- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Technology
- By Omega Team

As artificial intelligence (AI) continues to advance and integrate into various industries, the concern about job displacement has become a prominent issue as seen with a recent study from Rutgers University showing that 3 out of 10 U.S. workers worry that their job will be eliminated by AI. Automation, driven by AI technologies, promises increased efficiency, cost savings, and new opportunities, yet it also raises questions about the future of human employment. While many jobs are susceptible to automation, there exist certain roles that AI cannot easily replace due to their unique requirements for human creativity, emotional intelligence, and complex problem-solving abilities.
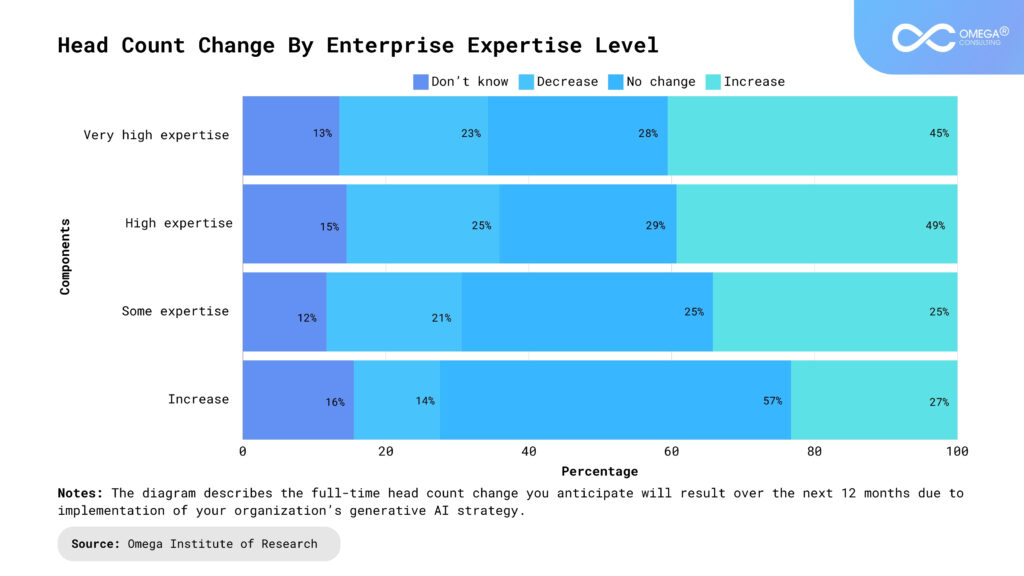
The Scope of AI in the Workplace
AI and automation have significantly impacted tasks that are repetitive, data-driven, and rule-based. Industries like manufacturing, data entry, and customer service have seen substantial transformations. Machines and algorithms excel at handling large datasets, performing intricate calculations, and executing routine tasks with speed and precision. This technological integration has undoubtedly enhanced productivity and operational efficiency for businesses, but it has also led to a decreased demand for labor in certain traditional roles.
The Impact of Automation on the Workforce
While AI and automation reshape traditional job roles, they also create new opportunities and redefine the nature of work itself. The development, implementation, and oversight of AI systems require skilled professionals in emerging fields such as data science, AI ethics, cybersecurity, and software engineering. Moreover, as routine tasks become automated, humans can redirect their efforts towards more strategic, creative, and interpersonal aspects of their work, potentially leading to job enrichment and the emergence of entirely new roles.
In navigating this transformative era, adaptability and continuous learning are critical for workers to remain competitive and relevant. Emphasizing skills that complement AI technologies—such as critical thinking, creativity, emotional intelligence, and complex problem-solving—will be crucial in preparing the workforce for the jobs of the future.
Jobs Resistant to Automation
Despite the advancements in AI, several categories of jobs remain resilient to automation due to the distinctly human attributes they require.
Creative Professions: In fields such as art, design, writing, music, and filmmaking, creativity is a fundamental component that AI struggles to replicate authentically. While AI can generate art based on predefined patterns and data inputs, the ability to produce original, culturally resonant, and emotionally compelling works remains uniquely human. Artists and designers rely on intuition, cultural insight, and emotional expression to create impactful pieces that resonate with audiences on a deeper level. However, AI can be used as a tool to further enhance creators in this space. For example, an artist can utilize AI tools such as DALL-E (text-to-image) to generate beautiful visuals based on the description given by the artist. These AI-generated visuals can serve as a fundamental building block that an artist can further develop to their liking. This use of AI allows for the initial phase of the artistic process to be accelerated.
Jobs Requiring Emotional Intelligence: Roles that involve direct human interaction, empathy, and emotional understanding are challenging for AI to emulate. Healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, therapists, and caregivers, provide more than just medical treatment; they offer compassion, ethical judgment, and personalized care tailored to individual needs. Similarly, educators play a crucial role in fostering student development by understanding their emotional and cognitive needs, adapting teaching strategies accordingly, and providing mentorship beyond mere information dissemination.
Roles Involving Complex Problem Solving and Strategic Thinking: Leadership positions such as managers, executives, legal professionals, and crisis managers require a nuanced understanding of human dynamics, strategic decision-making, and complex problem-solving. While AI excels in data analysis and decision support, tasks involving negotiation, conflict resolution, ethical judgment, and navigating ambiguous situations necessitate human insight, empathy, and contextual understanding.
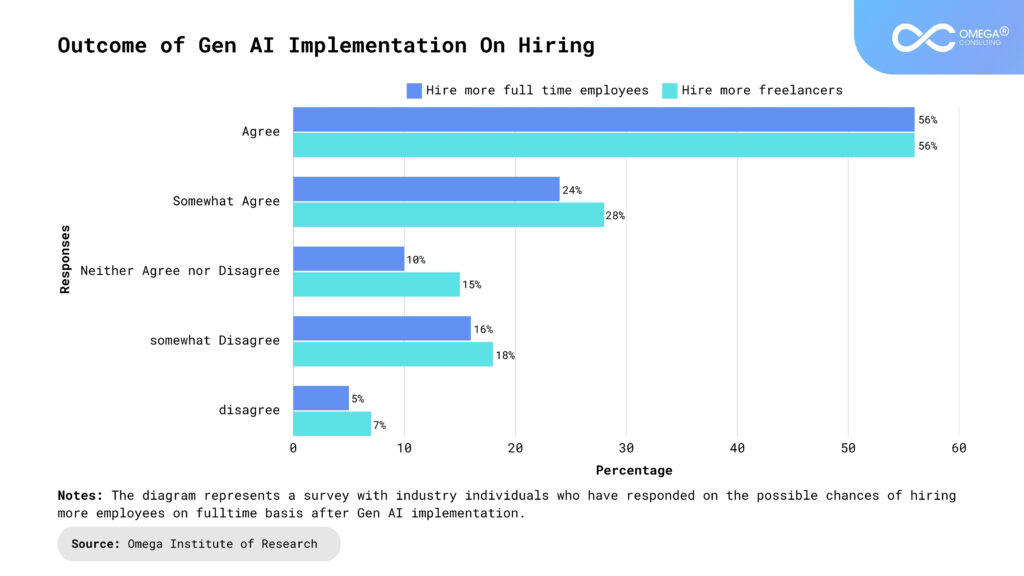
The Broader Impact of Automation
Redefining Job Roles: AI is increasingly augmenting human capabilities rather than replacing them entirely. In fields like healthcare, journalism, and customer service, AI assists in data analysis, diagnostic procedures, and customer interaction, allowing professionals to focus more on personalized care, investigative reporting, and creative problem-solving.
New Opportunities: As AI takes over routine tasks, it is transforming the job market. While The World Economic Forum predicts that AI may displace around 85 million jobs by 2025, it also believes that it will create 97 million new roles. This shift necessitates new job roles that focus on developing, managing, and optimizing AI systems. Demand will continue to grow for professionals who are skilled in AI development, ethical governance, cybersecurity, and the integration of AI within existing business practices.
Skills Shift: The shift towards automation necessitates a focus on skills that are uniquely human and difficult for AI to replicate. Soft skills such as creativity, emotional intelligence, adaptability, and interpersonal communication are becoming increasingly valuable in a technology-driven workplace.
Economic and Social Implications
Inequality and Displacement: The automation of routine tasks may lead to economic displacement for workers in traditional industries, potentially widening income inequality. Addressing this requires proactive policies that ensure equitable access to education, training, and economic opportunities.
Skill Development and Training: Investments in reskilling and upskilling programs are essential to equip the workforce with the skills needed for emerging job roles. Governments, educational institutions, and businesses must collaborate to provide accessible training programs that prepare individuals for the evolving job market.
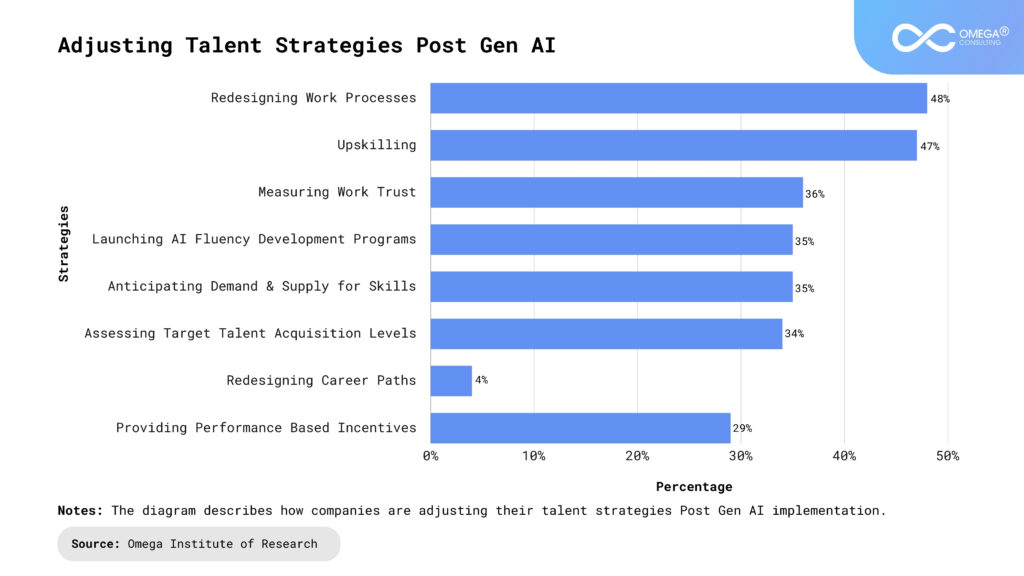
Navigating the Future of Work
Educational Reform: Educational systems must evolve to emphasize interdisciplinary learning, combining technical skills with humanities and social sciences. This holistic approach prepares students to leverage AI technologies while emphasizing human-centric skills essential for future employment.
Corporate Responsibility: Businesses play a crucial role in fostering a culture of lifelong learning and professional development. Investing in employee training programs that focus on both technical proficiency and soft skills enables workers to adapt to technological changes and contribute effectively to organizational growth.
Challenges & Considerations
Ethical and Regulatory Concerns: Ensuring ethical AI deployment and robust regulatory frameworks is essential to mitigate risks. Transparency, fairness, accountability, and privacy protection are critical in AI system development and implementation.
- Transparency: Clear Communication as to how AI systems work.
- Fairness: Proactively identifying and removing potential bias in AI algorithms to prevent discriminatory practices.
- Accountability: Creating mechanisms that hold AI developers and users accountable for its impact.
- Privacy Protection: Building trust by safeguarding personal information and adhering to data protection regulations.
Economic Impact: AI threatens jobs involving routine tasks, leading to economic instability and widening income inequality. High-skilled workers benefit more, exacerbating social divides.
Skill Gaps: Bridging the gap between current skills and those needed for AI-driven industries is crucial. Continuous reskilling and upskilling initiatives are needed, but equitable access remains a challenge, especially for marginalized communities.
Regulatory Challenges: Robust frameworks are required to keep pace with AI advancements and ensure responsible deployment, especially in sensitive fields like healthcare and law.
Ethical AI Frameworks: Prioritizing bias mitigation and transparency is key to building trust and ensuring ethical AI use. To avoid scenarios such as the failed project from a group of software engineers at Amazon that constructed a program to automate the hiring process with AI. Their algorithm, which was based on a dataset of resumes of existing male engineers in the company, favored keywords and experiences more common to men which unintentionally discriminated against women even when they had the necessary qualification. This underscores the risk of AI inheriting biases from its training data. Mitigating bias and ensuring transparency are crucial for ethical AI use.
Social Safety Nets: Enhancing unemployment benefits and exploring initiatives like universal basic income can provide stability for displaced workers.
Innovation and Job Creation: Supporting innovation and entrepreneurship can create new job opportunities that complement AI technologies.
Worker Well-being: Promoting work-life balance and mental health support can improve job satisfaction and productivity in an AI-driven economy.
How working professionals can thrive with the rise of AI
As AI and automation continue to reshape the job market, working professionals must adopt proactive strategies to ensure their careers remain relevant and secure. Here are several approaches to help professionals evade job displacement by AI:
Continuous Learning and Skill Development
Lifelong Learning: Professionals should commit to lifelong learning to stay ahead of technological advancements. This involves regularly updating technical skills and gaining knowledge in emerging fields relevant to their industry.
Online Courses and Certifications: Leveraging online learning platforms such as Coursera, edX, and LinkedIn Learning can help professionals acquire new skills and certifications that enhance their employability.
Industry-Specific Training: Participating in industry-specific training programs can provide deeper insights into how AI is transforming specific sectors, allowing professionals to tailor their skill sets accordingly.
Embracing Human-Centric Skills
Emotional Intelligence: Developing emotional intelligence (EQ) is crucial as AI cannot replicate the ability to understand and manage human emotions. Professionals can improve their EQ through mindfulness practices, active listening, and empathy-building exercises.
Creativity and Innovation: Fostering creativity and innovative thinking can set professionals apart from automated systems. Engaging in creative problem-solving activities and staying curious about new ideas and perspectives can help maintain a competitive edge.
Complex Problem-Solving: AI excels at data-driven tasks but often falls short in scenarios requiring complex problem-solving and strategic thinking. Professionals should seek opportunities to engage in strategic planning and critical thinking exercises.
Enhancing Interpersonal and Leadership Skills
Effective Communication: Strong communication skills, both verbal and written, are invaluable. Professionals should practice clear and concise communication and adapt their style to different audiences.
Leadership and Management: AI cannot replicate the nuanced skills required for effective leadership and management. Developing skills in team building, conflict resolution, and motivational leadership can ensure career longevity.
Networking: Building and maintaining a strong professional network can provide support and opportunities for career growth. Networking helps professionals stay informed about industry trends and potential job openings.
Leveraging Technology and AI
AI Literacy: Understanding how AI works and its applications in one’s field can be a significant advantage. Professionals should familiarize themselves with basic AI concepts and tools relevant to their industry. This can be accomplished by the following:
- Online courses : Enroll in online courses via platforms such as Coursera and Udacity that cover basic concepts of AI that can be tailored to different industries.
- Following AI Networks: Engage with diverse AI communities across social media, podcasts, and blogs to stay current on the latest advancements and applications.
- Experiment with AI Tools: Practice and experiment with AI tools that are available and free.
Collaboration with AI: Instead of viewing AI as a threat, professionals should learn how to collaborate with AI tools to enhance their productivity. This includes using AI for data analysis, project management, and other tasks where AI can provide support.
Adapting to Changing Job Roles
Flexibility and Adaptability: Being open to change and willing to adapt to new roles or responsibilities is essential. Professionals should embrace new job roles that emerge due to AI and automation.
Interdisciplinary Skills: Combining skills from different disciplines can create unique career opportunities. For example, merging technical skills with a background in humanities can provide a broader perspective and open up diverse job roles.
Pursuing Higher Education and Specialization
Advanced Degrees: Pursuing advanced degrees in fields less susceptible to automation, such as healthcare, education, and social sciences, can provide job security.
Specialization: Specializing in niche areas within one’s profession can make it harder for AI to fully replicate the job. Professionals should identify and develop expertise in areas requiring deep knowledge and specific skills.
Staying Informed and Involved
Industry Trends: Staying informed about the latest industry trends and how AI is impacting various sectors can help professionals anticipate changes and prepare accordingly.
Professional Organizations: Joining professional organizations and participating in conferences, workshops, and seminars can provide insights into industry developments and networking opportunities.
Case Studies
Case Study 1: Healthcare Industry – IBM Watson
Overview: IBM Watson, an AI system capable of analyzing large volumes of medical data, has been integrated into various healthcare settings to assist doctors in diagnosing diseases and developing treatment plans.
Impact
Improved Diagnostics: Watson’s ability to process and analyze extensive medical literature has improved diagnostic accuracy, particularly in oncology. This can be seen with its work at Memorial Sloan Kettering Hospital, where it aided treatment decisions for 30,000 cancer patients in 2014. By looking at patient data, Watson AI was able to identify treatment options based on therapies that were successful in the past. (AAPC, 2019)
Enhanced Efficiency: By handling time-consuming data analysis, Watson allows healthcare professionals to spend more time on patient care.
Job Transformation: While Watson has not replaced doctors, it has transformed their roles, emphasizing the need for continuous learning to work effectively alongside AI tools.
Challenges
Data Privacy: Ensuring patient data privacy and security remains a critical concern in the healthcare industry. Unauthorized access to patient data is a significant issue, often resulting from weak security measures or internal threats, allowing individuals without proper authorization to view sensitive information. Additionally, data sharing with third parties for research purposes poses risks, as mishandling of data can occur once it is out of the original holder’s control. Furthermore, inaccurate data entry within an organization can lead to errors in patients’ medical histories, directly impacting the quality of care they receive.
Adaptation: Healthcare professionals must adapt to integrating AI tools into their workflows. As highlighted by Harvard Medical School, doctors in the future can utilize AI language models for consultations. Potential AI-generated prompts include providing advice on the diagnosis and treatment for specific symptoms, creating personalized treatment plans based on a patient’s age and lifestyle, analyzing X-rays to detect abnormalities, identifying risk factors from a patient’s electronic health record (EHR), and writing letters to explain the medical necessity of treatments.
Future Implications: The continued development of AI in healthcare suggests a future where AI aids in preventive care, personalized medicine, and remote patient monitoring, further transforming healthcare roles but requiring significant adaptation and skill development from professionals.
Case Study 2: Manufacturing Sector – Amazon Robotics
Overview: In a move highlighting its commitment to automation and innovation in logistics, Amazon made a hefty $775 million acquisition in 2012: Kiva Systems, a robotics company. Since then, Amazon has integrated Kiva’s solutions and deployed thousands of robots across its fulfillment centers, significantly automating the processes of picking, packing, and sorting items.
Impact
Increased Productivity: Robots have significantly increased productivity and operational efficiency in warehouses, reducing processing times by 200-300%, according to a 2022 Forbes report. For Amazon, this means faster order fulfillment, as robots can retrieve items quicker and maintain speed and accuracy during peak periods. Additionally, automating repetitive tasks allows human workers to focus on other areas, such as processing returns and addressing customer complaints.
Job Creation and Transformation: While robots have automated many manual tasks, Amazon has also created new job roles in robot maintenance, AI management, and logistics planning. According to the company itself, they have created over 700 categories of new skilled jobs that didn’t exist before within the company.
Challenges
Job Displacement: Routine, manual jobs have been most affected, leading to concerns about economic displacement for low-skilled workers.
Skill Requirements: New roles require advanced technical skills, highlighting the need for reskilling programs.
Future Implications: The trend towards automation in manufacturing is likely to continue, with AI and robotics becoming more advanced. Future trends may include fully automated warehouses and the integration of AI for predictive maintenance and supply chain optimization.
Case Study 3: Financial Services – JPMorgan Chase’s COIN
Overview: JPMorgan Chase developed the Contract Intelligence (COIN) platform. This AI system interprets commercial loan agreements in seconds, a task that previously took 360,000 hours annually for lawyers and loan officers.
Impact
Efficiency Gains: COIN has dramatically increased the speed and accuracy of processing loan agreements.
Job Role Shift: While COIN has automated routine document review, it has allowed lawyers and loan officers to focus on more complex, strategic tasks that require human judgment such as negotiating terms and managing relationships which are things that AI has not yet been able to do better than humans.
Future Implications: AI in financial services is expected to expand into areas such as fraud detection, personalized banking services, and risk management, creating new opportunities but also requiring continuous adaptation from the workforce.
Future Trends of Gen AI & Automation
Increased Emphasis on Human-AI Collaboration
As AI continues to advance, the future workforce will see an increased emphasis on human-AI collaboration. AI will handle routine, data-driven tasks, allowing humans to focus on areas requiring creativity, emotional intelligence, and complex problem-solving. This trend will necessitate workers developing complementary skills and the ability to work effectively alongside AI.Growth in AI-related Job Roles
The proliferation of AI technologies will create new job roles in areas such as AI ethics, AI system training, and AI maintenance. Data scientists, machine learning engineers, and AI ethicists will be in high demand. This growth will drive educational institutions and training programs emphasizing AI-related skills and interdisciplinary learning.Ethical and Regulatory Framework Development
As AI becomes more integrated into various sectors, there will be a growing need for robust ethical and regulatory frameworks to address concerns related to bias, data privacy, and accountability. Policymakers, businesses, and academic institutions will collaborate to develop guidelines ensuring responsible AI deployment.Evolution of Educational and Training Systems
Educational systems will evolve to prepare students for an AI-driven world, focusing on developing critical thinking, creativity, and emotional intelligence. Lifelong learning will become a standard expectation, with continuous upskilling and reskilling programs becoming integral to career development.Rise of Personalized and Remote Work Environments
AI will enable more personalized and flexible work environments, with remote work becoming increasingly feasible and efficient. AI tools will facilitate virtual collaboration, personalized learning paths, and adaptive work schedules, enhancing work-life balance and job satisfaction.Conclusion
As AI continues to evolve, its impact on the workforce will be profound. While automation promises efficiency gains and new opportunities, it also presents challenges related to job displacement, economic inequality, and ethical considerations. Recognizing and valuing jobs that AI cannot replace—due to their reliance on human creativity, emotional intelligence, and complex problem-solving—will be crucial in shaping a future where technology complements, rather than replaces, human capabilities. By prioritizing skills development, educational reform, ethical deployment of AI, and supportive policy initiatives, societies can navigate the transition toward an inclusive and resilient workforce in the age of automation.
- https://www.nytimes.com/2023/07/29/business/robots-workers-future.html
- https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2014/08/06/future-of-jobs/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/341600851_Artificial_Intelligence_Meets_IS_Researchers_Can_It_Replace_Us
- https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/16094069231201504
- https://global.oup.com/academic/product/the-ethics-of-artificial-intelligence-9780198883098
- https://www.heldrich.rutgers.edu/news/us-workers-assess-impacts-artificial-intelligence-jobs-press-release#:~:text=Seven%20in%2010%20U.S.%20workers,jobs%20being%20eliminated%20(30%25).
Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions