- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Sustainability
- By Omega Team

EV, the acronym used for electric vehicles, is the automobile that operates with an electric motor instead of an ICE (Internal combustion engine), like gasoline-powered cars. A large battery pack is charged by being plugged into a specially designed charging station or outlet at the user’s home.
Electric vehicles work with the help of Lithium-ion batteries having a charging port in many cases which allows the EV to be connected to an external power supply. The traction battery pack which is the “green fuel tank” runs most of the components by acting as the electricity source. The thermal cooling system maintains optimal operating conditions in the EV and an Electrical transmission component finally transfers mechanical power from the traction motor to ultimately drive the EV wheels.
Much like traditional ICE cars, electric vehicles must be refueled in order to be driven. Unlike gas cars, however, most of an EV’s charging will be done at home, rather than on the road. There are three types of chargers for EVs, and each one corresponds to the speed at which they refuel the vehicle. A level one charger plugs into a standard electrical outlet, and it takes between 24 and 48 hours to charge from full to empty. A level two charger uses a specialized outlet or hardwired connection, and it is capable of charging to full in 6 to 8 hours. A level three charger, meanwhile, is only found at dedicated charging stations, and it can completely recharge an electric vehicle in 30 to 45 minutes.
The dramatic increase in speed is possible because they deliver power directly to the battery pack, but the cost is orders of magnitude higher than level one or two chargers. There is a lot of development happening with level three chargers, as they are the ones utilized the most during road trips. Tesla has been building out their Supercharger network, and other automakers entering the EV space have collaborated with charging providers. Both Tesla and legacy automakers are working on solutions to make level three charging faster and more convenient for drivers, so that early adopters of electric vehicles will be able to go for long drives as easily as their gasoline-powered counterparts.
Market Current Trends and Future Forecasting
The global EV market valuation in 2019 was $162.34 Billion, and it was projected to soar to $802.81 billion by 2027. Recent technological advancements in terms of battery performance and private charging infrastructure and proactive government initiatives supplement the growth of the electric vehicle market.
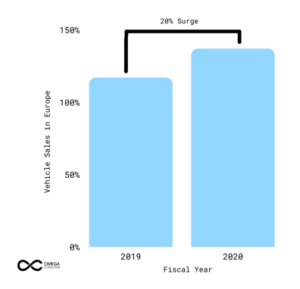
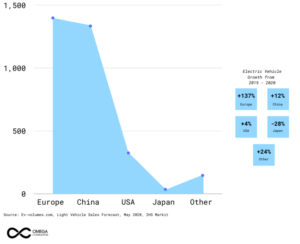
In the end, 2020 has proved to be a benchmark year in terms of global EV sales. Although 2020 started with an unprecedented economic downturn caused by COVID-19, it became a success story for the EVs market in Europe. During 2020, Around 1.4 million BEVs (battery and PHEVs were registered in Europe alone, 137 % more than in 2019, in a vehicle market that slumped by 20 % year-over-year. The combination of new attractive models, incentive boosts by green recovery funds, the 95g CO2 mandate, much-improved availability, and intense promotion of EVs helped in driving the growth in 2020.
Figure 1: Vehicle Sales between 2019 & 2020
Europe has surpassed China as the main driving force of EV growth. Since 2015, EV sales in Europe have outpaced NEV sales in China for the first time. Outside Europe growth of EVs was slower, but still significant.
The 3-S factor of EV Omega
Figure 2: 3S Factor Diagram
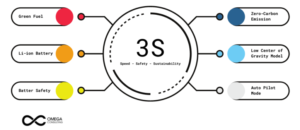
Tesla’s EV venture is now the 5th largest in the world by market capitalization and has an 18% market share in global EV sales. Tesla created a blue ocean for itself by designing a car that integrates the features of a green vehicle with that of a high-octane-driven premium sports vehicle. Analyzing the key drivers of the leading EV manufacturing firm of 2021: Tesla Incorporation, we, at Omega created “The 3S factor of EV”:
Sustainability: EVs is the one-stop solution to prevent prevailing environmental crises like the greenhouse effect and global warming as Tesla Incorporation. launched its Roadster EV- a lithium-ion battery-fueled car that clocked 0-60 mph in 4 seconds with zero emissions along with eliminating fossil fuel usage, producing no tailpipe emission.
Speed: Tesla abandoned the conventional ICE layout and mounted the battery pack on a large rigid and flat floor. This led to a low center of gravity and good weight distribution between the front and rear axles, which in turn gave very good speed. It can accelerate from 0 to 60 miles (96 km) per hour in less than 4 seconds and could reach a top speed of 125 miles (200 km) per hour.
Safety: The Tesla Autopilot, a form of semi-autonomous driving, was made available in 2014 on the Model S (and later on other models). Combining safety, performance, and efficiency, the Model S has reset the world’s expectations for the car of the 21st century with the longest range of any electric vehicle, over-the-air software updates that make it better over time. Model S has reset the world’s expectations for the car of the 21st century with the longest range for any electric vehicle, over-the-air software updates that make it better over time.
With the global EV market anticipated to reach 30,758,000 units by 2027, at a CAGR of 46.6% annually, the need for the automobile industry to transform is further cemented. There is full support to implement this eco-friendly transportation technology all across the world.
According to Omega, the demand for EVs is strongest in Europe. Whereas in 2020 in China, the EV sales decreased by 57% as compared to its previous year and by 33% in the U.S. from 2019. To promote EVs China is making an economic stimulus program by 2022 by providing tax exemption for new energy vehicles along with their new infrastructure in the country. The European Union’s new emission standard is not behind, stating that 95 gm of CO2 per km for passenger cars should be the limit, which eventually increases the EV sales because it is compulsory now in 2021 that 100% of the population there must follow the standard.
Figure 3: International Overview of EV
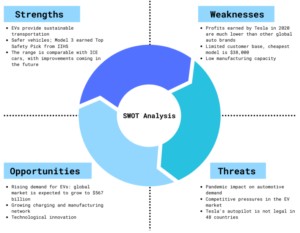
SWOT Analysis of EV Industry
Figure 4: SWOT of EV Industry
Strategies:
- Catering to revamped government policies and subsidies across various countries for a sustainable ecosystem.
- Heavy investments from automakers in EVs for innovation using technologies like neural networks, AI, ML, etc.
- Generate employment through battery station installations, repair, maintenance, Research and development, and data analytics for car automation.
- Promoting growing concerns over environmental pollution, leading to new standards across various countries.
- Expanding and Collaborating with Carpool, online ride-booking services like Ola, Uber, etc, and catering to the demand for increased vehicle range per charge.
Conclusion
It has become an inevitable trend for EV to replace traditional ICE. Except in 2020, EV’s global market continues to grow. This trend is particularly significant in Europe. In order to achieve the goal of sustainability, governments of various countries provide friendly policies and subsidies to EV. With substantial investment and high-tech innovations such as AI and ML applied to EVs, in addition to meeting environmental requirements, they also outperform traditional ICE cars in functionality and safety. With more Level 3 charging stations in the future, long-distance travel will also become convenient for EV cars.
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions