- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Technology
- By Omega Team

Text-to-Audio AI is the transformative technology that converts written text into spoken words, becoming increasingly integral to our digital interactions. From the helpful voices of virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa to the engaging narration of audiobooks and the accessibility features empowering visually impaired individuals, synthesized speech is reshaping how we consume and interact with information. Driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, particularly deep learning, modern TTS systems have moved beyond robotic outputs to generate remarkably natural and expressive voices, capable of conveying nuances in language and even subtle emotions. This technology underpins a vast array of applications, enhancing accessibility, revolutionizing content creation, streamlining customer service, and enriching educational and entertainment experiences. As AI continues to evolve, the capabilities and applications of TTS are poised for further expansion, promising even more seamless and intuitive human-computer interactions in the future.
What is Text to Audio AI?
At its core, Text to Audio AI is a technology that synthesizes human speech from text input. It involves a complex process that goes beyond simply reading words aloud. A sophisticated TTA system analyzes the text, understands its linguistic structure, identifies phonemes (the basic units of sound), determines pronunciation, inflects the speech with appropriate prosody (rhythm, stress, and intonation), and finally generates an audio waveform that sounds natural and engaging to the human ear.
Modern TTA systems leverage deep learning models, particularly neural networks, which are trained on vast datasets of human speech. These models learn the intricate patterns and nuances of spoken language, enabling them to generate speech that closely mimics human voice in terms of:
Pronunciation: Accurately articulating words, including variations based on context and regional accents.
Intonation: Varying pitch to convey meaning, emotion, and emphasis, making the speech sound expressive and natural.
Rhythm and Timing: Incorporating pauses, speaking rate variations, and natural phrasing to avoid a monotonous delivery.
Voice Quality: Offering a range of voices with different characteristics such as gender, age, and accent, allowing for customization and brand consistency.
Emotional Inflection: Some advanced systems can even imbue the synthesized speech with emotions like happiness, sadness, or excitement, further enhancing engagement and understanding.
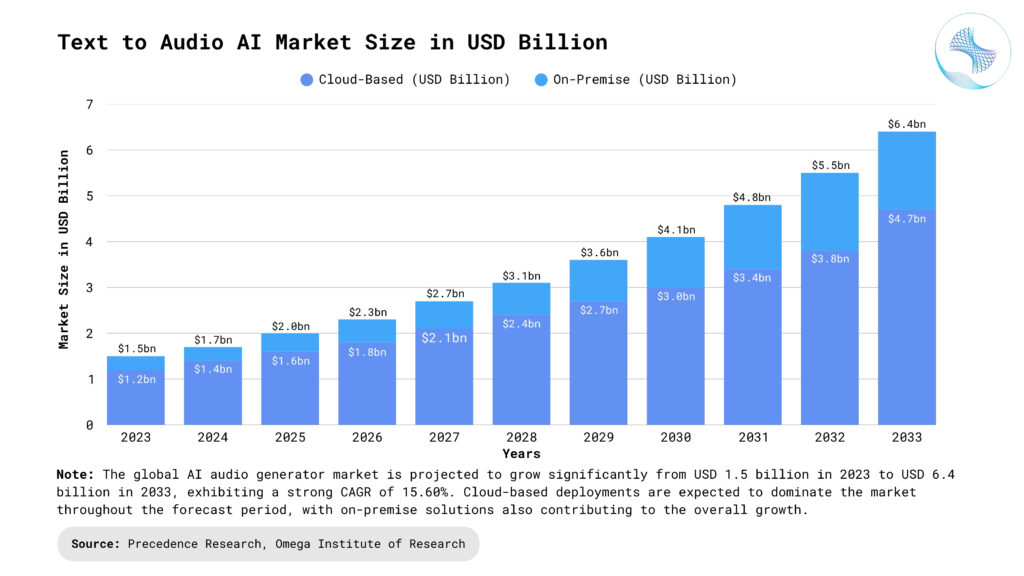
The evolution of TTA AI can be traced through several stages, from early rule-based systems that produced robotic-sounding speech to statistical parametric speech synthesis that offered more flexibility. The advent of deep learning has ushered in a new era of neural text-to-speech (TTS), which has significantly improved the naturalness and expressiveness of synthesized speech, making it virtually indistinguishable from human voice in many applications.
Key Features of Text to Audio AI
Contemporary Text to Audio AI systems boast a range of impressive features and capabilities that make them versatile and powerful tools:
Multi-Lingual Support: Many advanced TTA platforms support a wide array of languages, enabling the generation of audio content for a global audience. This includes accurate pronunciation and natural-sounding speech patterns for different linguistic structures.
Voice Customization and Cloning: Users can often choose from a diverse library of pre-built voices or even create custom voices tailored to their brand or specific needs. Voice cloning technology allows for the creation of a digital replica of a human voice, which can then be used to narrate text.
Style and Emotion Control: Some sophisticated systems offer granular control over the style and emotion of the synthesized speech. Users can adjust parameters like speaking rate, pitch variation, emphasis, and even inject specific emotional tones into the narration.
Integration Capabilities: TTA AI can be seamlessly integrated into various applications and platforms through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) and SDKs (Software Development Kits). This allows developers to embed speech synthesis functionality into websites, mobile apps, software, and hardware devices.
Real-time Synthesis: Modern Text to Audio AI excels in real-time speech, powering interactive platforms like virtual assistants and screen readers with instant auditory feedback. This immediacy enhances user experience..
High-Quality Audio Output: The audio generated by advanced TTA systems is typically of high quality, ensuring clear and pleasant listening experiences across different devices and playback systems.
SSML (Speech Synthesis Markup Language) Support: Many TTA platforms support SSML, a markup language that provides fine-grained control over various aspects of speech synthesis, such as pronunciation, intonation, pauses, and voice selection.
Diverse Applications Across Industries
The ability to convert text into natural-sounding audio has opened up a vast landscape of applications across numerous industries:
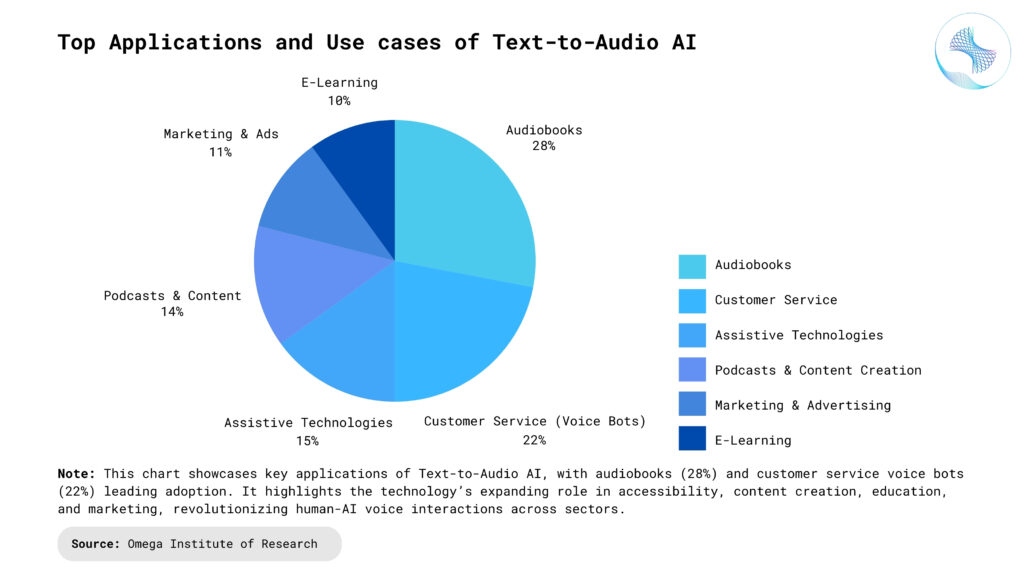
Audiobooks: Text to Audio AI revolutionizes audiobooks by converting written text into engaging spoken narration. This technology expands accessibility for visually impaired individuals, caters to diverse learning styles, and offers a hands-free way to enjoy literature and information on the go, enhancing the overall reading experience.
Accessibility: TTA AI plays a crucial role in enhancing accessibility for individuals with visual impairments, dyslexia, and other learning disabilities. Screen readers utilize TTA to vocalize on-screen text, enabling these individuals to access digital content, navigate interfaces, and participate more fully in the digital world.
Education and E-learning: TTA can transform static text-based learning materials into engaging audio lectures, narrated e-books, and interactive learning modules. This caters to different learning styles, improves comprehension, and allows students to learn on the go.
Content Creation and Marketing: TTA tools enable the rapid creation of audio versions of blog posts, articles, marketing materials, and social media content. This expands the reach of content, caters to audio-first audiences, and allows for multitasking consumption.
Customer Service and Support: Text to Audio AI powers conversational AI agents and chatbots, enabling natural-sounding voice responses for customer inquiries. This enhances user experience by providing more intuitive interactions and improves efficiency in customer service operations through automated vocal communication.
Navigation and Transportation: Voice assistants in vehicles use Text to Audio AI to offer turn-by-turn navigation, traffic alerts, and other vital updates, increasing driver safety and convenience. This integration allows drivers to receive crucial information audibly, minimizing distractions.
Smart Devices and IoT (Internet of Things): Text to Audio AI powers voice interaction and auditory feedback in smart speakers, virtual assistants, and IoT devices. This crucial functionality enables users to communicate with and receive information from these devices using natural language.
Corporate Training and Communication: Text to Audio AI offers versatile applications, including creating engaging audio-based training modules, internal communications, and announcements for employees, enhancing information delivery and accessibility within organizations. Its ability to convert text to natural-sounding speech improves communication effectiveness.
Challenges in Text to Audio AI
Despite the remarkable advancements in Text to Audio AI, several challenges and considerations still exist:
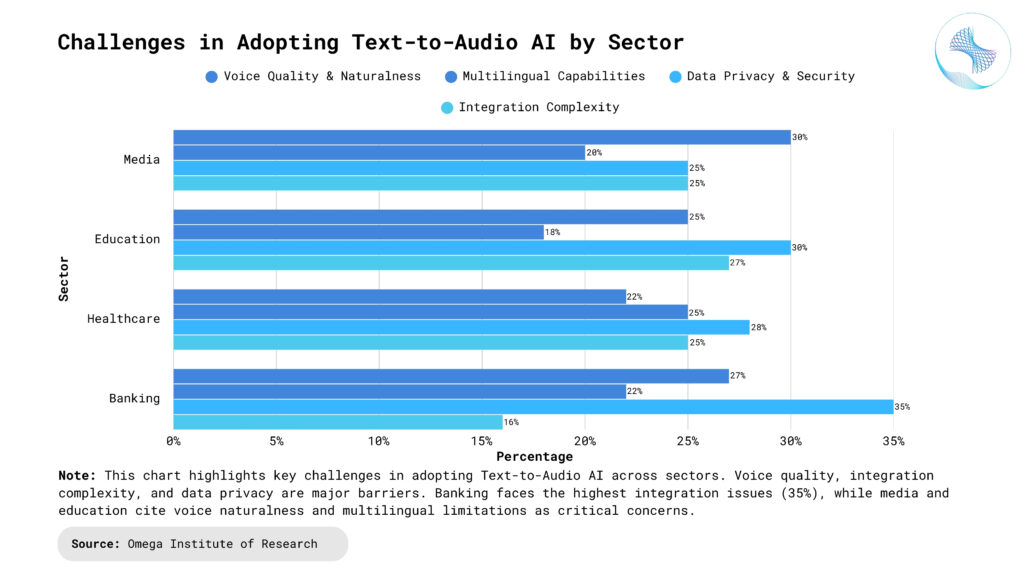
Naturalness and Expressiveness: While modern TTA is significantly more natural than previous generations, achieving truly indistinguishable human-like speech with nuanced emotional expression remains an ongoing challenge. Replicating the subtle variations in tone, emphasis, and pacing that characterize human conversation requires further research and development.
Contextual Understanding: Ensuring that the TTA system understands the context of the text is crucial for accurate pronunciation and appropriate intonation. Ambiguous words or phrases can be mispronounced or delivered with the wrong emphasis if the system lacks a deep understanding of the surrounding text.
Handling Disfluencies and Pauses: Natural human speech often includes disfluencies like “um” and “uh,” as well as natural pauses for emphasis or thought. Replicating these in a way that sounds authentic rather than like errors is a complex task.
Cross-Lingual and Accent Variations: Achieving native-level fluency and accurate pronunciation across diverse regional accents within a language remains a key challenge for many multilingual text-to-audio AI systems, despite their wide language support.
Emotional Consistency and Appropriateness: Accurately conveying emotions and ensuring the emotional tone of synthesized speech aligns with the text’s context remains a significant research challenge in Text to Audio AI. Replicating the nuances of human emotional expression requires further development.
Data Requirements and Bias: Training high-quality neural TTS models requires massive datasets of human speech. Bias in these datasets can lead to synthesized speech that reflects those biases in terms of accent, dialect, or even sentiment.
Ethical Considerations: Voice cloning technology presents ethical dilemmas concerning intellectual property rights, the necessity of obtaining consent before replication, and the risk of malicious applications, notably the creation of deceptive deepfake audio. These issues necessitate careful consideration and the development of ethical guidelines to prevent misuse.
Cost and Accessibility of Advanced Systems: While basic TTA functionality is widely available, advanced systems with highly natural voices and extensive customization options can be expensive, potentially limiting access for some individuals and organizations.
Integration Complexity: Integrating advanced Text to Audio AI into current applications can be challenging, demanding specific technical skills. This complexity might hinder broader adoption despite the technology’s benefits. Streamlining integration processes is key for wider accessibility.
Future Trends Shaping Text to Audio AI
The field of Text to Audio AI is rapidly evolving, driven by ongoing research and technological advancements. Several key trends are poised to shape its future:
Enhanced Naturalness and Human-like Quality: Continued advancements in deep learning and neural network architectures will lead to even more natural-sounding synthesized speech that is increasingly indistinguishable from human voice, including more nuanced emotional expression and conversational flow.
Improved Contextual Understanding: Future Text to Audio AI will see improved contextual understanding, leading to more accurate pronunciation and intonation. AI models will better handle ambiguities in text, enhancing the naturalness and effectiveness of synthesized speech.
Greater Personalization and Customization: Future Text to Audio AI will offer greater personalization, allowing users to fine-tune voice style and emotion, and even create branded or highly personalized voices. This enhanced customization will provide more control over the characteristics of synthesized speech.
Advancements in Low-Resource Languages and Accents: Research efforts will focus on developing high-quality TTA systems for languages and accents with limited available training data, improving accessibility for a broader global audience.
Integration with Other AI Modalities: TTA AI will increasingly be integrated with other AI technologies such as natural language understanding (NLU), computer vision, and multimodal learning, enabling more sophisticated and interactive AI-powered experiences.
Ethical Frameworks and Responsible Development: Increased attention will be paid to developing ethical guidelines and responsible practices for the development and deployment of TTA AI, particularly concerning voice cloning and the potential for misuse.
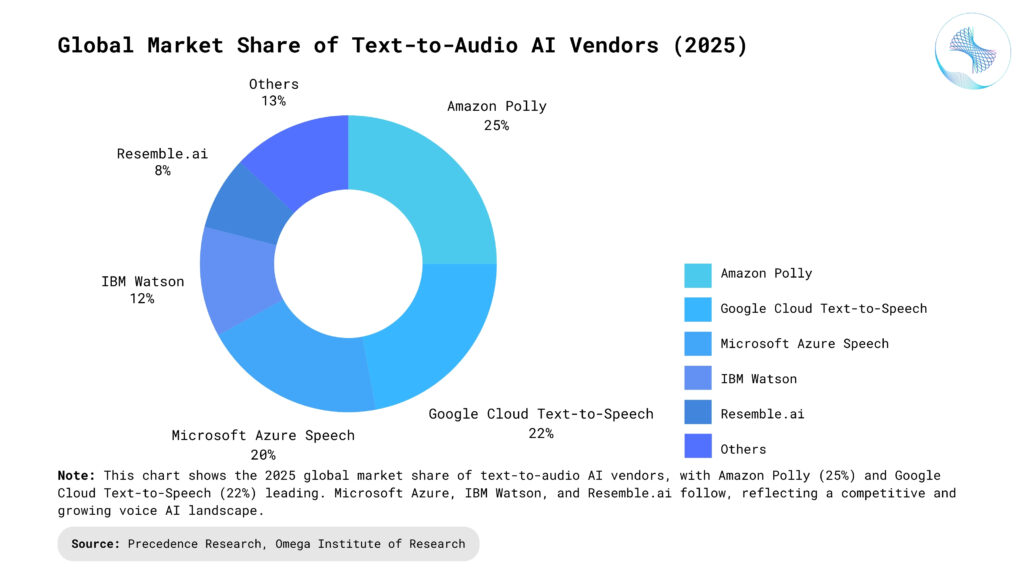
Conclusion
Text to Audio AI has emerged as a powerful and transformative technology with the potential to revolutionize how we interact with textual information. By converting written words into natural-sounding speech, TTA AI enhances accessibility, improves content consumption, and enables a wide range of innovative applications across diverse industries. While challenges related to naturalness, context understanding, and ethical considerations remain, the rapid pace of advancements in artificial intelligence and deep learning promises an exciting future for this technology. As TTA AI continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly play an increasingly central role in our digital lives, bridging the gap between text and audio and creating more engaging, accessible, and user-friendly experiences for everyone. Businesses and individuals who understand and embrace the power of Text to Audio AI will be well-positioned to leverage its capabilities for enhanced communication, improved accessibility, and future innovation.
- https://www.liveperson.com/blog/text-to-speech-ai/
- https://www.teneo.ai/blog/7-challenges-with-voice-ai-the-hidden-secrets
- https://deepgram.com/learn/text-to-speech-ai
- https://market.us/report/ai-voice-generator-market/
- https://www.lyzr.ai/glossaries/text-to-speech/#:~:text=Improved%20Accessibility:%20TTS%20technology%20makes,narration%2C%20saving%20time%20and%20resources.
- https://fliki.ai/blog/future-text-to-speech
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions