- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Healthcare
- By Omega Team
Medication non-adherence is a major problem in which patients do not take their medications as prescribed. Other sorts of technology have been developed to assist patients in taking their prescription, however, these technologies do not track whether or not the patient has consumed their tablets. Because there is no mechanism for doctors and medical professionals to communicate with each other, their forms of medication adherence are not completely reliable. As a result of this problem, the smart pill, often known as a digital pill, was created.
In 2017, the FDA authorized the first digital pill, which contains a built-in digital ingestion tracking system. The pill is named Abilify MyCite and was created by Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. Smart pills are ingestible sensors that can record a variety of physiological measurements after being swallowed. They can also be used to verify that a patient has taken their prescribed medication and to assess the medication’s effects.
How do smart pills work?
The pill can detect whether you have taken medicine or not using a sensor consisting of silicone, copper, and magnesium is included in the pill. A specific electrical signal can be sent from the sensor to a device connected to the pill. When the pill has successfully mingled with the person’s stomach fluids, a signal is sent to the external receiver.
The patient will need to wear an external receiver on a patch on their rib cage during this time. The patch uses Bluetooth to transfer the data it collects to a phone app. The app collects and saves information such as when the drug was taken, the date, and the time. This important information can be communicated with medical professionals, family members, and caregivers to guarantee that the patient has taken a pill keeping in mind all the instructions.
A sensor is placed in a digital pill that can effectively track drug compliance. Essentially, the pill can convey critical information to a medical practitioner from a person’s bloodstream or digestive tract, letting them know how the drug is working, whether the medication is working, and if the patient ever took the pills in the first place.
Digital pills and medication adherence
To get authentic and substantial information on how digital pills are affecting medication adherence, we need few years. There’s still a chance that people who are prescribed smart tablets may wear the skin patch that allows the smart pill to communicate with their phone and provide information and data. Patients may forget to attach the patch to their skin, and some may even refuse to put it on in the first place. The patch must also be replaced every seven days at this time, which may be a concern for some people — forgetting to change the patch is a typical occurrence. But with all these possibilities, digital pills can still be very useful and likely to increase medication adherence in the coming years.
Smart pills market overview
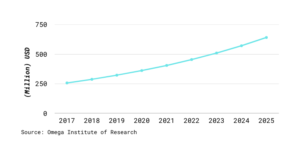
Because smart tablets are non-invasive, they can be a good alternative to invasive procedures like gastrointestinal endoscopy and colonoscopy. From 2018 to 2025, the global smart pill market is predicted to grow at a CAGR of 12.1 percent, from $257 million in 2017 to $650 million in 2025. The rise in the prevalence of lifestyle-related conditions such as obesity, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), stomach ulcers, and others, as well as a significant increase in the senior population, all contribute to the expansion of the smart pill market. Furthermore, higher R&D efforts in the development of smart pills are boosting the market growth.
However, strict government rules regulating the rising usage of these devices, as well as the expensive cost of ingestible sensors, are expected to limit the market’s growth. Furthermore, developments in smart pill technology such as bioelectronics, microprocessor availability, micro-cameras, miniaturization, and others are expected to deliver lucrative opportunities in the future.
Figure 1: Smart Pills Market
Segmentation
The market for smart pills has been categorized by application, target area, disease indication, and end-user. The market has been divided into four categories based on application: capsule endoscopy, drug delivery, patient monitoring, and others. Small bowel capsule endoscopy, controlled capsule endoscopy, colon capsule endoscopy, and colon capsule endoscopy are the different types of capsule endoscopy. The capsule pH monitoring and other patient monitoring segments have been separated.
Smart pills have been divided into four categories based on the target area: esophagus, small intestine, large intestine, and stomach. Esophageal diseases, small bowel diseases, colon diseases, and other diseases make up the disease indication segment. The market has been divided into the Americas, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and the Middle East, and Africa, according to region. The smart pill market in the Americas has been separated into North America and South America, with the US and Canada making up the North American market.
Western Europe and Eastern Europe are the two segments of the European smart pill market. Germany, France, the United Kingdom, Italy, Spain, and the rest of Western Europe are the subcategories of Western Europe. In Asia-Pacific, the smart pill market is divided into Japan, China, India, South Korea, Australia, and the rest of Asia-Pacific. The Middle East and Africa smart pill markets have been divided into two sections: the Middle East and Africa.
Key Benefits
The study examines the smart pill market in full, including current trends and forecasts, to identify potential investment opportunities. A thorough examination of the elements that drive and limit market growth is offered. From 2018 to 2025, a comprehensive quantitative analysis of the industry is offered to assist players in capitalizing on current market opportunities. Extensive research of the industry’s core segments aids in understanding worldwide trends in smart pills. To comprehend the competitive picture of the sector, key competitors and their strategies are offered.
Conclusion
Smart pills are generated to increase medication adherence. They use the sensor to make sure whether the patient has taken the medicine or not. How much it affects medication adherence can only be told after few years of using and having a strong database to make strong conclusions and insights on. By 2025, the global market of smart pills is expected to go up to $650 million with a CAGR of 12.1%. Which is showing some good opportunities for MedTech.
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions