- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Information Technology
- By Omega Team
Edge computing is a distributed computing model that puts processing and data management closer to the point of use to increase response times and reduce bandwidth consumption. Edge computing brings workloads closer to the sources of data and the steps that must be taken. It deals with the enormous volume and complexities of data produced by connected devices. It’s getting increasingly necessary to respond rapidly to data coming in from remote edge devices and servers. Edge computing is revolutionizing how data is handled, stored, and distributed from billions of computers all over the world.
Edge computing has the following advantages & disadvantages:
- It eliminates the use of cloud services.
- Faster and more reliable answers.
- No communication gaps.
- There is a need for additional resources
The Operation of Edge Computing
Edge computing refers to data processing that happens at the network’s edge to minimize latency and pressure on cloud compute and data center services. Edge computing happens in intelligent systems right where sensors and other instruments are collecting and analyzing data to speed up the processing before the devices link to the Internet of Things (IoT) and pass the data on to enterprise applications and professionals for further processing. The efficiency of edge computing is the major reason for its growth. All of the information gathered must be processed. With the growing volume of IoT data, more and more processing is happening at the edge and devices are giving desired results faster. Edge computing allows data from the internet of things to be analyzed at the edge before being sent to a data center or cloud.
Figure 1: Overview of Edge Computing Architecture
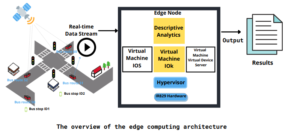
Nokia networks launched Mobile Edge Computing with the aim of enabling a base station to act as an intelligent service node capable of collecting real-time network data such as cell congestion and subscriber locations. This edge computing platform consists of a mobile edge node. The platform supports running different descriptive analytics tasks at the mobile edge node. The scenario can be described as a moving bus that generates real-time data streams which are fetched by a mobile edge node installed in this bus which performs pre-processing tasks as well.
It performs various tasks for the desired results:
- Real-Time Data Streaming
- Mobile Edge Node
- Data Pre-Processing at the Mobile Edge Node
- Descriptive Analytics at the Mobile Edge Node
Figure 2: Total trip times during the week
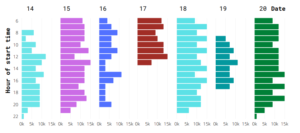
The results from descriptive analytics platforms are visualized to provide actionable information about what is happening in the transit network. The output of descriptive analytics platforms is visualized to provide actionable information. The focus was on some prominent abnormalities found in the transit network and some of them were recorded. It was recorded that buses didn’t run from 6 to 7 a.m. on February 14th, and there were no trips at 2 a.m. on the 15th, 16th, and 18th. Furthermore, missing trips occurred after 12 a.m. on the 17th, early in the morning (6 a.m. and 7 a.m.) on the 19th, and in the evening on the 19th (18h to 22h). This is important real-time data for a transit manager to have for a single bus trip or a series of trips throughout the day.
Figure 3: Number of moves and Stops at 8th, 12th
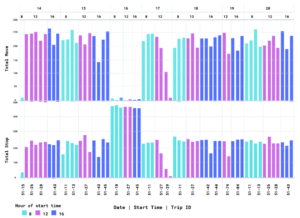
The computation of a total trip time in real-time is an interesting result from descriptive analytics. The transit manager will keep an eye on the hourly trends and be mindful of any outliers in real time. It was also important to note that identical real-time trends appeared on different days of the week. Any of them may have arisen as a result of road congestion and snowstorms. At different times of the day and on different days of the week, the allocation of trips is irregular.
Figure 4: Total Number of trips and average trip time
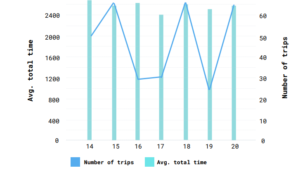
The total number of trips and the average duration of all trips in the graph is explained, there are many outliers to be found. The 16th digital and mobile banking initiatives have created a demand for fast payments. Also, the industry’s adoption of blockchain technology and mobile payments are two factors that are fueling and 17th of February, in particular, saw 30 and 31 trips. On weekdays, there were normally over 60 journeys. Despite the fact that the number of trips on February 14th, 16th, 17th, and 19th is smaller than on other days, their average total time is close, and some of them have the highest average total time. The average travel time column indicates that a trip takes around 40-45 minutes on average.
