- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Information Technology
- By Omega Team

Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a transformative technology that has gained significant momentum in the business world. It involves the use of software robots or “bots” to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks, enhancing efficiency and enabling employees to focus on higher-value activities. Automation has become a vital component of modern business strategies, enabling organizations to streamline their operations and gain a competitive edge. This article provides an in-depth exploration of RPA, covering its definition, working principles, benefits, use cases, and future trends.
Understanding Robotic Process Automation
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that utilizes software robots or bots to mimic human actions and interact with digital systems. These bots are designed to execute predefined rules and algorithms, performing tasks that are repetitive and rule-based in nature. RPA allows organizations to automate various activities, such as data entry, data extraction, report generation, and more, without the need for complex system integrations.
The Mechanism of Robotic Process Automation
RPA interacts with user interfaces of existing applications and systems, navigating through screens, inputting to operate by following predefined instructions data and triggering responses. This technology operates non-invasively, sitting on top of existing applications and systems, and it can handle a wide array of tasks across various platforms. The typical steps involved in an RPA process include bot initialization, process execution, data processing, output generation, and task completion.
The Benefits of Embracing Robotic Process Automation
Robotic Process Automation offers several advantages that significantly impact organizational efficiency and productivity:
Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: RPA automates repetitive tasks, enabling employees to focus on higher-value activities, thereby boosting productivity.
Accuracy and Error Reduction: Bots perform tasks with high accuracy, reducing the risk of human errors associated with manual data entry.
Cost Savings: RPA leads to significant cost savings in labor, time, and operational expenses due to automation.
Scalability: RPA can easily scale to handle increased workloads without requiring additional human resources.
Compliance and Audit-ability: RPA provides a structured and auditable way of executing processes, ensuring regulatory compliance.
Quick Implementation: Implementing RPA involves minimal disruption to existing systems and processes, enabling organizations to realize benefits relatively quickly.
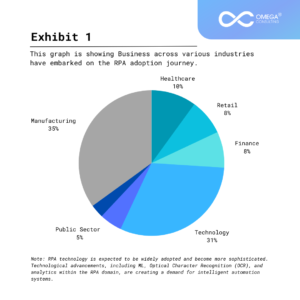
Practical Applications of Robotic Process Automation
Robotic Process Automation finds applications across various industries and business functions:
Finance and Accounting: Automating financial processes, such as reconciliation, report generation, and compliance reporting.
Human Resources: Automating HR processes, including employee onboarding, leave requests, and benefits administration.
Customer Service: Automating responses to customer inquiries and routing them to the appropriate departments for resolution.
Healthcare: Automating appointment scheduling, claims processing, and billing.
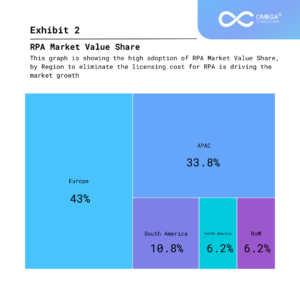
How Combining RPA and AI Can Digitally Transform Your Organization
In the contemporary business landscape, digital transformation is no longer an option but a necessity for organizations striving to stay competitive and relevant. Leveraging emerging technologies to enhance operations, automate processes, and derive actionable insights from data is paramount. Among these technologies, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) stand out as transformative forces. When combined, RPA and AI create a powerful synergy that can significantly accelerate the journey towards digital transformation.
The Speed of Predictability of Execution: RPA vs. Other Automation Technologies
One of the key benefits of RPA is that it can help businesses to improve the speed and predictability of their operations. RPA robots can execute tasks much faster than humans, and they are not prone to human errors. This can lead to significant reductions in processing times and improved accuracy.
The graph you have provided shows the speed of predictability of execution for different types of RPA. As you can see, RPA is the fastest and most predictable type of automation, followed by business process management (BPM) and IT transformation. Outsourcing is the least predictable type of automation, as it is subject to factors such as the performance of the third-party vendor and the quality of the data they provide.
Here are some specific examples of how RPA can be used to improve the speed and predictability of execution in different industries:
- Manufacturing: RPA can be used to automate tasks such as order processing, inventory management, and quality control. This can help manufacturers to reduce production lead times and improve product quality.
- Construction: RPA can be used to automate tasks such as project management, schedule management, and cost control. This can help construction companies to improve project efficiency and reduce costs.
- Healthcare: RPA can be used to automate tasks such as patient registration, medical records management, and insurance processing. This can help healthcare providers to improve patient care and reduce administrative costs.
Understanding Robotic Process Automation and Artificial Intelligence
Robotic Process Automation involves the use of software robots or “bots” to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks. RPA bots emulate human interactions with digital systems and applications, automating tasks like data entry, file manipulation, form processing, and more. RPA excels at enhancing efficiency, reducing errors, and enabling round-the-clock task execution.

AI: Intelligence and Decision-Making
Artificial Intelligence, on the other hand, refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines. AI technologies like machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision enable systems to learn, reason, and make decisions. AI can analyze and derive insights from vast amounts of data, enabling organizations to automate complex tasks and make informed decisions.
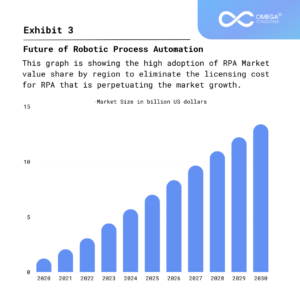
Future of Robotic Process Automation
The future of RPA is promising, with advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) playing a significant role. Integration with cognitive technologies will enable RPA bots to handle more complex tasks and engage in sophisticated interactions. Additionally, the integration of RPA with technologies such as natural language processing (NLP) and predictive analytics will further enhance its capabilities. RPA is expected to become an integral part of digital transformation initiatives, driving efficiency and innovation across various industries.
Conclusion
Robotic Process Automation is a powerful tool for organizations aiming to optimize their operations and achieve greater efficiency. By automating routine and rule-based tasks, RPA frees up human resources to focus on strategic and creative endeavors, ultimately leading to improved productivity and a competitive edge in today’s dynamic business landscape. As technology continues to advance, RPA is set to play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping the future of work.
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions