- Industries
Industries
- Functions
Functions
- Insights
Insights
- Careers
Careers
- About Us
- Marketing & Advertising
- By Omega Team

About AR
AR stands for Augmented Reality. It is a technology that enhances the real world with computer-generated perceptual information, such as visuals, sounds, or other sensory stimuli. Unlike virtual reality (VR), which immerses the user in a completely simulated environment, augmented reality overlays digital elements in the real-world environment.The purpose of AR is to provide an enhanced perception and interaction with the physical world by blending digital content seamlessly into the user’s real-world environment. AR technology has a wide range of applications across various industries, including gaming, entertainment, education, healthcare, marketing, design, and many others. AR can be used for various purposes, such as gaming, entertainment, education, training, retail and Marketing.
About VR
VR stands for Virtual Reality. It is a technology that uses computer-generated simulations to create a simulated environment. VR typically involves the use of a headset or goggles that provide a visual and auditory immersive experience, making users feel like they are actually present in a virtual environment. The main goal of virtual reality is to create a sense of presence where the user feels fully immersed and engaged in the virtual world. This is achieved through a combination of various technologies, such as head-mounted displays, motion tracking, and 3D audio. In addition to visual and auditory experiences, VR can also incorporate other sensory feedback, such as haptic (touch) feedback, allowing users to interact with virtual objects and environments. This can be achieved through specialized gloves, controllers, or even full-body suits that provide tactile sensations.Virtual reality has applications in various fields, including gaming, entertainment, education, training, simulation, healthcare, and more. In gaming and entertainment, VR can provide an immersive and interactive experience, allowing users to explore virtual worlds, play games, and watch videos in a more engaging way.
Overall, virtual reality has the potential to revolutionize the interaction with digital content and experience virtual environments, opening up new possibilities for entertainment, education, and various other industries.
Difference Between AR And VR
AR (Augmented Reality) and VR (Virtual Reality) are both immersive technologies that alter our perception of reality, but they differ in how they achieve this and the level of immersion they provide.Augmented Reality (AR): AR refers to the technology that overlays digital information or virtual objects onto the real world, enhancing our perception of reality. It combines computer-generated elements with the real environment. AR enhances the real world experience by adding digital elements to it. Users can still see and interact with the real environment while viewing additional virtual information overlaid on top of it. AR does not completely block out the real world. In AR, users interact with both the real world and the virtual elements. They can see and manipulate virtual objects or access digital information through devices like smartphones or AR glasses. Interaction occurs within the context of the real-world environment. AR finds applications in various fields, such as gaming, education, healthcare, architecture, retail, and navigation. Examples include AR games like Pokémon Go, AR educational apps, virtual try-on for shopping, and AR-assisted surgery.
Virtual Reality (VR): VR, on the other hand, refers to a simulated digital environment that completely replaces the real world. It immerses users in a computer-generated world, typically accessed through a headset or goggles. VR provides a fully immersive experience by completely replacing the real world with a simulated digital environment. Users wearing VR headsets are visually and audibly cut off from the real environment, entering a virtual world that responds to their movements. In VR, users interact primarily with the virtual environment. They can move, look around, and interact with virtual objects using specialized controllers or motion-tracking devices. Interaction is typically limited to the virtual world. VR is commonly used in gaming, entertainment, training simulations, virtual tours, and therapy. Examples include VR gaming experiences, virtual travel experiences, VR-based training programs, and immersive therapy for phobias or PTSD.
While both AR and VR offer unique experiences, their applications and immersion levels set them apart. The choice between AR and VR depends on the desired level of immersion and the specific use case or application.
Market Outlook
The Internet’s increasing accessibility and the expansion of the video game industry are the primary market drivers with applications of augmented reality and virtual reality in various industries such as healthcare, retail, entertainment, media, manufacturing, aerospace, and the military will result in robust development for the AR & VR market.Exhibit 1
The global AR and VR marketThe global AR and VR market was valued at USD 41.56 billion in 2022 and is anticipated to reach USD 859.35 billion by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 46.03% from 2022 to 2030.
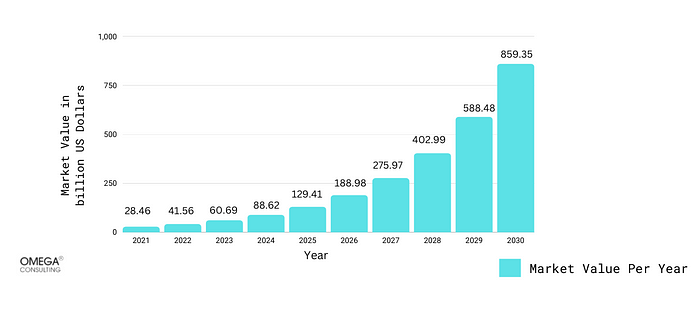
Exhibit 2
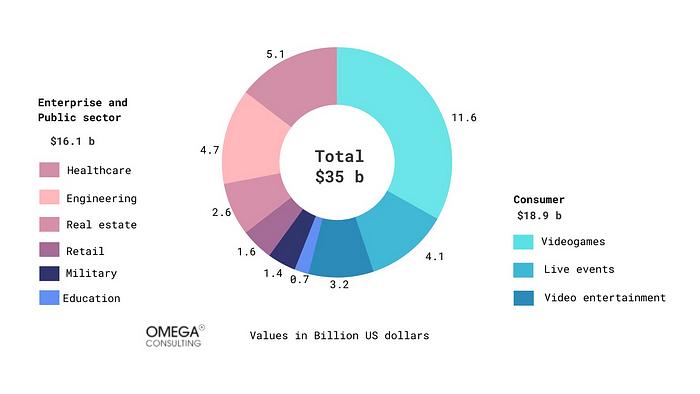
The Diverse potential applications of Augmented Reality and Virtual RealityThe potential of new technologies extends far beyond the consumer market. According to Goldman Sachs, almost half of the industry’s revenue will come from the enterprise and public sector, with engineering and healthcare being the most prospective applications.
AR/VR as a marketing tool
Many firms have adopted or are considering adopting creative methods of product promotion. Conventionally, digital advertising technology employs online video, pop-ups, pop-unders, banners, etc. Multiple users found these intrusive and irritating. This led to the emergence of ad blockers, which diminished the efficacy of the advertisements. It was determined that novel experiences for the target audience required the use of novel techniques. The use of VR and AR in marketing significantly altered the playing field. Their application is expanding in a range of industries, including healthcare, medicine, astronomy, education, and consumer products.AR and VR technologies enable digital technology integration with marketing strategies, transforming the purchasing experience.AR and VR also provide in-store experiences in the convenience of one’s own residence, eliminating the need to physically visit a store. The use of augmented reality and virtual reality in retail stores, e-commerce, and advertising is the next major thing poised to disrupt marketing concepts.
Artificial reality marketing (ARM) is a multi-media promotional activity that encourages consumer interaction with the brand, thereby increasing engagement, customer loyalty, publicity, and the development of long-term relationships. For instance, while browsing for a car, users can experiment with various colors, examine the vehicle’s features, and conduct a virtual test drive. Realtors use virtual reality (VR) to create virtual tours that provide a 360-degree walkthrough of a property, to try out various paint hues on the walls, or to simply add furniture to visualize how the property will appear. ARM integrates traditional advertising with mobile devices to attract consumers’ attention by projecting 3D images of products onto the screens of their mobile devices, providing a unique and individualized experience. ARM campaigns must be aligned with the company’s objectives, utility-focused, and provide consumers with a valuable experience.
AR/VR marketing in various industries
E-commerceVirtual, augmented, and mixed reality are revolutionizing all industries. Consider spatial computing, the latest technique for visualizing and interacting with content. If we narrow our focus to marketing, mobile augmented reality is a very promising technology. Using a mobile device, you can view a watch on your wrist, and eyeglasses in portrait mode, try on shoes, and apply makeup. Mobile presents the greatest opportunity for e-commerce.
Automotive
The process of purchasing a vehicle is already transitioning towards omni-commerce. Consumers can now research vehicles, make a purchase, and secure financing without ever entering a dealership. The technology will accelerate the digital transformation of the buyer’s journey by enabling consumers to experience new features, comprehend vehicle dimensions, and accessorize vehicles.
Fashion
Utilizing AR and VR in the fashion industry is revolutionary. Due to COVID-19, many brick-and-mortar stores are closed, and few of those that remain open allow consumers to try on clothing. If online apparel purchases continue to rise, providing an augmented reality (AR) experience (so consumers can see items in the “real world”) will be an enormous benefit to the customer and boost their purchasing confidence.
Gaming
I believe VR and AR will continue to thrive in the gaming industry, as there are countless applications. Emerging augmented reality (AR) applications in retail allow customers to virtually try on clothing or obtain additional product information. For virtual reality, I believe the entertainment and education verticals have the potential to develop but are limited by consumer adoption of VR headsets.
Hospitality And Tourism
Hospitality and tourism are two industries that can benefit from VR/AR marketing. Hotels that provide a virtual tour of their rooms and amenities may see an increase in bookings, while tour companies can provide a sample of what travelers can expect on their tours.
Events
Events is the only industry where VR and AR should be implemented immediately. Since no one can travel as they once did, the opportunity to reconsider how events are organized and elevate them to something far beyond a Zoom meeting is primed for the picking. Imagine being able to travel to distant locations between meeting sessions or holding entire conferences in virtual reality.
Higher Education
Higher education is a sector that will be affected by this development. Due to the current state of affairs, emerging high school juniors and seniors cannot take campus excursions. In the interim, prospective students and their families must be offered VR and AR excursions in order to maintain enrollment levels.
furnish their new residences. The ability to visualize household goods and furniture in house space is a fantastic and widely-used feature.
Use cases of AR/VR in marketing
To promote their holiday campaign, John Lewis, a UK department store, launched a virtual reality (VR) campaign titled Monty’s Christmas, which featured a young child named Sam and his best companion, Monty the Penguin. Using a Google Cardboard VR headset, children as well as adults were able to investigate the story of Monty and Sam. The campaign increased sales and left an enduring impression on customers, making them anxious to return the following season.Merrell launched TrailScape, a virtual reality (VR) campaign using an Oculus Rift headset to promote its Capra hiking footwear. It was a 4D, motion-tracking, multisensory virtual experience that simulated extreme landscapes such as shaky bridges and mudslides. Motion capture technology placed hikers in situations they would not typically encounter.
Thomas Cook, a travel agency, allowed prospective vacationers to explore a variety of virtual vacations using Samsung Gear VR. Try Before You Fly is a collection of 360-degree VR films showcasing available vacation options. They even required tourists to take helicopter excursions to sites such as the Egyptian pyramids. To complement the in-store experience, Thomas Cook developed an app that allows users to view content from the convenience of their own homes. The VR experience generated approximately US$ 15,600, representing a return on investment of 40%.
The French clothing company Lacoste has released a 3D augmented reality app that activates interactive 3D representations of its new line of trainers. To virtually test the trainer shoes, customers placed their foot on the floor graphic and scanned it with their smartphones. The shoe image was superimposed on their feet without requiring them to remove their shoes or wait for a salesperson. They were able to inspect the features and swipe to view other trainers in the selection. Additionally, they could share images via social media.
Sephora, an Italian beauty retailer, introduced an augmented reality (AR) mirror that allowed customers to virtually apply makeup to images of their faces and, just as they would in real life, mix and match various hues of cosmetics by touching a palette on the screen.
Ikea developed the Ikea Catalogue app to create augmented reality (AR) images of its products that appeared on mobile screens as if they were in the customers’ homes. This allowed consumers to virtually test out various products in terms of size, shape, colour, and placement to determine how the products would actually fit in the space.
The Volvo X-ray app transforms iPads into portable X-ray scanners, allowing consumers to view the interior components and features of a Volvo vehicle using augmented reality. Using a 360-degree viewing element, customers can observe the car’s undercarriage, inner mechanics, and components, as well as investigate the car’s features.
Starbucks offers customers in its Starbucks Reserve Roastery in Shanghai an app for immersive augmented reality (AR) in-store experience. The experience includes a virtual marketplace, Tmall, where consumers can purchase merchandise or sample specially curated coffee. Starbucks is also experimenting with virtual reality (VR) technology to transport customers to coffee plantations in various countries so they can feel confident about their purchases.
Pros and Cons of Using AR in marketing
Pros of AR are as follows:
Enhanced Experience
Augmented Reality (AR) offers the advantage of enhancing the user experience by allowing them to use their phones to view specific locations, such as buildings or natural landmarks. By holding up their devices, users can witness an overlay of information that adds depth to their perception, going beyond what is visible without AR technology. This augmentation of reality provides users with a richer and more immersive encounter compared to simply observing the subject without the assistance of AR.Ease of Use
Augmented reality on mobile phones offers effortless usability. By pointing the camera at an object, the app instantly displays relevant information or visualizations. For instance, users can discover the calorie count of a pizza slice by viewing an image on their screen. The abundance of information is readily available and seamlessly integrated into their surroundings.
Supports Business Activities
AR is predicted to revolutionize various industries by offering enhanced benefits to customers and influencing their investment decisions. AR aids in cost-effective designing and remodeling processes, reducing upfront expenses by providing a preview of the final product before manufacturing.
Cons of AR are as follows:
UnaffordableThe development of augmented reality (AR) can be costly, making it inaccessible for many due to its complexity and expenses. Consequently, only larger organizations with substantial resources can afford to invest in AR technology, while smaller companies may find it financially challenging.
Privacy and Security Problems
Privacy and security concerns can arise from the use of Augmented Reality (AR) due to the blurring of the line between reality and virtual content, leading to apprehension about potential deceptive attacks.
Health issues
Discussions surrounding the limitations of augmented reality (AR) highlight various potential health risks. Studies suggest that prolonged use of AR devices may result in hearing loss, eye damage, and behavioral changes.
Pros and cons of using VR in marketing
Pros of VR in Marketing:
Immersive Brand ExperiencesVR allows marketers to create immersive and memorable brand experiences that deeply engage consumers. By transporting them to virtual environments, brands can showcase products, services, or narratives in a highly interactive and compelling way, leaving a lasting impression.
Enhanced Product Visualization
VR enables customers to visualize and experience products before making a purchase. This can be particularly useful for industries like real estate, interior design, or automotive, where customers can virtually explore properties, customize interiors, or test-drive vehicles, leading to increased confidence and informed decision-making.
Virtual Showrooms and Retail Experiences
VR allows brands to create virtual showrooms and retail spaces, providing customers with an immersive shopping experience from the comfort of their homes. This can expand reach, reduce physical space constraints, and offer personalized interactions, ultimately driving sales and customer satisfaction.
Cons of VR in Marketing:
Cost and AccessibilityImplementing VR in marketing campaigns can be expensive, requiring investments in hardware, software development, and content creation. Additionally, not all consumers have access to VR devices, limiting the potential reach and engagement of VR marketing initiatives.
Technical Limitations
VR experiences can be resource-intensive, requiring high-performance devices and stable internet connections. Technical issues such as latency, motion sickness, or compatibility problems may arise, impacting the overall user experience and potentially deterring users from engaging with VR marketing content.
Limited Reach and Target Audience
VR is still a niche technology with a relatively smaller user base compared to traditional media channels. This can limit the reach and effectiveness of VR marketing campaigns, especially when targeting broader audiences or demographics that are less inclined to adopt VR technology.
Future
The future outlook for augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) in marketing is very promising. The technologies have the potential to revolutionize the way various businesses market their products and services, as it provides a more immersive and interactive experience for consumers. As AR and VR technologies become more accessible and affordable, more businesses will be able to incorporate them into their marketing strategies. This will exponentially increase the number of AR/VR experiences available to consumers, which will drive adoption and further innovation in this field. The latest market forecasts say that the AR/VR industry will generate revenues of $13.8 billion in 2022, which will increase to $50.9 billion in 2026, with a CAGR of 32.3%. This projected development is substantial, adding to the numerous ways in which AR/VR technologies are already utilized by a variety of industries.Conclusion
The AR and VR technologies have been around for some time, but they are still relatively new marketing tools. Consider your business requirements and take note of what other brands are doing and what consumers are saying about their online experiences. Staying ahead of the trends requires nothing more than paying attention. If VR and AR marketing experiences skyrocket in prominence and become a must-have strategy, the businesses will already know how to adopt them.Subscribe
Select topics and stay current with our latest insights
- Functions