Figure 5: Average number of moves and stops
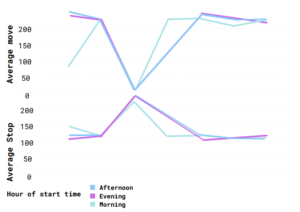
The proposed edge computing platform has the potential to scale up to an entire transit system. It also paves the way for new analytical services to be developed at the edge network in the near future to address the challenge of rapidly rising data provided by edge devices and sensors. We used this experiment to demonstrate the benefits of real-time descriptive analysis in gaining new insights and assisting the actionable decision making. Moreover, we see the potential for our edge analytical platform to be used in other applications.
Key Marketing Trends
1. The financial services sector is expected to be the one to implement Edge Computing technologies: The growing use of digital and mobile banking initiatives has created a demand for fast payments. Also, the industry’s adoption of blockchain technology and mobile payments are two factors that are fueling the market for edge computing. For example, through its bPay service, Barclays Bank has adopted several technological innovations by supporting payment through smartwatches such as the Apple Watch and Fitbit.
2. Partnerships between cloud and edge providers are being developed: Edge computing will be a part of a wider computing fabric that includes public cloud platforms as well as on-premises locations. Organizations are already storing more data at the edge, and this trend will continue as more use cases for the technology are developed. Organizations would most likely design their IT environments so that cloud services are used for heavy-duty applications and edge computing is used for lighter applications.
3. Edge computing in manufacturing network: Edge computing’s reduced latency problems could lead to quicker, more flexible improvements in manufacturing workflows, allowing for real-time analysis and action. This might include turning off a computer until it overheats. Edge computing can help in smart manufacturing.
4. Edge computing can be used for agriculture and smart farms: Edge computing is a good cost-effective option for the hostile conditions of the farms that may have bandwidth and connectivity concerns. Sensors could be used to monitor soil conditions, temperature, and weather conditions on smart farms. As data becomes available, edge computing could provide farmers with detailed insight quickly.
5. The adoption of a linked ecosystem is made easier by edge computing: Edge not only allows and improves IoT usage but also makes it easier for businesses to participate in the connected ecosystem by reducing network latency and bandwidth.
6. Data protection is improved by Edge Computing: In comparison to the cloud, data quality at the edge improves, lowering internet and data prices. The user interface is improved by the extra layer of protection at the edge.” Edge computing isn’t reliant on a particular application or storage location. Rather, it dissolves processes through a large number of different devices.
7. COVID-19 drives innovation at the edge: Nothing like a pandemic to deny technology’s effectiveness. From social distancing to thermal imaging, safety system assurance, and organizational improvements such as regular cleaning and sanitation operations, there are a variety of options available. And Edge computing has helped everything fall into in a very short time.
Some upcoming trends for edge computing in 2021 are:
- Edge computing: EdgeOps
- Edge computing: Advertising
- Edge computing: Virtual reality
- Edge computing: Digital transformation
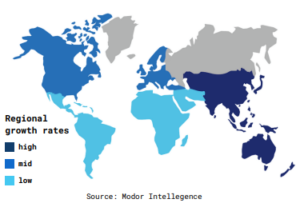
Figure 6: Edge computing market growth rate by region (2019-2024)
The Conclusion from the Research
Edge computing has become a popular topic of study. Edge computing offers data storage and computing at the network’s edge, as well as Internet intelligent services close by, assisting in the digital transformation of various industries and meeting the data diversification needs of various industries. IoT devices are growing rapidly across the globe, from wearables to cars to robots. Data generation will continue to rise as we move toward a more connected ecosystem, particularly as 5G technology takes off and enables faster connections. Although data management, retrieval, and storage has historically been handled by a centralized cloud or data center, each has its own set of limitations.
Future Outlook
The market for edge computing is expanding at a rapid pace. In 2024, spending on edge computing is expected to reach $250 billion. Edge computing services are expanding from the data center and cloud to the network edge, telco edge, and device edge. If the edge computing market continues to expand at a breakneck pace, as many analysts predict, more edge data centers will be built closer to where data is produced. Edge computing’s future will certainly be possible. Edge computing can combine with the use of data to turn insight into behavior that supports companies and their customers, thanks to artificial intelligence and machine learning. It will ultimately be regarded like any other location where applications can be put in a consistent and uncompromised manner.
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions