate misleading predictions, posing risks in sectors like finance, healthcare, and cybersecurity. Techniques like adversarial training and robust model testing can enhance AI security by making models resilient against attacks. AI developers must incorporate multi-layered security protocols, including encryption and anomaly detection, to safeguard AI applications. Continuous threat monitoring and real-time updates are essential to counter evolving adversarial strategies.
Best Practices for Implementing Responsible AI
Establish AI Ethics Committees: Organizations should create AI ethics committees comprising diverse stakeholders, including ethicists, policymakers, engineers, and end-users. These committees can guide AI development and ensure ethical considerations are prioritized. Having an independent ethics board ensures accountability in AI projects and prevents potential biases from going unnoticed. Ethical committees should conduct regular AI impact assessments to evaluate societal and legal implications. Establishing clear AI governance policies ensures that AI development aligns with corporate values and ethical standards. Furthermore, cross-functional collaboration within these committees strengthens the integration of ethical AI across various departments.
Conduct Bias Audits and Fairness Testing: Regularly auditing AI models for biases and fairness helps in identifying and mitigating potential ethical risks. Open-source tools like IBM AI Fairness 360 and Google’s What-If Tool can assist in fairness testing. Organizations should implement ongoing fairness monitoring to detect bias drift over time. Bias audits should be performed during model development, deployment, and post-production phases to ensure continuous fairness. Transparent documentation of bias detection and mitigation strategies fosters trust among users and regulatory bodies. Engaging external auditors or third-party reviewers can provide an unbiased evaluation of AI fairness.
Implement Explainability Techniques: Using techniques like SHAP (SHapley Additive Explanations) and LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) can enhance model transparency and provide insights into AI decision-making processes. Explainability frameworks should be tailored to different stakeholders, ensuring both technical and non-technical users can understand AI outputs. Providing interactive visualization tools can further improve the accessibility of AI explanations for end-users. Companies should document and communicate the rationale behind AI-driven decisions to ensure accountability. The use of human-in-the-loop approaches can further validate AI explanations and improve system reliability.
Adopt Privacy-Preserving AI Methods: Techniques such as federated learning, homomorphic encryption, and synthetic data generation help protect user privacy while enabling AI innovation. Federated learning allows AI models to be trained across decentralized data sources, reducing the risk of data breaches. Homomorphic encryption enables computation on encrypted data, ensuring privacy without compromising functionality. Synthetic data generation helps in creating diverse datasets while safeguarding sensitive user information. Implementing privacy-enhancing AI techniques is crucial for industries dealing with sensitive data, such as healthcare and finance.
Engage in Ethical AI Research and Collaboration: Companies should collaborate with academic institutions, industry peers, and regulatory bodies to advance ethical AI research and establish best practices. Open collaboration enables the development of standardized AI ethics frameworks that can be widely adopted. Engaging in public discourse on AI ethics fosters transparency and builds public trust in AI applications. Joint research initiatives can lead to innovations in responsible AI methodologies, improving fairness, transparency, and security. Establishing partnerships with governmental and non-governmental organizations ensures AI is developed in alignment with societal needs.
The Role of AI in Social Good
Healthcare and AI Ethics: AI-driven innovations in healthcare, such as diagnostics, predictive analytics, and personalized medicine, require ethical considerations to ensure patient data privacy, fairness in treatment, and avoidance of algorithmic bias. AI models should undergo rigorous validation and testing to ensure accurate and unbiased medical recommendations. Ethical AI in healthcare must prioritize patient consent and transparency in AI-assisted diagnoses. Regulatory frameworks such as HIPAA and GDPR must be integrated into AI-driven healthcare solutions to maintain compliance. Additionally, AI should be designed to assist medical professionals rather than replace human expertise in critical decision-making.
AI for Climate Change Mitigation: AI can support sustainability efforts by optimizing energy usage, predicting climate patterns, and aiding in resource management. Ethical AI ensures that environmental applications align with long-term sustainability goals. AI-driven climate models can help governments and organizations make data-driven decisions on carbon emissions reduction. Smart grid technology powered by AI can optimize energy distribution, reducing waste and increasing efficiency. AI-powered monitoring systems can track deforestation and biodiversity loss, aiding conservation efforts. Additionally, sustainable AI practices should prioritize energy-efficient model training to reduce the carbon footprint of AI systems.
AI in Education and Workforce Development: AI-powered personalized learning and workforce training solutions should be designed to be inclusive, unbiased, and accessible to diverse populations to bridge digital and educational gaps. AI-driven tutoring systems must ensure equitable access to quality education, regardless of socioeconomic status. Workforce training programs should incorporate AI-driven skills assessments to identify and address individual learning needs. AI should support teachers and trainers rather than replace human educators, ensuring a balanced approach to education. Additionally, AI-based career guidance tools can help students and professionals make informed decisions about their future careers.
Future of Responsible AI
The future of AI is deeply tied to ethical considerations and regulatory frameworks. As AI adoption grows, we can expect increased regulatory scrutiny, stronger ethical guidelines, and more robust AI governance mechanisms. Innovations in AI fairness, explainability, and sustainability will drive the development of more responsible AI systems. Advances in privacy-preserving AI, such as differential privacy and federated learning, will help mitigate risks associated with data security. AI-driven automation will require enhanced human oversight to prevent unintended consequences and ensure ethical alignment.
Organizations that prioritize responsible AI today will gain a competitive edge by building trust with users, regulators, and society. By embedding ethical principles into AI development and deployment, businesses can harness the power of AI while ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability. Collaboration between governments, tech leaders, and research institutions will be crucial in shaping global AI policies. The integration of AI ethics into educational curricula will help train the next generation of responsible AI practitioners. Ultimately, a proactive approach to AI ethics will drive sustainable innovation and long-term societal benefits.
Conclusion
Responsible AI is not just an ethical obligation but a business imperative, requiring organizations to proactively address fairness, transparency, accountability, privacy, and sustainability challenges as AI continues to reshape industries. By adopting responsible AI practices, businesses can create ethical, trustworthy systems that align with human values while fostering innovation, inclusivity, and risk mitigation. Companies that integrate ethical AI principles will gain a competitive edge, navigate evolving regulatory landscapes, and build long-term trust with users and stakeholders. Collaboration among policymakers, technology leaders, and researchers will be essential in establishing global AI governance frameworks that ensure AI serves humanity in a fair, transparent, and sustainable manner. As AI advances, maintaining a long-term commitment to responsible AI will be crucial in driving ethical innovation and maximizing AI’s benefits for society.
- https://blog.google/technology/ai/responsible-ai-2024-report-ongoing-work/
- https://www.dasca.org/world-of-data-science/article/responsible-ai-ethics-challenges-and-benefits
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00146-024-01880-9
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/machine-learning/concept-responsible-ai?view=azureml-api-2
- https://www.ibm.com/think/insights/responsible-ai-is-a-competitive-advantage
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions