- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Marketing & Advertising
- By Omega Team
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is a group of activities carried out with the purpose of making a website page rank higher on SERP (search engine results page). The primary difference between Google Ads and SEO is that SEO improves ranking organically, whereas Google ads is a PPC (pay-per-click) advertising solution. Therefore, SEO is a comprehensive activity that produces results over time, while PPC is a method that generates immediate results within a short period of time, often with a targeted audience.
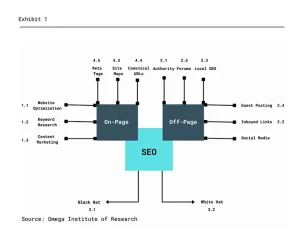
On-Page SEO
1.1 Website OptimizationSEO involves technical factors related to the website that are taken into consideration by search engines when crawling. The perfect time to address these factors is at the onset because the complexity of a website grows with time. The more content on the website and the older the web domain is, the more complicated it is to improve these aspects. The design of the website and the architecture should be in sync with the requirements of the visitor. From the website viewer’s point of view, it should answer questions like:
- Does this website have the information I am looking for?
- What action cant I take to meet my goal?
The search bar should be clearly visible, which makes the navigation of the visitor easy.
Page load time highly affects the performance of the website. According to HubSpot, the ideal page load time is 1.5 seconds, which the top 20% of web pages maintain. It is equally important to optimize the website for crawlers.
Some of the ways to achieve this include providing the crawlers with the Sitemap. Sitemaps must be linked to the Google Search Console and the Bing Webmaster Tools. Interlinking the website appropriately is imperative to decrease the bounce rate. Mobile Optimization of the website is extremely important, as not doing so will hamper a major part of potential traffic. Another factor that is taken into account when ranking is user security, which can be conveyed by HTTPS and SSL to indicate that the user visiting the website has a safe connection.
1.2 Keyword Research
Keywords, which are queries that user enters in the SERP to reflect search intent, are one of the most important factors that contribute to the ranking of a page. Therefore, keyword research is the most crucial process within SEO.
On the basis of these keywords/entered queries, the search engines find out the relevant information and present it on the SERP.
Primarily, the keyword should match the search intent of the user, as this not only brings in search traffic but is also critical in driving revenue. It is also important to note that stuffing the content with repeated keywords without adding value to the page is an outdated practice and does not work. This is because Google has grown smart enough to understand the relevancy of the content and the value that it provides to the user.
Hence, it focuses on fulfilling the search intent of the user. When executing SEO for a new website, the keywords should be low in competition and should have decent search volume. This method can help to avoid competing with highly competitive keywords where it is almost impossible to rank for a new website.
It is also important to keep an eye on competitors and analyze what keywords they are targeting. There are a lot of tools available in the market for keyword research, including Uber suggest, Google Keyword Planner, etc.
1.3 Content CreationContent is rightly considered to be the “King,” in the digital marketing industry as it determines whether or not users actually spend time on a website. Consistently publishing relevant and quality content after duly researching and using the right keywords can lead to spectacular results.
Having a content plan is crucial. The first step in a content plan is to define the goal behind creating content. This could be engaging the user, making the user spend time on the website, or prompting the user to take some action. Consequently, based on this goal, one must decide what type of content should be published in order to best achieve it.
For example: If we intend to collect user data such as E-mail IDs, the use of lead magnets can be helpful.
Major content types include (Lead Magnets):
- Blogs
- E-books
- Videos
- Infographics
- User guide
- Templates
- Podcasts
It is important that the content is optimized for ranking before updating it on the website. In order to execute this, there are many tools available in the market. These tools aid in the addition of SEO-friendly meta descriptions, titles, keywords, and custom titles for tags, categories, etc.
The essence of the rule is to insert the keyword two or three times with some modifications because focusing only on density can make the content look like spam. If the site is content-heavy and includes diverse subjects, it is important to have appropriate tags and categories to ease the navigation of the user through the site.
Interlinking can also be extremely helpful as it makes the user stay on the same site and it also makes it easier for crawlers to find relevant content on the site. Implementing these content principles and planning strategies can help ensure that one fully leverages SEO to fulfill the intended goal.
Off-Page SEO
2.1 AuthorityMoz created the ranking factor known as authority. This metric can be anywhere between 1 and 100–the higher the number, the greater the authority. There are two types of authority to work with:
- Page Authority is the rank ability of a specific page.
- Domain Authority is a metric that represents the rank ability of an entire domain.
Authority is a competitive metric and nearly 40 factors are taken into account for the score. Authority can be improved through promoting genuinely helpful content, achieving relevance to the reader, and placing emphasis on quality reviews.
2.2 Inbound Links/Backlinks
An inbound link or backlink for a given website is a link to one of its webpages from some external website. When an external website includes a link in its content that directs the user to our website, it is considered an inbound link. Having more inbound links from websites that publish relevant content can improve the authority of the website which eventually improves the ranking.
The most basic way to accomplish this is to create good quality, original content. Bloggers and specialists will not hesitate to include links to reliable and helpful resources in their content.
2.3 Local SEO
Google my Business: Registering on Google My Business is one of the most important, yet overlooked parts of SEO. According to HubSpot, 46% of all the Google Search queries are looking for local information, and 4 in 5 customers use search engines to find local information.
Hence, opening a Google My Business Account and updating all the information along with using the right keywords in the description can help to rank a business. The image on the right shows how Google My Business Results look in SERP.
Business Listing: A citation is an online reference of a company that usually includes a company’s NAP (name, address, and phone number). It is known as the business listing. For this, the businesses are usually supposed to register with the online business directories. It is important for the businesses that serve local clients.
2.4 Guest Posting/Content Marketing
Content Marketing is often construed to be only an On-Page activity. However, when one composes and publishes a guest blog article on some external website, or posts an infographic that is connected to a leading newspaper, it is also considered to be content marketing.
Guest posting entails posting content to another website in order to cater information and value to their viewer base. Guest posting can be extremely helpful in allowing a website to reach new viewers, get attention from the traffic on a concerned site, and expand its reach.
2.5 Forums
Forums can yield substantial benefits when considered as a part of a marketing strategy. Instead of using forums to create links, one should approach them with a different attitude. Consider using forums to become actively engaged in discussions that relate to your know-how, and to represent yourself as an expert, e.g. Quora.
Black Hat SEO
3.1 Black Hat SEO refers to the practices that involve breaking the search engine rules in order to receive a higher ranking on SERP. It involves practices like Duplicate Content, Keyword Spamming, and Links from the site with content that is not relevant.
White Hat SEO
3.1 White Hat SEO uses long-term and sustainable approaches to building an online presence that benefits the user and drives genuine traffic. White Hat SEO involves putting in relevant Content, Well-labeled images, Standards-compliant HTML, and relevant links and references.
Case Study-Investopedia
Investopedia began with finance and investing dictionary definitions, which meant giving the user a brief definition and then topping it off with a layman’s version and actual instances.
Now, Investopedia provides timely, trustworthy, and implementable financial information for all investors, from first-time investors to experienced money managers. With publishing companies like Bloomberg and MarketWatch constantly churning out finance and investment stories, it’s difficult for any financial firm to attract more customers/viewers with content. However, Investopedia considers Organic Search as their largest traffic source.
In order to optimize their content, these are a few practices they carry out:
- In order to attract organic search, Investopedia makes sure to match the intent of the viewer and tries to tailor the content accordingly.
- It observes if the search interest for a particular topic has increased and tries to find relevant search terms that it can work on.
- Investopedia practices rigorous competitive analysis to understand how they can set their content apart from that of competitors and deliver something unique.
- Optimizing underperforming content is a continuous activity for the company.It has also been proven that updating content in the same URL on time can sometimes be proven better than posting content in new URLs.
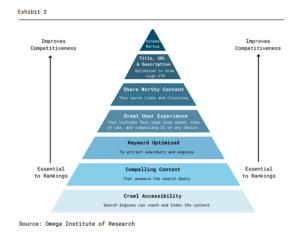
Key Performance Indicators for SEO
Keyword Ranking: A Google search is a simple way to monitor Google ranking for keywords that are relevant to the company or products. The analysis will indicate where the website ranks for the competitive keywords in question.
Visibility in SERPs: Search engine visibility is the number of people who see the webpage in results pages, which can be influenced by the authority of the SERP features.
Click-Through Rate: The percentage of viewers who clicked on the website from the SERP is represented by the click-through rate (CTR).
Bounce Rate: Bounce rate is the percentage of viewers who come to the website but end up leaving without interacting further. If a viewer clicks on more than one page, Google Analytics considers the visit to be an interaction.
Backlinks: Backlinks are among the top criteria for website ranking according to Google.
Page Speed: Page speed is also a significant factor that influences the majority of the other metrics.
Depth of scroll: This metric tracks how far down specific web pages viewers scroll.
Conclusion
Search Engine Optimization is a practice that has been carried out in the Digital Marketing Industry from its inception. The Google search engine focuses on becoming user-centric and providing the users with the exact information that they are looking for. With the same purpose, the algorithms of Google have evolved. Hence, old SEO techniques have now become redundant. Executing SEO as discussed in this article along with maintaining authenticity can aid a business in producing the best results.Contact us at info@omegaconsultingonline.com if you expect sustainable business growth through Digital Marketing.You can also watch a detailed discussion on SEO on our YouTube Channel.
4.1 SERP: SERP stands for search engine research page i.e., the page that displays the set of web pages related to the search query that we entered.
4.2 Crawling: Crawling is the activity that search engines perform by dispatching a team of robots (referred to as crawlers or spiders) to find new and improved content.
4.3 Site Map: A sitemap is essentially an in-depth prototype of how the website will appear. Sitemaps offer search engines useful information about the pages as well as content on the website.
4.4 Canonical URLs: Canonical URLs help to avoid duplicate content issues by highlighting the canonical or “preferred” version of the web pages to the search engine.
4.5 Meta Tags: Meta tags are short descriptions that display on SERP what a web page is about.
4.6 SSL: SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates are a website security measure.
4.7 HTTPS: HTTPS pages will benefit in terms of SEO and will be the de facto result for searchers.
4.8 Lead Magnets: Lead Magnets represent the free document/service that a webpage provides in exchange for the contact details of the user.
4.9 Schema Markup: Schema markup is an organized data vocabulary that allows browsers to better understand the information on the website and serve more relevant results. These markups enable search engines to understand the meaning and relationships of entities mentioned on the website.
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions